Flash
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
Definition
“Adobe Flash (previously called Macromedia Flash) is a multimedia platform originally acquired by Macromedia and currently developed and distributed by Adobe Systems. Since its introduction in 1996, Flash has become a popular method for adding animation and interactivity to web pages. Flash is commonly used to create animation, advertisements, and various web page components, to integrate video into web pages, and more recently, to develop rich Internet applications. Flash can manipulate vector and raster graphics and supports bidirectional streaming of audio and video. It contains a scripting language called ActionScript. Several software products, systems, and devices are able to create or display Flash content, including Adobe Flash Player, which is available free for most common web browsers, some mobile phones and for other electronic devices (using Flash Lite).” (Wikipedia, retrieved May 23 2009).
In addition, Flash is used as a format for desktop applications under the name of "Adobe Integrated Runtime" ( [[Adobe AIR]).
Today, many tools can produce runnable Flash contents. However only Adobe's commercial Flash authoring tools allow to exploit the full capabilities of this format. Programmers, however, can use Adobe's free Flex compiler.
Flash tutorials and articles in EduTech wiki
EduTech Wiki includes introductory Flash and ActionScript 3 (AS3) tutorials for Flash version 9 using Adobe Flash CS3 Professional. Some CS4 tutorials are under preparation. I used these tutorials in my COAP 2110 (Fall 1 2007) at Webster University (Geneva) and in my STIC III courses at University of Geneva. Some tutoraisl better than others and none has reached top quality so far, but most can serve to support teaching and self-learning Daniel K. Schneider May 2009.
We produced three families of tutorials with some overlaps:
- Flash tutorials (Flash CS3 plus ActionScript 3 for non-programmers, and some CS4)
- Actionscript 3 (Beginner's tutorials for "pure" AS3, i.e. tool independant coding)
- Flex tutorials (very few)
In addition, all materials (*.fla, *.swf, etc.) are available at http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/flash/ex under a CC BY-NC-SA licence.
- Other Flash articles in EduTech Wiki (e.g. overviews and cheatsheets)
- Flash CS3 keyboard shortcuts
- Flash ActionScript 3 overview -- a conceptual little overview of AS3
- Flash formats and objects overview (not ActionScript objects !)
- Flash - being organized (some advice for beginning Flash CS3 designers)
- Actionscript 3 -- a complete programming language. An entry page for AS3 tutorials
- Flash 3D -- overview page of of Flash 3D tools and AS3 libraries
The Flash framework
In the past, Flash was just a web animation/interactive multimedia technology. Today (2008) Flash is a serious contender for one-stop rich internet application technology as the following picture shows:
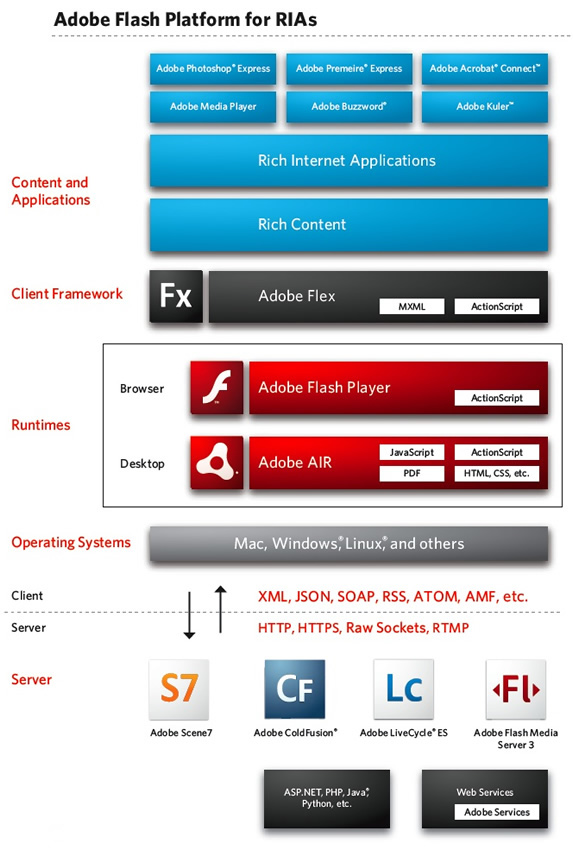
Alternative technologies
- General formats
- DHTML, i.e. the combination of HTML, CSS, DOM and Javascript and AJAX, the same combo plus server-client communciation trough JavaScript.
- SVG, an XML-based vector graphics format sponsored by WC3. SVG is a powerful format, but lacks support from authoring tool and web browser makers. Adobe, before it acquired Macromedia, used to support SVG. SVG works well in the Opera browser and increasingly better in Firefox.
- SMIL, an XML-based multi-media integration language that supports timing, layout, animations, etc. SMIL is included in the full SVG profile. SMILE works with several media players (e.g. RealPlayer and Adobe Media Player). A variant exists for Internet Explorer.
- Microsoft Silverlight, a new Microsoft attempt to have its own "Flash"
- Others
See also multimedia authoring systems and computer games. Some of these have their own format, some can export to more common formats.
Links for software and media elements
General / Indexes
- OsFlash has a large comprehensive list of links to Open Source Flash projects, both those hosted on OSFlash and elsewhere. Of particular interest are tools that generate flash in various ways.
Viewers
- Adobe (Flash player download)
- Gnash (Wikipedia article) A project which aims to create a player and browser plugin for the Adobe Flash file format which is free software.
Authoring tools
- Adobe Flash CS3 Professional. The commercial authoring tool. Students: You can get huge discounts either through some stores or Adobe's education program (takes some times to fight through this web site and to find the appropriate page). In both cases you will have to send proof to Adobe before you will get a key. Teachers pay more, institutions can make deals that are more difficult to get.
Adobe Flash CS3 Professional was released in April 2007 and CS4 Professional released in october 2008. CS4 adds inverse kinematics, easier motion tweening (i.e. object-based animation finally!) and some basic support for 3D animations of 2D objects.
- SWISH. An alternative set of commercial products to produce Flash. Much cheaper and somewhat easier it seems, but doesn't export to *.fla files (so you can't import to the Adobe authoring tool). See the Wikipedia article.
- Salasaga. An free (and OSS) Integrated Development Environment for producing animated swf files, similar to Adobe Captivate. Goal is to create a free, easy to use GUI authoring environment that helps you create visually impressive and actually useful learning material. Example swf output here.
Decompilers
A decompiler can translate an *.swf to *.fla. Useful if you want to learn (not steal) from examples on the web or if you lost by mistake your *.fla sources.
- Flash Decompiler Trillix
- See also Flash Decompiler Trillix (strange website without any documentation)
Special purpose authoring tools
There is an increasing variety of tools and for a wide range of people, covering casual users to programmers.
- Adobe Captivate. An authoring environment to create simulations, scenario-based training, and robust quizzes. Can importexport to Flash *.fla documents.
- Adobe Acrobat Connect (formerly called Breeze) is a flash-based videoconferencing software.
- Adobe Flex is a software development kit and an IDE for a group of technologies to make rich internet applications with Flash, HTML, JavaScript etc.).
- Toufee, an online tool to make Flash presentations (movies). Free in a basic version. Drag and drop pictures or special elements to a stage, add special effects, buttons, etc. Also saves in other formats.
- OpenOffice Impress (the power point clone) can produce *.swf
- Some capturing tools (see screen capture, photo gallery makers, and video editing software can export to Flash.
Server technology
- red 5 is an open source Flash Server. I supports Streaming Audio/Video (FLV and MP3, Recording Client Streams (FLV only), Shared Objects, Live Stream Publishing and Remoting (AMF) (nov/2008)
- Adobe has a global Flash framework that includes e.g. a Flash Media Server Family.
Generating Flash
- Ming Ming is a C library for generating SWF ("Flash") format movies, plus a set of wrappers for using the library from C++ and popular scripting languages like PHP, Perl, Python, and Ruby.
- SWFMill xml2swf and swf2xml processor that can be used to create (non interactive) multiframe SWF animations.
- HaXe. Programming language very similar to actionscript that can compile a SWF file for Flash Players 6 to 9. Free to use.
In addition, you also should know that you can import several vector graphics formats. e.g. Windows Metafile formats into Flash CS3 (speeds up drawing).
Programming Editors for ActionScript
- Flashdevelop. Free and open source tool that provides syntax support and an interface with the Flex compilers.
- Some multi-purpose editors (like emacs also may support Actionscript 3 programming
- Adobe Flex Builder - a commercial Eclipse plugin from Adobe, but that is free for education upon request.
Media for building your own scenes
Extra Resources
- Flash and AS3 links - general
- Flash and AS3 links - tutorials
- Flash and AS3 links - documentation (Flash and AS3 Books, Reference Manuals and Cheatsheets)
- Flash and AS3 links - toolkits (AS 3 Toolkits, Libraries, Flash reusable components, AS 3 reusable code, etc.)