Doblo factory
This article or section is currently under construction
In principle, someone is working on it and there should be a better version in a not so distant future.
If you want to modify this page, please discuss it with the person working on it (see the "history")
- See also Doblo factory version 1
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
Introduction
Doblo Factory is the name of a set of OpenScad modules to generate Lego and Duplo-compatible structures and bricks. An inititial version was written by Daniel K. Schneider in 2010. Daniel Taub created a refactored version in 2012. This new version documented here also included several interesting additions.
As of september 2015, this library is fully functional and compatible with current OpenSCAD implementation.
Download:
- https://github.com/dmtaub/DobloFactory (owned by Daniel Taub)
Since OpenScad allows to "union" bricks, it is fairly easy to stack up bricks made from parametric OpenScad modules in order to create larger structures.
Doblo factory modules use a grid-based positioning system. The library can be used by non-programmers to create complex Lego-like structures just by making function calls with the right position and size parameters. However, users are expected to be familiar with using a formal language (e.g. HTML or SPSS or a simple scripting language). See the example section for some module usage code.
See also: Lego Dacta, i.e. an article describing a Lego product line for education.
Concepts
Basic Units
Doble factory uses a simple unit and position system that allows thinking in high-level units, as opposed to fractions of millimeters. Lego measures are quite complex and sometimes controversial as you could see from reading informations on various fan sites.
Doblo factory has been tested quite extensively with Duplo and Lego sizes. You even can combine the two systems to create a single brick. Mini (nano size) and Quadro size has not been really tested. While outsize size of various systems is always 2 times smaller or bigger, this is not the case for walls, nibbles, cylinders, etc.
Lugos, Doblos, etc.
- Doblo bricks are compatible with Duplos
- Lugo bricks are compatible with Legos. Legos are half as wide, long and high as Duplos, i.e. en 8th of the volume
- Minis are an 8th of Legos, i.e. the same size as Nanoblocks but Lego compatible
- Cadros are the biggest units and compatible with Quadros, but have not been tested very much. Also, they need support for printing.
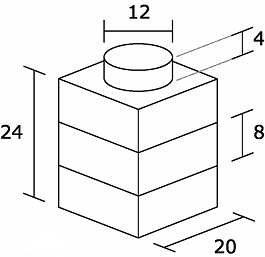
Height units
Height of a standard brick is defined as 6 units. E.g. a height of 5 for a Lego brick would mean 5/6 of a standard brick. Common heights are also defined by the parameters FULL, HALF and THIRD.
- FULL = 6 units
- HALF = 3 units
- THIRD = 2 units
The unit size in mm depends on the brick system
- Cadro (Quatro compatible) = 6.4mm
- Doblo (Duplo compatible) = 3.2mm
- Lugo (Lego compatible) = 1.6mm
- Mini (Nanoblock size, but not compatible) = 0.8mm
For example, a standard Lego brick has a height of 6 units * 1.6mm = 9.6mm
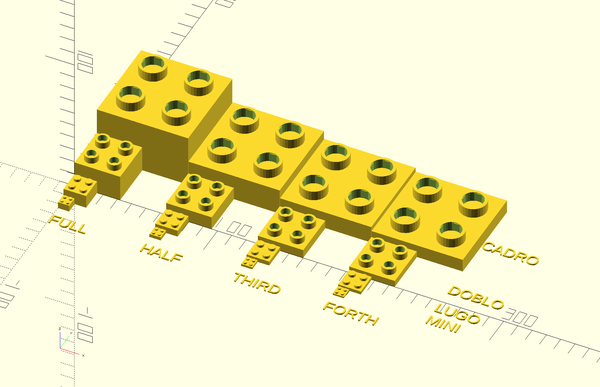
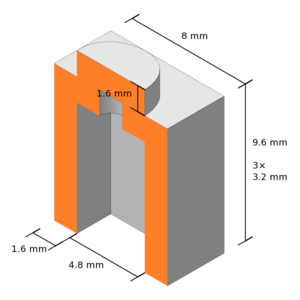
The following picture shows left to right (x axis) the FULL, HALF and THIRD height of the various brick types. Back to front (y axis) shows the brick types: Doblo, Lego, Mini. These are compatible with DUPLO, LEGO, and can be stacked on top of Nano blocks (but not underneath).
Width and length units
Units for columns, rows, with and length are standardized with respect to the smallest Lego size
- DUPLO = 16mm
- LEGO = 8mm
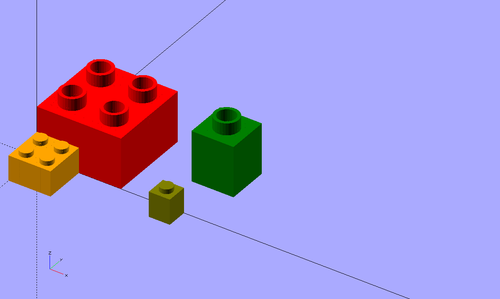
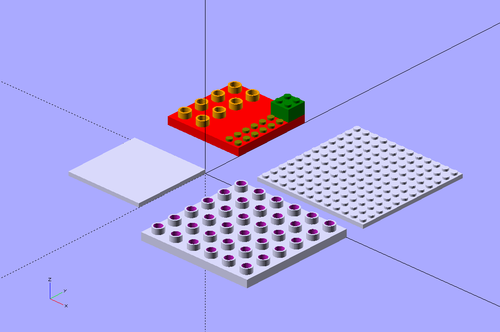
The following picture shows in the back row a 2x2 Duplo (red), a 1x1 Duplo (green), and in the front row a 2x2 Lego (orange) and an olive 1x1 Lego. Positioning uses the same units (see below)
For example, as we shall explain again in more detail, a standard small Lego brick is defined as "2x2xFULL" = 2x2x6 = 16mm x 16mm x 9.6mm
Rotation
Some bricks can be rotated through rotation parameters. You only should try 0, 90, 180, 270, else the result is unpredictable
The positioning framework
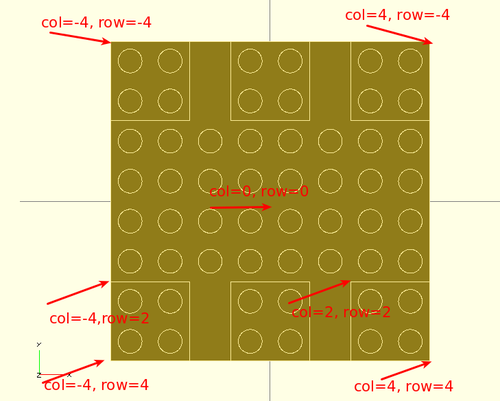
Doblo uses a grid like a chessboard. Origin is in the middle like in most 3D representation languages.
- Column = left to right (x axis)
- Row = forward to backward (y axis). This can be considered a good decision if you look at your model from top. Else it isn't. I wasn't sure about this, but now it's done. So remember: y is reversed with respect to OpenScad.
- up = upwards (z axis)
Blocks have the x/y origin in the origin in the upper left.
Let us illustrate this with an example picture:
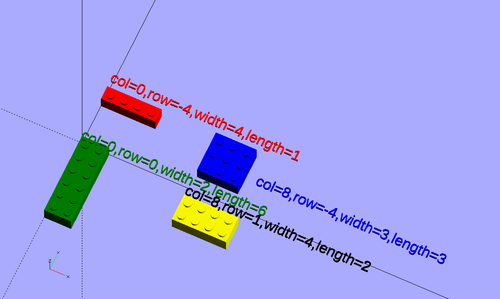
Parameter names used in the source code
- col: the x axis (left-to-right)
- row: the y axis (forward to backward)
- up: the z axis (down to up), Z origin is the bottom of a block. I.e. a block of up=1 would sit on a block of height=1.
- width: length on the x-axis. Except for the doblo block whose origin is in the middle, origin is upper left
- length: length on the y-axis, Except for the doblo block whose origin is in the middle, origin is upper left
- nibbles_on_off: true = nibbles on top, false = no nibbles
Parameters to identify the Duplo/Lego scale
Each function that defines a brick has a scale parameter that you can use to render it in either Doblo, Lugo or mini size.
- DOBLO = 1; // Duplo size
- LUGO = 0.5; // Lego size
- MINI = 0.25; // Nano size
Alternatively, you could set the SCALE parameter in the beginning of your file, e.g. scale = 0.5;
Calibration of parameters
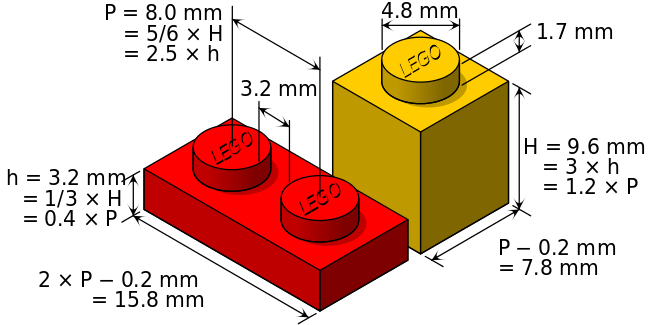
About Lego and Duplo dimensions
According to the german-speaking 1000steine.de forum , retrieved 13:12, 15 April 2010 (UTC), the approximate dimensions of a Lego brick are the following. Duplo bricks are double in each dimension (i.e. 8 times the volume). However, there are important differences between Duplo and Lego bricks. In the code, we deal with this by using conditionals when defining parameters.
Another theory from the same forum thread claims that Legos have been designed in terms of special Lego units, i.e 1/64 inches.
Wikipedia also includes a diagram with dimensions
Finally, I suggest to buy a digital calliper (about 17 Euros) and measure both original bricks and your own bricks.
- Duplo vs. lego heights
(1) Most Duplo pieces are either "normal" (19.2mm) or half height (9.6mm)
- In our unit system, FULL or HALF
(2) Most Lego pieces are either "normal" (9.6mm) or third height (3.2mm).
- In our unit system, FULL or THIRD
Doblo factory parameters
To create somewhat DUPLO and Lego-compatible bricks, one does not necessarily use real dimensions. For example, filament-based 3D printers will not produce accurate nibbles. Therefore, if you provide correct data, your blocks won't be compatible. You will have to adjust for your printer and your print settings by editing the parameters in the *.scad file.
Doblo factory is fully parametrized and you certainly will have to adjust the nibble-related parameters with respect to your type of 3D printer, polymers used, and your print setting like print speed, extrusion speed, layer width, and Perimeter Width over Thickness ratio. See for example the Skeinforge for RapMan article for an explanation of these concepts.
Depending on your printer and your layer/thickness printing parameters you may need to change parameters for nibbles and walls.
Parameters were by default set for a Felix V2 printer, i.e. typical mid-range PLA printer. Printing with "normal" slicers profiles should work fairly well, although you may add an extra shell to the first layer and and extra full layer for the bridges (roofs).
- Layer thickness (mm): Between 0.2 and 0.25 for DUPLOS and Legos. But you can go lower for Legos (0.1 to 02mm).
- Fit with real Legos and Duplos is rather tight (as least with our printer/slicer combination). After printing - while still warm - you can press the brick onto a real brick to make some adjustement. You also could heat a brick with heat gun, e.g. to 60 - 90 degrees before doing so.
- Adjust wall with, insets and nibble outer radius, if needed.
Parameters are wrong in order to compensate for the characteristics of the printer and the print parameters. If you do precision printing, e.g. with a 0.1 mm layer you may go closer to the real DUPLO/Lego values.
All units are mm.
Dimensions:
- A typical small 2x2 nibbles on top DUPLO compatible brick with one nibble underneath is approximately 32mm x 32mm x 19.2mm (plus a nibble height of 4.5mm)
- LEGO-compatible bricks are half that size in all three dimensions. However walls and nibbles are not proportionally smaller !. This is why we use conditionals in the parameter section. we assume that any size smaller than 0.6 should adopt the Lego proportions.
- DUPLO compatible bricks: use SCALE = 1
- Lego compatible bricks: Use SCALE = 0.5
Below we show the settings part of the doblo-params.scad file in Doblo Factory, version 2.1
// Normal size (DUPLO)
// SCALE = 1;
// Lego size - see also the hacks in the code for fixing wall and nibble dimensions
// SCALE = 0.5 ;
// Mini Lego size
// SCALE = 0.25
CADRO = 2; // not yet tested
DOBLO = 1;
LUGO = 0.5;
MINI = 0.25;
HALF=3;
THIRD=2;
FULL=6;
// LEGO SCALE - don't change, allows to create nano legos, should be 1 if real Legos
function LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) = 2 * SCALE;
// Doblo block size
// Real DUPLO Block = 31.7 / 2 = 15.85 (with some variations)
function PART_WIDTH(SCALE) = 16.0 * SCALE;
// Block height (a typical block is 4 * PART_HEIGHT)
// Real Duplo Block = 19.17 / 4 = 4.8, we also measured 19.09, 19.16
function PART_HEIGHT(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? ( 1.6 * LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) ) : ( 3.2 * SCALE );
// Diamonds - size of anti-warping holes - used optionally
DIAMOND = 4;
// Top nibble size definitions
// Must be adjusted with respect to layer resolution and other slicing considerations
function NO(SCALE) = PART_WIDTH(SCALE) / 2.0; //nibble offset
function NBO(SCALE) = PART_WIDTH(SCALE); // nibble bottom offset
function NH(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 1.75 * LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) : 4.55 * SCALE; // LEGO vs. DUPLO
function NB_RADIUS(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? (4.9 / 2 * LEGO_SCALE(SCALE)) : (9.2 / 2.0 * SCALE); // Lego vs. DUPLO
// Real DUPLO Block = 9.38
function NB_RADIUS_INSIDE(SCALE) = 6.8/2 * SCALE;
// 6.44 = Real DUPLO block
function NB_THICKNESS(SCALE)=NB_RADIUS(SCALE)-NB_RADIUS_INSIDE(SCALE);
// For square nibble supports in 1xM or Nx1 blocks
function ALONG_LEN(SCALE) = (PART_WIDTH(SCALE)-NB_RADIUS(SCALE))/1.7; //tighter fit than 1.8
function CROSS_LEN(SCALE) = (PART_WIDTH(SCALE)-NB_RADIUS(SCALE)/2);
// Bottom nibbles size definitions
// Must be adjusted with respect to layer resolution and other slicing considerations
function NB_BOTTOM_RADIUS(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 6.5/2*LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) : 13.4/2*SCALE;
function NB_BOTTOM_RADIUS_THIN(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 3.5/2*LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) : 7.2/2*SCALE;
// Real DUPLO = 13.48
function NB_BOTTOM_RADIUS_INSIDE(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 4.8/2*LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) : 10.8/2*SCALE;
// Real DUPLO = 10.73
// rapman 10.6
// Real Lego = 4.9
// walls - IMPORTANT: must be adjusted with respect to layer resolution and other slicing considerations
function DOBLOWALL(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 1.2 * LEGO_SCALE(SCALE): 1.55 *SCALE; // Lego vs. Duplo, Lego is not 2x smaller
function USE_INSET(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? true : true;
function INSET_WIDTH(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 0.4 *LEGO_SCALE(SCALE) : 1.50 * SCALE; //little inset walls to make it stick
function INSET_LENGTH(SCALE) = (SCALE < 0.6) ? 3*DOBLOWALL(SCALE) : 4*DOBLOWALL(SCALE); // Legos have proportionally smaller insets
//lattice width and height (optional, see LATTICE_TYPE)
// A grid underneath the flat bridge, crossing through the nibbles underneath
function LATTICE_WIDTH(SCALE) = 1.50 * SCALE;
// 0 means none, 1 means more spacing (same as nibbles underneath),
// 2 means denser
LATTICE_TYPE = 1;
// Sizes of a standard 2x2 square brick, normal height
// Not used, but are practical in your custom modules
function DOBLOWIDTH(SCALE) = PART_WIDTH(SCALE) * 2.0 * SCALE;
function DOBLOHEIGHT(SCALE) = PART_HEIGHT(SCALE) * 6.0 * SCALE;
function LEGOHEIGHT(SCALE) = PART_HEIGHT(SCALE) * 6.0 * SCALE;
Using openscad doblo modules
From a user point of view, Doble factory, is a set of functions (called modules in OpenSCAD) that will produce various Lego geometries.
You could use Doblo factory to generate various types of isolated bricks, but its main purpose is to assemble various smaller pieces into a bigger whole that then can printed.
Most doblo modules work in the same way, the use the same parameters in the same order if appropriate.
Getting started
Getting started - e.g. producing a canonical 4x2 Lego brick - is simple
- Create a Scad file that includes the doblo-factory library and a parameter file
- Call the doblo module with some parameters.
Creation of simple Lego brick using a list of parameters
include <doblo-factory.scad>;
include <lib/doblo-params-repl.scad>;
// column line z-pos width length height nibbles diamonds, size
doblo (0, 0, 0, 4, 2, FULL, true, false, LUGO);
This will create a brick that looks like this and that is positioned at x,y,z origin. As you can see in the code, we added a line with comments so that we could remember what each parameter represents.
Alternatively - and we recomment this - you can use a more verbose syntax that uses parameter names in the module call. The following code will produce two identical Lego compatible bricks. We use both short and long notation (named parameters).
include <doblo-factory.scad>;
include <lib/doblo-params-repl.scad>;
//doblo (0, 0, 0, 2, 2, FULL, true, false, DOBLO);
//doblo (0, 0, 0, 2, 2, FULL, true, false, LUGO);
// col row up width length height
doblo (0, 0, 0, 4, 2, FULL, true, false, LUGO);
doblo (col=0, row=4, up=0,
width=4, length=2, height=FULL,
nibbles_on_off=true, diamonds_on_off=false,
scale=LUGO);
Overview of doblo modules
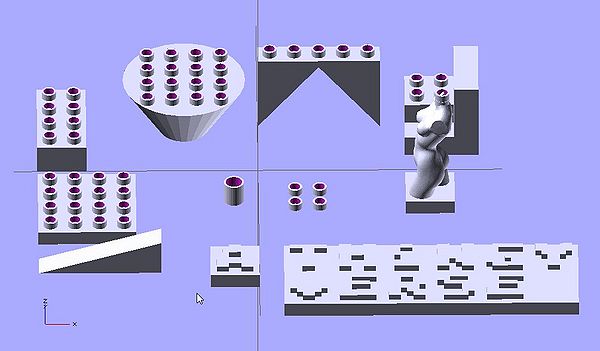
The following picture shows of few types of bricks that you could generate (and combine).
- Doblo brick
- Base plate
- Merge STL files
- Block
- Nibbles
- Support triangles
- Ramp
- Cylinder
- [ New elements ]
List of doblo modules
Below, we shall attempt to document each type of brick. The documentation is not complete yet, look at the source code please - Daniel K. Schneider (talk) 17:25, 28 September 2015 (CEST)
doblo brick
Creates a typical duplo-compatible brick. Typical use is to create a Doblo base on which you then can add other structures. You also can pile up (union) these bricks, but that may lead to a waste of processing time and plastic. Doblo bricks are just like Duplo bricks, however you can make the nibbles on top optional.
- Short Syntax
doblo (col, row, up, width, length, height, nibbles_on_off, holes_on_off, system)
col = number, the x position of the brick
row = number, the y position of the brick
width = number, the size in x axis. 2 refers to brick size of 2
length = number (y axis). 4 referes to brick size of 4
height = either a number for the sixth of a standard brick height or THIRD, HALF, FULL
nibbles_on_off = wether you want nibbles or not, i.e. true or false
system = either LUGO or DOBLO
- Named parameters syntax with default parameter values
doblo (col=0,
row=4,
up=0,
width=4,
length=2,
height=FULL,
nibbles_on_off=true,
diamonds_on_off=false,
scale=LUGO);
Example
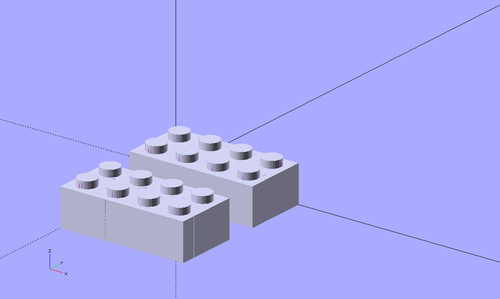
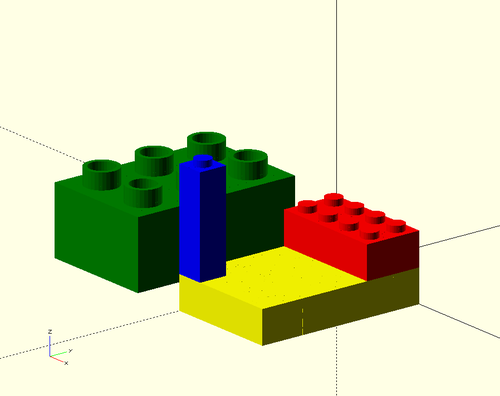
The following picture shows four bricks:
- Yellow: A larger yellow Lego-compatible brick (4x6x6 or 4x6xFULL size) without nibbles
- Red: A standard 2x2xFULL sized Lego-compatible brick
- Blue: A 1x1x18 = 1x1x 3*FULL Lego-compatible brick
- Green: A 2x3xFULL Duplo-compatible block
The code (including an extra "color("....") statements goes like this:
include <doblo-factory.scad>;
include <lib/doblo-params-repl.scad>;
color ("yellow") doblo (col=0, row=0, up=0,
width=4, length=6, height=FULL,
nibbles_on_off=false,
diamonds_on_off=false,
scale=LUGO);
color ("red") doblo (col=0, row=0, up=FULL,
width=4, length=2, height=FULL,
nibbles_on_off=true,
diamonds_on_off=false,
scale=LUGO);
color ("blue") doblo (col=0, row=5, up=FULL,
width=1, length=1, height=3*FULL,
nibbles_on_off=true,
diamonds_on_off=false,
scale=LUGO);
color ("green") doblo (col=-3, row=0, up=0,
width=2, length=3, height=FULL,
nibbles_on_off=true,
diamonds_on_off=false,
scale=DOBLO);
Base plate
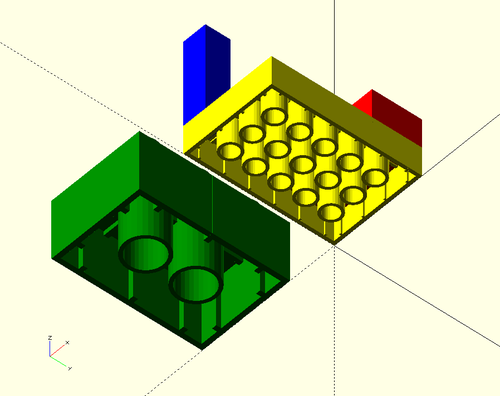
This is an easy to print non-stackable base plate. In order to prevent warping on the print bed, it has smaller squares underneath if you print them in exactly the same heights as below (there is a bug as of sept. 2015). Up should be always 0. You also can "glue" other elements on top in order to create play-mobile like structures. In that case you also should nibbles in certain areas as shown in the following example:
- Short Syntax
base_plate (col, row, up, width, length, height, nibbles_on_off, scale)
- Long Syntax
module base_plate (col=0, row=0, up=0, width=8,length=8,height=THIRD,nibbles_on_off, scale=LUGO)
Example that shows how to add a few nibbles on top:
include <doblo-factory.scad>;
base_plate (4, -14, 0, 12,12,2,true, LUGO);
base_plate (2, 0, 0, 6, 6, 2,true, DOBLO);
base_plate(col=-8);
// A stack of doblos/lugos just for the fun of it.
// Note how DOBLOs and LUGOs have a different coordinate system
color ("red") base_plate (-4, -6, 0, 4, 4, 2, false, DOBLO);
color ("orange") nibbles (col=-4, row=-6, up=2, width=2, length=4, scale=DOBLO);
color ("green") doblo (-2, -12, 4, 2, 2, 6, true, false, LUGO);
color ("olive") nibbles (col=-2, row=-10, up=4, width=2, length=6, scale=LUGO);
As this example shows, it could be useful to add a bit of color in front of some bricks. This way you can identify them. Below is the picture:
Merge STL files
Positions an stl file, you may have to find out by trial and error what z offset to use. Tip: embed the STL into a doblo or a block.
- Syntax
merge_stl (file, col, row, stl_z_offset_mm, shrink, scale)
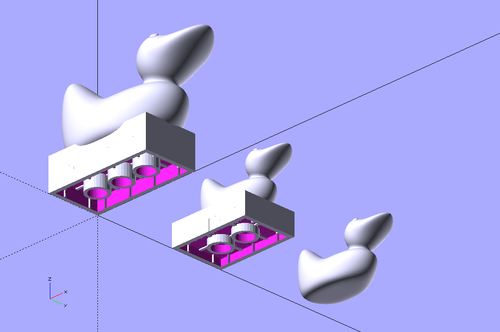
If you plan to create blocks with some animal on top, also consider using the little stl-merge-display extension like this:
include <doblo-factory.scad>;
include <lib/doblo-params.scad>;
include <ext/stl-merge-display.scad>;
// One in front
merge_brick(stl_file="stls/duck.stl");
// A second one in the back
translate([0,40,0])
merge_brick (doblo_width=3, doblo_length=2, doblo_height=2, doblo_nibbles=false,
stl_file="stls/duck.stl", stl_lift=-1, stl_shrink=1.66,
STL_col=1, STL_row=0,
block_height=2, block_width=3, block_length=2);
// A simple merge without brick and block using the doblo-factory module
translate([0,80,0]) scale (0.5) merge_stl ("stls/duck.stl", shrink=0.8);
Block
Creates a building block for larger structures with x,y,z positioning. A block does not have nibbles underneath and may or may not have nibbles on top. Also could be used to print a base plate.
- Syntax
block (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off, scale)module block (col=0, row=0, up=0, width=2,length=4,height=FULL,nibbles_on_off=false, scale=LUGO)
Blocks are essential for building larger structures. The following examples shows how we could create a simple stairway by stacking a series of blocks next to each other.
include <doblo-factory.scad>;
include <lib/doblo-params.scad>;
module stairs_world_light ()
{
// (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off)
color ("green") doblo (-5, -5, 0, 10, 10, 1, false, scale=DOBLO);
// staircase
// (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off, SCALE)
color ("red") block (1, 3, 1, 2, 2, 2, false, DOBLO);
color ("pink") block (-1, 3, 1, 2, 2, 4, false, DOBLO);
color ("red") block (-3, 3, 1, 2, 2, 6, false, DOBLO);
color ("pink") block (-5, 3, 1, 2, 2, 8, false, DOBLO);
color ("red") block (-5, 1, 1, 2, 2, 10, false, DOBLO);
color ("pink") block (-5, -1, 1, 2, 2, 12, false, DOBLO);
color ("red") block (-5, -3, 1, 2, 2, 14, false, DOBLO);
color ("pink") block (-5, -5, 1, 2, 2, 16, true, DOBLO);
color ("blue") block (3, -5, 1, 2, 6, 1, true, scale=DOBLO);
}
// call the module, else it won't draw
stairs_world_light();
Nibbles
To insert nibbles on some spots of a nibble-less block or an imported STL. For use in larger structures.
- Syntax
- nibbles (col, row, up, width, length)
Bottom nibbles
To insert underneath an imported STL. Not very usefull I think, I'd rather stick a doblo block to the feet of an imported object.
- Syntax
- bottom_nibbles (col, row, up, width, length, N_height)
Support triangles
Support triangles are used in larger structures to support a roof.
- Thickness = 1 doblo width, e.g. = PART_WIDTH.
- Sometimes you may want rational numbers. E.g. 1.5
- Height/length proportion is 4.8/4 (i.e. typical Duplo proportions).
- Only use angle arg of 0,90,180,270 !!
WARNING: You may want to have these bricks overlap a bit, e.g. if 2 corners are just touching, the model will be not be "simple" and can't be exported as STL. In other words, make them a bit higher and position a bit off (embed into the block that you will put on the back and embed the back in a side block). See the stronghold example included.
- Syntax
- support (col,row,up,height,rotation_angle,thickness)
ramp
ramp is the opposite of the support triangle, but with a flatter angle. Can be used to anchor a high and slim block or also to build a real ramp (then you might place 2-4 next to each other.
- Height/length proportion is 4.8/16 (i.e. typical Lego proportions)
Syntax:
- ramp (col,row,up,height,rotation_angle)
Notice: I'll have to add width to this one
Cylinder
cylinder is like a block, but round.
- Can have nibbles on top.
Syntax:
- cyl_block (col, row, up, bottom_r, top_r, height, nibbles_on_off)
Glyph
Is a letter, a number or a special character. This module is based on OpenSCAD Bitmap Fonts Module
Syntax:
- glyph (col, row, up, height_mm, char)
Text
Is a text with glyph characters (see above).
Syntax:
- text (col, row, up, height_mm, chars, count)
count is the number of letters
chars is an array.
Example
- text (1, 6, 2, 4, ["T","H","i","N","G","Y"], 6);
Examples
A simple brick
A simple 4x4 brick without nibbles (for mashups) and a typical 2x2 brick with nibbles commented out
// define a module if you like
module doblo_brick ()
{
// (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off)
doblo (0, 0, 0, 4, 4, 3, false);
// doblo (0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 4, true);
}
// Call the module
doblo_brick ();
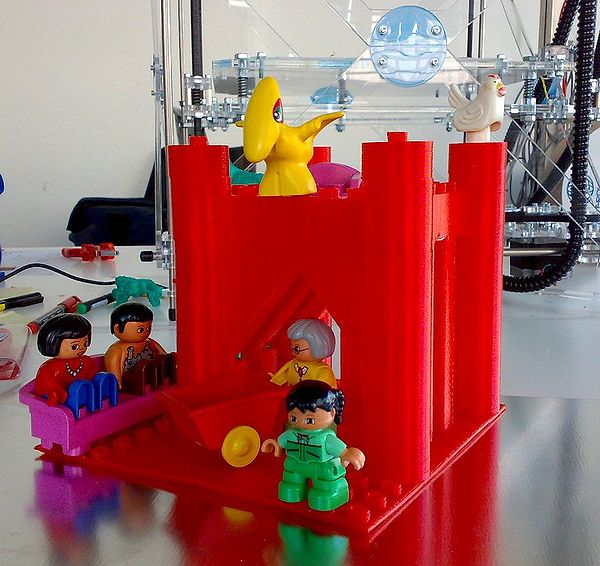
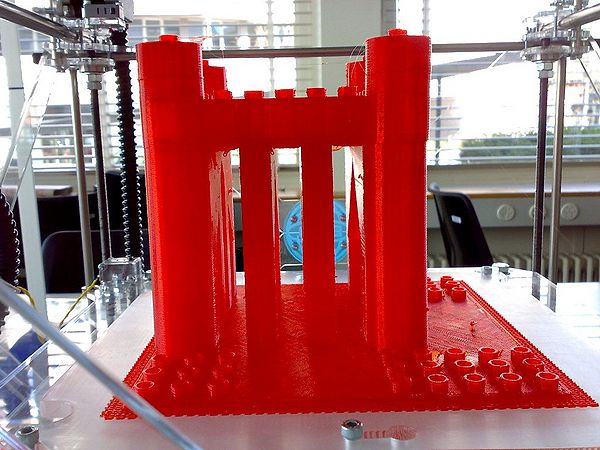
Doblo structure - A stronghold
The following structure was my first creation and it did have some design flaws. But it did print.
But it did print:
See the happy Duplo persons !
- Module name
- stronghold ()
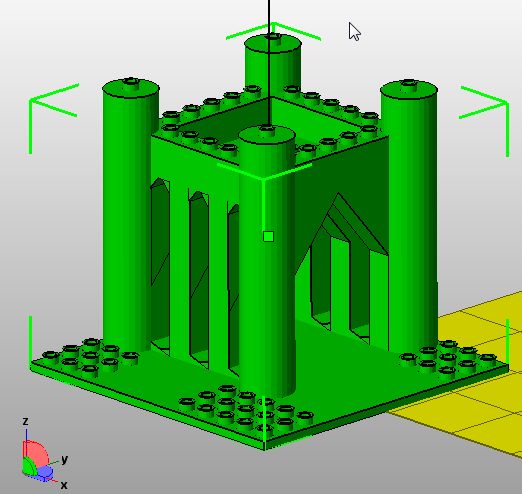
Below is a revised design which I didn't print yet. It's included in the doblo-factory-1.scad file.
The code is fairly complex, because we needed some support triangles. These should be replaced by pillars some day ...
module stronghold ()
{
union()
{
// Base plate, for faster printing replace by block
// (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off)
// doblo (-5, -5, 0, 10, 10, 1, false);
doblo_light (-6, -6, 0, 12, 12, 1, false);
// (col, row, up, width, length)
nibbles (3, -6, 1, 3, 3 );
nibbles (1, 3, 1, 5, 3 );
nibbles (-6, 3, 1, 3, 3 );
// (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off) - blocks
// (col, row, up, height,degrees) - ramps
// back
ramp (-5, -5, 1, 2, 0);
block (-5, -5, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
ramp (-3, -5, 1, 2, 0);
ramp (-3, -5, 1, 2, 180);
block (-3, -5, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
ramp (-1, -5, 1, 2, 0);
ramp (-1, -5, 1, 2, 180);
block (-1, -5, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
ramp (1, -5, 1, 2, 180);
block (1, -5, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
// left
block (-5, -3, 1, 1, 1, 22, false);
block (-5, -1, 1, 1, 1, 22, false);
// front
ramp (-5, 1, 1, 2, 0);
block (-5, 1, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
ramp (-3, 1, 1, 2, 0);
ramp (-3, 1, 1, 2, 180);
block (-3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
ramp (-1, 1, 1, 2, 0);
ramp (-1, 1, 1, 2, 180);
block (-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
ramp (1, 1, 1, 2, 180);
block (1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 12, false);
// right
// block (0, -4, 1, 1, 3, 8, false);
// big arc
// (col, row, up, height,degrees)
support (-5, -5, 9, 14, 270, 1) ;
support (-4.1, -5, 21, 2.2, 0, 7);
support (-3.9, -5, 21, 2.2, 180, 7);
support (-3, -5, 9, 14, 270, 1) ;
support (-2.1, -5, 21, 2.2, 0, 7);
support (-1.9, -5, 21, 2.2, 180, 7);
support (-1, -5, 9, 14, 270, 1) ;
support (-0.1, -5, 21, 2.2, 0, 7);
support (0.1, -5, 21, 2.2, 180, 7);
support (1, -5, 9, 14, 270, 1) ;
support (-5, 1, 9, 14, 90, 1) ;
support (-3, 1, 9, 14, 90, 1) ;
support (-1, 1, 9, 14, 90, 1) ;
support (1, 1, 9, 14, 90, 1) ;
// Roof
// (col, row, up, width,length,height,nibbles_on_off)
block (-5, -5, 23, 7, 7, 1, false);
nibbles (-3, -3, 24, 3, 3);
block (-5, -5, 24, 7, 1, 4, false);
nibbles (-4, -5, 28, 5, 1);
block (-5, 1, 24, 7, 1, 4, false);
nibbles (-5, -4, 28, 1, 5);
block (-5, -4, 24, 1, 5, 4, false);
nibbles (-4, 1, 28, 5, 1);
block (1, -4, 24, 1, 5, 4, false);
nibbles (1, -4, 28, 1, 5);
// (col, row, up, bottom_r, top_r, height, nibbles_on_off)
cyl_block (-6, -6, 1, 2, 2, 32, true) ;
cyl_block (1, -6, 1, 2, 2, 32, true) ;
cyl_block (-6, 1, 1, 2, 2, 32, true) ;
cyl_block (1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 32, true) ;
}
}
To use this "as is", just uncomment the following line in the doblo-factory-examples.scad file:
// stronghold ();
Some mashups
In the following picture you can see two kinds of mashups made in 2010 with a Rapman printer and a rather coarse 0.4mm layer resolution.
- Larger STL models put on top of bricks. I actually did these with Meshlab before I learnt how to use OpenScad.
- Doblo bricks with webdings on top. Produced with either OpenScad alone or with Netfabb Studio. The basic version of Netfabb does have a 3D text. The pro version can directly export a mashup. Users of Netfabb Studio basic should also use either OpenScad or Meshlab for merging.
Printing
RapMan / RepRap Mendel
We shall discuss some skeinforge printing settings for the RapMan below. You may consult the Skeinforge for RapMan to understand these. Also, Netfabb engine for RapMan will be able to print high quality DUPLOs in some near future. The current 4.5.1 Beta version cannot correctly print the overhangs of the Duplo tops yet - Daniel K. Schneider 20:14, 30 April 2010 (UTC).
- Try small objects first, e.g. a 3x3x3 doblo brick with PLA or a 2x2x3 block with ABS. ABS warps !
Calibration
We used the following setup for larger structures
- Layer Thickness (mm) : 0.4
- Perimeter Width over Thickness (ratio), i.e. how wide the filament should be compared to it´s height: 1.8
- Fill
- Fill of 0.1 should be ok (I tested with 0.05)
- PLA
- Use PLA on large objects to prevent warping (Notice: I should create a version of the bricks with big holes in the side walls for ABS printing)
- Temperature: 210 (all) and Fan on
- Raft: One interface layer
- Flow rate: At least 380 for a layer thickness of 0.4 (for horizontal structures)
- Other
- Solid Surface Thickness for both ABS and PLA: 4
- ABS
- We only made smaller objects so far, e.g. simple doblo bricks and mashups. You can see some of these in the Meshlab for RapMan tutorial and Netfabb Studio tutorial.
- One of the major difficulties is to create a raft that really sticks both to the print bed and the object. See the duplo bricks for color ABS section in our Skeinforge entry.
Since skeinforge does not really produce what I want, I'd suggest to produce sort of a normal "fat" raft code, then edit the g-code file and double up M108 and Fxxx values. Make it twice as fast, else it takes hours to get just the raft printed ....
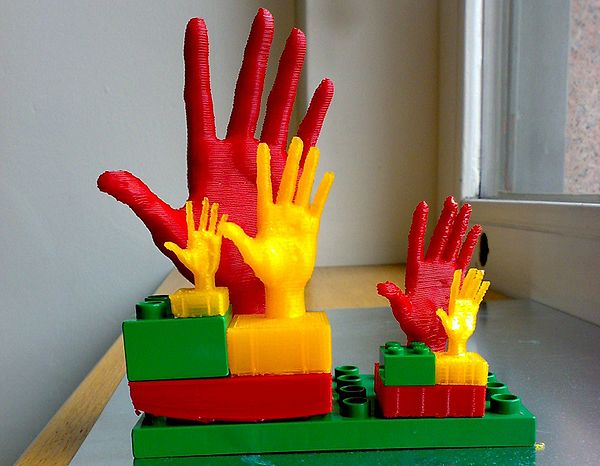
- Precision objects
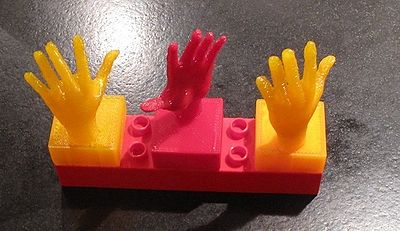
- See the Hand on duplo-compatible block example discussed on Thingyverse. E.g. a good quality/print time setting for Skeinforge is:
- Layer Thickness = 0.35
- Clip Over Perimeter Width = 0.15
- Cool Type = Orbit
- Min Layer time = 1
- Extra shells on Base = 2
- Infill perimeter Overlap
- Infill solidity = 0.3
- Solid surface layers = 4
- Jitter = activated
- Temperature = 210 for ALL
- Flow Rate = 250
- Feed Rate = 16
Felixprinter and fabbster
Start with default "normal" profiles, i.e. something between draft and high-quality printing.
Can your printer do it ?
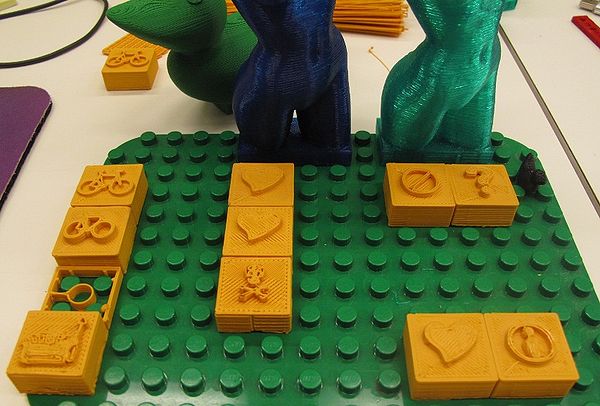
We designed a simple suite of benchmarking pieces that you can
use to test drive both DUPLO-compatible and LEGO-compatible sized blocks. Start with the DUPLOs pieces. Note however, that different kinds of structures may need different calibration. Print time is also a big factor.
Download: http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2714
Print the four pieces and see if they fit like in the picture. The green blocks are Duplos/Legos. Pieces must fit in each possible combination.
If you know how to use OpenScad, it's better to generate the STLs again, since I had to cheat a bit with the width parameters in order to compensate the way the printer works. See also http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2106 for the blocks generator.
The *.zip file includes all files (except the picture)
Evaluation criteria:
- 1a) Fit with real Duplos, i.e. respect dimensions of real Duplo and Lego bricks
- 1b) First good good 5 layers of the brick. That's important for both esthetics and also vertical fit. That includes no warping !
- 1c) Roof of the brick on top, must be flat and smooth
- 1d) Roof of the brick underneath, no hanging filament
- 2a) Overhang of the thumb
- 2b) Smoothness of the palm and the back (difficult, of course faster prints will use bigger filament)
- 2c) Smoothness of the fingers, nails (difficult)
- 2d) Correct position of fingers
- 3a) Amount of post-processing needed
- 3b) Solidity (with respect to polymers used and size)
- 4) I don't know exactly how - but all this should be put into relation with print time
Printing pauses and recovery from print abortion
A larger structure like the stronghold takes over 24 hours to print. If you use PLA, it's ok to interrupt (hit the ESC key) while you sleep or do other stuff. I don't know about ABS.
However, if you encounter a card read error or a filament problem after 20 hours of printing, frustration can be high ! In the g-code article, we described how we managed to recover. It's not so easy, but certainly less painful than to restart.
Educational use
(will be completed later, probably as a separate piece - 14:33, 13 April 2010 (UTC) ....)
Design of constructivist play kits
One of our goals is create a kit that allows the creation of 3D duplo-compatible "play" boards for various purposes from Kindergarten to Master level.
“In the LEGO System, complex cause-and-effect relationships can be built from the ground up by the relatively simple act of combining individual elements” (Ackerman et al. 2009: 76). While ready-made playmobil-like boards to not necessarily favor creativity, building such boards does. LEGO (ibid:77) argues that the benefits of playing with LEGO Systems are: Curiosity (bricks encourage exploration naturally), courage (one can take risks and make mistakes), exploration and investigation (Lego has an easy start, but can reach high levels), experimentation (change and fiddle), imagination (infinite combinations), reason and discipoline (uses a fixed logical structure), sociability (can be shared) and reflection (builders can step back and evaluate).
The same paper (p. 81)also argues that the system will support systematic creativity:
- Preparation (problems that arrise curiosity)
- Incubation (ideas being generated and unlocked)
- Insight (thing falls in place and construction can begin)
- Evaluation (decide if the insight is worth pursuing and may lead to "hard fun")
- Elaboration (create the final form)
“The LEGO System is a system to think with. It encourages the process of making and reflecting, then making and reflecting again, in a thoughtful circuit of activity. In LEGO Serious Play participants are encouraged to build quickly and spontaneously, but then to take a step back and consider what they have made, and then review and change it as they see fit, with multiple iterations of individual and the collective activity. This build-then-reflect approach is really just one of the standard ways of using LEGO bricks which people naturally adopt.”
- Teacher and educational technologists training
In a fall 2010, class we will work with a small group of students to create both half-baked play platforms that leave enough space for thinking and new kinds of little blocks to support some classes of pedagogical scenarios. - 14:12, 13 April 2010 (UTC).
- A few notes on childhood learning
Ackerman, in an interview (retrieved 11:22, 13 April 2010 (UTC)) states that “LEGO provides a unique building system that encourages children to give form, or expression, to their wildest ideas in the most rigorous ways (hard fun)! Two things I enjoy most about LEGO: 1) the system offers endless possibilities. Yet, at the same time, not anything goes! The bricks have a mind [or logic] of their own, that the child learns to compose with to achieve their creations; 2) the system grows with the child, thus allowing the children to grow with it. As a constructivist at heart, I like play materials that let you in at different levels, and you can add complexity at will (low floor, high ceiling). Most children love to build things, and then bring them to life through play – or for real by adding special bricks, such as a motor, a light, or even a sensor.”
“Systems are crucial for creativity. Systems of science channel creativity towards asking specific questions, and solving or problems as in maths, chemistry and engineering. Systems of art channel creativity into many different and unique expressions, giving form to our imagination, feelings and identities, as in painting, music and sculpture. LEGO offers a unique—and widely recognized—system capable of channelling both, simultaneously. With LEGO you can bridge a stream, or transport an apple from A to B (scientific creativity) or build a fantasy creature, spaceship or landscape; or create metaphorical arrangements to evoke, project and represent feelings or identities (artistic creativity).” (Defining Systematic Creativity, retrieved 11:22, 13 April 2010 (UTC)).
Frans Orsted Andersen (2004) also argues that high PISA performances of the Danish Schools can be partly explained by the fact the learners more often encounter flow through "optimal learning environments". Scandinavian education is based on the three child i'es:
- initiative
- independence
- intrinsic motivation (which in turn is part-of flow). “Being able to base the learning processes on high levels of pupil
intrinsic motivation through a special teaching model enhancing flow experiences - indeed seems to be the key to understanding the successful optimal learning environments of the sampled Danish schools in this study.” ([Anderson, 2004: 14).
In addition to using such bricks and systems in normal schools and at home, DUPLOs and other construction kits seem to popular in special education (refs. needed).
- Adult learning
Another potential avenue for the doblo factory comes from so-called simulation and gaming. Some adult gaming environments only use physical support, others rely entirely on computer-support and, finally, others on mixed support.
Our aim is to procude visual, mostly 2D, iconic languages to support various kinds of project-oriented learning.
CAD/CAM, 3D and CS education
- Introduction to 3D graphics and design (learn about positions) and simple use of OpenSCAD
- "End-user 3D programming" environment (e.g. students could add other primitives)
Bugs, to do
- Bugs
- cyl_block nibbles can't handle top_r < 2 and rational numbers
- Needed
- a pillar with both supports for bottom and top (i.e. 2x4 directions)
- Improvements
- replace support modules by triangle_forward, triangle_right, etc.
- Parametrize all numbers
- Make it also Lego compatible
- Adjustments
- make the nibbles underneath a bit fatter maybe
- Figure out the best skeinforge settings for ABS and PLA
Links
Credits for the OpenScad code
- parametric lego duplo, prior work by by Domonoky.
- OpenScad
- End-user programming / microworlds
- Lego
- In this wiki, Lego Dacta and LEGO Mindstorms (includes links to Lego-fan sites that describe the 1000s of parts., good for inspiration)
- Parents at Lego.com
- LEGO Learning Institute (home page)
- legolearning.net
- Lego-related articles at MakeZine
- What's the relationship between playing with Lego and creation of Google ?
- Meet The Google Guys, Time magazine, Sunday, Feb. 12, 2006
Bibliography
- Ackermann Edith; David Gauntlett and Cecilia Weckstrom (2009). Defining Systematic Creativity, LEGO Learning Institute, Summary, PDF download
- Andersen, Frans Ørsted (2004), Optimal Learning Environments at Danish Primary Schools, LEGO Learning Institute Abstract/PDF download
- Claxton, Guy (1997). Hare Brain, Tortoise Mind, Fourth Estate, London.
- Claxton, Guy, What’s the Point of School, One World Publications, Oxford, 2008.
- LEGO Group (2004), The whole child development guide, LEGO Group, PDF dowload. Also can be found through Lego Learning Institute Research Page.
- Winnicott, D.W. (1989) Playing and Reality. London, New York: Routledge.