Flash: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (→Definition) |
||
| (167 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Incomplete}}{{Flash tutorial|CS4 (CS5)|beginner|}} | ||
<!-- <pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/> --> | |||
This page needs to be updated for Flash CS6, but principles remain the same ... | |||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
Adobe Flash, or | {{quotation|Adobe Flash (previously called Macromedia Flash) is a multimedia platform originally acquired by Macromedia and currently developed and distributed by Adobe Systems. Since its introduction in 1996, Flash has become a popular method for adding animation and interactivity to web pages. Flash is commonly used to create animation, advertisements, and various web page components, to integrate video into web pages, and more recently, to develop rich Internet applications. | ||
and | Flash can manipulate vector and raster graphics and supports bidirectional streaming of audio and video. It contains a scripting language called ActionScript. Several software products, systems, and devices are able to create or display Flash content, including Adobe Flash Player, which is available free for most common web browsers, some mobile phones and for other electronic devices (using Flash Lite).}} | ||
(Wikipedia, retrieved May 23 2009). | |||
In addition, Flash is used as a format for desktop applications under the name of "Adobe Integrated Runtime" ([[Adobe AIR]]). | |||
We could distinguish four kinds of Flash authors: (a) People who use simple offline or online tools to generate applications like slide shows. (b) Multi-media authors who create good looking Flash movies. (c) Multi-media / light-weight programmers who create interactive Flash applications and (d) "Real programmers" who write so-called [[rich internet application]]s. Today, many tools can produce runnable Flash contents. However, only Adobe's commercial Flash authoring tools allow non-programmers to exploit the full capabilities of this format. Programmers, on the other hand, may use Adobe's free [[Adobe Flex|Flex]] software development kit instead of the commercial Flex builder. | |||
{{Hide in print|This page contains an overview of Flash-related articles in [[Main_Page|EduTechWiki]], some general definitions, as well as links to software. References to tutorials, documentation and other websites are available on [[#Extra_Resources|different pages]].}} | |||
See also: | |||
* [[Animate CC]] | |||
== Flash tutorials and articles in EduTech wiki == | |||
EduTech Wiki includes introductory Flash and ActionScript 3 (AS3) tutorials for Flash version 11 using mostly Adobe Flash CS6 Professional and for Flash version 9 using CS3, plus some CS4/CS5 tutorials that introduced new features not in CS3). | |||
We used these in [[Help:COAP-2110|COAP 2110]] (Fall 1 2007, Fall 2008, Spring 2010, Sprint 2013, Webster University), [[STIC:STIC_III|STIC III]] (Fall 2007, fall 2008, Geneva university), and [[:fr:STIC:STIC_IV|STIC IV]] (spring 2010, in french, Geneva university) courses. Some tutorials better than others and none is top quality so far, but most can serve as lecture notes and for some self-study. | |||
Most tutorials have been upgraded to CS6 in winter 2013. CS4 and CS5 users can read CS6 tutorials, but should take files from tutorials developed for CS3 and CS4. The interface changes between CS3 and CS4/CS5/CS6 are substantial but not major. The differences between CS4, CS5 and CS6 are rather minor. | |||
We produced three families of tutorials with some overlaps: | |||
* [[Flash tutorials]] (Flash CS6 plus ActionScript 3 for non-programmers, and links to deprecated CS3/4/5 versions) | |||
* [[Actionscript 3]] (Beginner's tutorials for "pure" AS3, i.e. tool independent coding, these should be further expanded, but are not so far ...) | |||
* [[Flex tutorials]] (very few) | |||
* | All materials (*.fla, *.swf, etc.) are available at http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/flash/ under a | ||
[[EduTech Wiki:Copyrights|CC BY-NC-SA licence]]. | |||
{{Hide in print| | |||
; Other Flash articles in EduTech Wiki (e.g. overviews and cheat-sheets): | |||
( | # [[Flash CS3 keyboard shortcuts]] | ||
# [[Flash ActionScript 3 overview]] -- a conceptual little overview of AS3 | |||
# [[Flash formats and objects overview]] (not ActionScript objects !) | |||
# [[Flash - being organized]] (some advice for beginning Flash CS3 designers) | |||
# [[Actionscript 3]] -- a complete programming language. An entry page for AS3 tutorials | |||
# [[Flash 3D]] -- overview page of of Flash 3D tools and AS3 libraries | |||
}} | |||
== The Flash framework == | |||
In the past, Flash was just a web animation/interactive multimedia technology. Today (2008) Flash is a serious contender for one-stop [[rich internet application]] technology as the following picture shows: | |||
[[image:atp_ria_guide_ria_picture.jpg|none|thumb|800px|Adobe Flash Platform for RIAs. Retrieved nov 2008 from http://www.adobe.com/devnet/actionscript/articles/atp_ria_guide.html]] | |||
== Flash versions compared == | |||
CS3 was a major break from earlier versions (Flash 8 and earlier) with respect to ActionScript. ActionScript 3 is much more difficult to learn than ActionScript since it uses a modern typical user interface paradigm. In Flash 8 one could directly attach scripts to objects. In Flash 9 and later scripts are attached to frames. | |||
* [ | Changes/Additions in CS4: | ||
* A completely redesigned interface | |||
* Easier [[Flash animation overview|motion tweening]] (CS 3 motion tweening was renamed "classic tween") | |||
* [[Flash CS4 inverse kinematics tutorial|inverse kinematics]] | |||
* Support for 3D animation of 2D objects. | |||
CS5 includes: | |||
* Better looping support in motion tweens. E.g. ctrl-select first keyframe, then ALT-drag to right after the tween span, then inverse keyframes with the right click menu) | |||
* Physic engine additions to [[Flash CS4 inverse kinematics tutorial|inverse kinematics]], e.g. spring functions | |||
* Support for IPhone applications (not sure that it works, since Apple doesn't like other's developing environments) | |||
* Much better text support | |||
* Code snippets (helps beginners to write AS3 code). | |||
* XML-based source code: Either compressed *.fla files or *.xfl folders. | |||
* Easier management of cue points in videos (directly in CS5) | |||
* Better deco brushes, e.g. you now can easily draw a tree... | |||
CS6 includes: | |||
* | * Better support for mobile technology | ||
* and more .... (to document) | |||
Since CS5, Flash includes [[flash actions-frame tutorial|code snippets]]. Therefore, these newer versions are better suited for teaching Flash to beginners. However, for learning modern Flash, it doesn't make a big difference whether you use CS3, CS4 or CS5 or CS6. Some schools simply can't afford upgrading at an 18 month rate ... | |||
== Alternative technologies == | |||
; General formats | |||
( | * [[DHTML]], i.e. the combination of HTML, CSS, DOM and JavaScript and [[AJAX]] (asynchronous server-client communication trough JavaScript). See various [[JavaScript libraries|JavaScript libraries]]. | ||
* [[SVG]], an XML-based vector graphics format sponsored by WC3. SVG is a powerful format, but lacks support from authoring tool and web browser makers. Adobe, before it acquired Macromedia, used to support SVG. SVG works well in the Opera browser and increasingly better in Firefox. | |||
* [[HTML5]]. It includes SVG and "DHTML". Adobe [[Animate CC]] (the successor product or Flash Professional) can produce code or HTML5 canvas. | |||
* [[SMIL]], an XML-based multi-media integration language that supports timing, layout, animations, etc. SMIL is included in the full SVG profile and as such works with [[HTML5]]. SMIL also works with other technologies that now seems outdated (e.g. RealPlayer). | |||
* [http://www.microsoft.com/silverlight/ Microsoft Silverlight], a mostly failed attempt by Microsoft attempt to have its own "Flash". | |||
; Others | |||
See also [[multimedia authoring system]]s and [[computer game]]s. Some of these have their own format, some can export to more common formats. | |||
== Links for software and media elements == | |||
=== General / Indexes === | |||
* | * [http://osflash.org/projects OsFlash] has a large comprehensive list of links to Open Source Flash projects, both those hosted on OSFlash and elsewhere. Of particular interest are tools that generate flash in various ways. | ||
=== Viewers === | |||
* | * [http://www.adobe.com/products/ Adobe] (Flash player download) | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gnash Gnash] (Wikipedia article) A project which aims to create a player and browser plugin for the Adobe Flash file format which is free software. | |||
=== Authoring tools === | |||
* [http://www.adobe.com/products/flash/ Adobe Flash CS5 Professional]. '''The''' commercial authoring tool. '''Students''': You can get huge discounts either through some stores or Adobe's [http://www.adobe.com/education/ education program] (takes some times to fight through this web site and to find the appropriate page). In both cases you will have to send proof to Adobe before you will get a key. '''Teachers''' pay more, institutions can make deals that are more difficult to get. | |||
Adobe Flash CS3 Professional was released in April 2007, CS4 Professional in October 2008 and CS5 in April 2010. CS4 adds inverse kinematics, easier motion tweening (i.e. object-based animation finally!) and some basic support for 3D animations of 2D objects. CS5 adds for example a physics engine. | |||
* [http://www.swishzone.com/index.php SWISH]. An alternative set of commercial products to produce Flash. Much cheaper and somewhat easier it seems, but doesn't export to *.fla files (so you can't import to the Adobe authoring tool). See the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SWiSH_Max Wikipedia] article. | |||
* [http://www.salasaga.org/ Salasaga]. An free (and OSS) Integrated Development Environment for producing animated swf files, similar to Adobe Captivate. Goal is to create a free, easy to use GUI authoring environment that helps you create visually impressive and actually useful learning material. Example swf output [http://www.salasaga.org/downloads/alpha3/projects/Installing_on_Ubuntu804.html here]. | |||
=== Decompilers === | |||
A decompiler can translate an *.swf to *.fla. Useful if you want to learn (not steal) from examples on the web or if you lost by mistake your *.fla sources. | |||
* Sothink decompiler: [http://www.sothink.com/product/flashdecompiler/index.htm Flash Decompiler], [http://www.swf-decompiler.com/ SWF Decompiler], [http://www.swf-to-fla.com/ SWF to FLA] | |||
* [http://www.eltima.com/products/flashdecompiler/ Flash Decompiler Trillix] | |||
** See also [http://www.flash-decompiler.com/ Flash Decompiler Trillix] (strange website without any documentation) | |||
=== Translators and common formats === | |||
E.g. *.fla to *.html | |||
* [http://labs.adobe.com/technologies/wallaby/ Wallaby] "Wallaby" is the codename for an experimental technology that converts the artwork and animation contained in FLA files (retrieved Feb 2011). | |||
* The *.fxp file format is used by Flash Catalyst to create a (compressed/zipped) Flex project archive that is understandable by Flash Builder. I.e. designers can create a project in Catalyst and then hand it over to a Flash/Flex programmer who will work with Flash Builder. | |||
* Conversely, *.fxg enables cross communication among Creative Suite, Flash Catalyst and Flash Builder. {{quotation|The FXG format is new to Flash Professional CS5. It allows Flash to exchange graphics with other Adobe applications such as Illustrator, Fireworks, and Photoshop with all of the complex graphic information preserved. Flash allows you to import FXG files (version 2.0 only) as well as save selections of objects on the Stage or the entire Stage in FXG format. FXG is based on a subset of MXML, the XML-based programming language used by the Flex framework.}} ([http://www.adobe.com/devnet/flash/articles/concept_fxg.html Flash glossary: FXG], retrieved March 7 2011). | |||
=== Special purpose authoring tools === | |||
There is an increasing variety of tools and for a wide range of people, covering casual users to programmers. | |||
* [http://www.adobe.com/products/captivate/ Adobe Captivate]. An authoring environment to create simulations, scenario-based training, and robust quizzes. Can import/export to Flash *.fla documents. | |||
* [http://www.adobe.com/products/acrobatconnect/ Adobe Acrobat Connect] (formerly called Breeze) is a flash-based [[videoconferencing]] software. | |||
* [http://www.adobe.com/products/flex/ Adobe Flex] is a software development kit and an IDE for a group of technologies to make [[rich internet application]]s with Flash, HTML, JavaScript etc.). | |||
* [http://www.toufee.com/ Toufee], an online tool to make Flash presentations (movies). Free in a basic version. Drag and drop pictures or special elements to a stage, add special effects, buttons, etc. Also saves in other formats. | |||
* OpenOffice Impress (the power point clone) can produce *.swf | |||
* Some capturing tools (see [[screen capture tutorial|screen capture]], photo gallery makers, and video editing software can export to Flash. | |||
=== Server technology === | |||
* [http://silex-ria.org Silex] is free open-source CMS with a Flash Interface (and AS API). Source Forge project of the month June 2009. | |||
* [http://osflash.org/red5 red 5] is an open source Flash Server. I supports Streaming Audio/Video (FLV and MP3, Recording Client Streams (FLV only), Shared Objects, Live Stream Publishing and Remoting (AMF) (nov/2008) | |||
* Adobe has a global [http://www.adobe.com/flashplatform/ Flash framework] that includes e.g. a Flash Media Server Family. | |||
=== Generating Flash === | |||
* [http://ming.sourceforge.net/ Ming] Ming is a C library for generating SWF ("Flash") format movies, plus a set of wrappers for using the library from C++ and popular scripting languages like PHP, Perl, Python, and Ruby. | |||
* [http://swfmill.org/ SWFMill] xml2swf and swf2xml processor that can be used to create (non interactive) multiframe SWF animations. | |||
* [http://haxe.org/ HaXe]. Programming language very similar to actionscript that can compile a SWF file for Flash Players 6 to 9. Free to use. | |||
In addition, you also should know that you can import several vector graphics formats. e.g. Windows Metafile formats into Flash CS3 (speeds up drawing). | |||
=== Programming Editors for ActionScript === | |||
* [http://www.flashdevelop.org/ Flashdevelop]. Free and open source tool that provides syntax support and an interface with the Flex compilers. | |||
* Some multi-purpose editors (like [[emacs]] also may support [[Actionscript 3]] programming | |||
* [http://www.adobe.com/products/flex/ Adobe Flex Builder] - a commercial Eclipse plugin from Adobe, but that is free for education upon request. | |||
{{Hide in print| | |||
=== Media for building your own scenes === | |||
* See [[clipart]] | |||
* See [[texture]] | |||
== Extra Resources == | |||
* [[Flash and AS3 links - general]] | |||
* [[Flash and AS3 links - tutorials]] | |||
* [[Flash and AS3 links - documentation]] (Flash and AS3 Books, Reference Manuals and Cheatsheets) | |||
* [[Flash and AS3 links - toolkits]] (AS 3 Toolkits, Libraries, Flash reusable components, AS 3 reusable code, etc.) | |||
}} | |||
[[Category: Multimedia]] | [[Category: Multimedia]] | ||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: Tutorials]] | |||
[[Category: Flash tutorials]] | |||
[[Category: Actionscript 3]] | |||
[[fr:Flash]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:39, 22 April 2018
This page needs to be updated for Flash CS6, but principles remain the same ...
Definition
“Adobe Flash (previously called Macromedia Flash) is a multimedia platform originally acquired by Macromedia and currently developed and distributed by Adobe Systems. Since its introduction in 1996, Flash has become a popular method for adding animation and interactivity to web pages. Flash is commonly used to create animation, advertisements, and various web page components, to integrate video into web pages, and more recently, to develop rich Internet applications. Flash can manipulate vector and raster graphics and supports bidirectional streaming of audio and video. It contains a scripting language called ActionScript. Several software products, systems, and devices are able to create or display Flash content, including Adobe Flash Player, which is available free for most common web browsers, some mobile phones and for other electronic devices (using Flash Lite).” (Wikipedia, retrieved May 23 2009).
In addition, Flash is used as a format for desktop applications under the name of "Adobe Integrated Runtime" (Adobe AIR).
We could distinguish four kinds of Flash authors: (a) People who use simple offline or online tools to generate applications like slide shows. (b) Multi-media authors who create good looking Flash movies. (c) Multi-media / light-weight programmers who create interactive Flash applications and (d) "Real programmers" who write so-called rich internet applications. Today, many tools can produce runnable Flash contents. However, only Adobe's commercial Flash authoring tools allow non-programmers to exploit the full capabilities of this format. Programmers, on the other hand, may use Adobe's free Flex software development kit instead of the commercial Flex builder.
See also:
Flash tutorials and articles in EduTech wiki
EduTech Wiki includes introductory Flash and ActionScript 3 (AS3) tutorials for Flash version 11 using mostly Adobe Flash CS6 Professional and for Flash version 9 using CS3, plus some CS4/CS5 tutorials that introduced new features not in CS3).
We used these in COAP 2110 (Fall 1 2007, Fall 2008, Spring 2010, Sprint 2013, Webster University), STIC III (Fall 2007, fall 2008, Geneva university), and STIC IV (spring 2010, in french, Geneva university) courses. Some tutorials better than others and none is top quality so far, but most can serve as lecture notes and for some self-study.
Most tutorials have been upgraded to CS6 in winter 2013. CS4 and CS5 users can read CS6 tutorials, but should take files from tutorials developed for CS3 and CS4. The interface changes between CS3 and CS4/CS5/CS6 are substantial but not major. The differences between CS4, CS5 and CS6 are rather minor.
We produced three families of tutorials with some overlaps:
- Flash tutorials (Flash CS6 plus ActionScript 3 for non-programmers, and links to deprecated CS3/4/5 versions)
- Actionscript 3 (Beginner's tutorials for "pure" AS3, i.e. tool independent coding, these should be further expanded, but are not so far ...)
- Flex tutorials (very few)
All materials (*.fla, *.swf, etc.) are available at http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/flash/ under a CC BY-NC-SA licence.
- Other Flash articles in EduTech Wiki (e.g. overviews and cheat-sheets)
- Flash CS3 keyboard shortcuts
- Flash ActionScript 3 overview -- a conceptual little overview of AS3
- Flash formats and objects overview (not ActionScript objects !)
- Flash - being organized (some advice for beginning Flash CS3 designers)
- Actionscript 3 -- a complete programming language. An entry page for AS3 tutorials
- Flash 3D -- overview page of of Flash 3D tools and AS3 libraries
The Flash framework
In the past, Flash was just a web animation/interactive multimedia technology. Today (2008) Flash is a serious contender for one-stop rich internet application technology as the following picture shows:
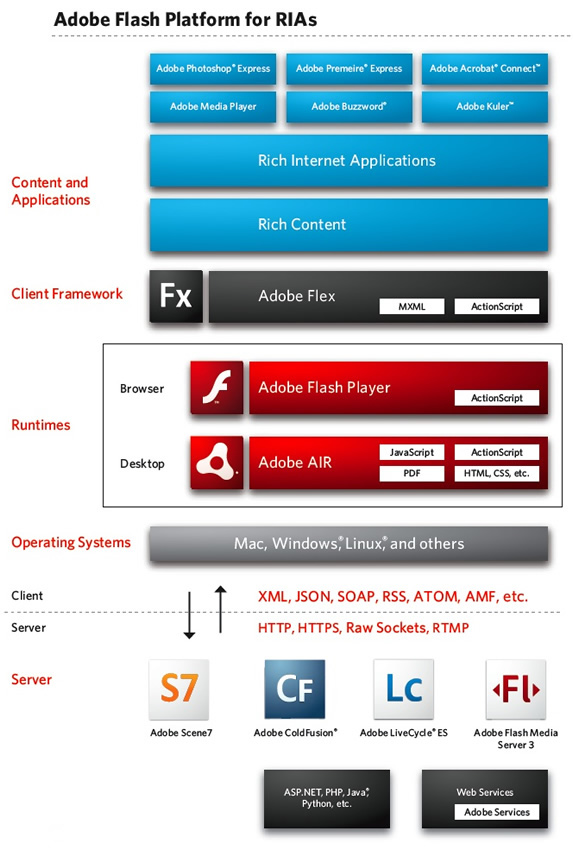
Flash versions compared
CS3 was a major break from earlier versions (Flash 8 and earlier) with respect to ActionScript. ActionScript 3 is much more difficult to learn than ActionScript since it uses a modern typical user interface paradigm. In Flash 8 one could directly attach scripts to objects. In Flash 9 and later scripts are attached to frames.
Changes/Additions in CS4:
- A completely redesigned interface
- Easier motion tweening (CS 3 motion tweening was renamed "classic tween")
- inverse kinematics
- Support for 3D animation of 2D objects.
CS5 includes:
- Better looping support in motion tweens. E.g. ctrl-select first keyframe, then ALT-drag to right after the tween span, then inverse keyframes with the right click menu)
- Physic engine additions to inverse kinematics, e.g. spring functions
- Support for IPhone applications (not sure that it works, since Apple doesn't like other's developing environments)
- Much better text support
- Code snippets (helps beginners to write AS3 code).
- XML-based source code: Either compressed *.fla files or *.xfl folders.
- Easier management of cue points in videos (directly in CS5)
- Better deco brushes, e.g. you now can easily draw a tree...
CS6 includes:
- Better support for mobile technology
- and more .... (to document)
Since CS5, Flash includes code snippets. Therefore, these newer versions are better suited for teaching Flash to beginners. However, for learning modern Flash, it doesn't make a big difference whether you use CS3, CS4 or CS5 or CS6. Some schools simply can't afford upgrading at an 18 month rate ...
Alternative technologies
- General formats
- DHTML, i.e. the combination of HTML, CSS, DOM and JavaScript and AJAX (asynchronous server-client communication trough JavaScript). See various JavaScript libraries.
- SVG, an XML-based vector graphics format sponsored by WC3. SVG is a powerful format, but lacks support from authoring tool and web browser makers. Adobe, before it acquired Macromedia, used to support SVG. SVG works well in the Opera browser and increasingly better in Firefox.
- HTML5. It includes SVG and "DHTML". Adobe Animate CC (the successor product or Flash Professional) can produce code or HTML5 canvas.
- SMIL, an XML-based multi-media integration language that supports timing, layout, animations, etc. SMIL is included in the full SVG profile and as such works with HTML5. SMIL also works with other technologies that now seems outdated (e.g. RealPlayer).
- Microsoft Silverlight, a mostly failed attempt by Microsoft attempt to have its own "Flash".
- Others
See also multimedia authoring systems and computer games. Some of these have their own format, some can export to more common formats.
Links for software and media elements
General / Indexes
- OsFlash has a large comprehensive list of links to Open Source Flash projects, both those hosted on OSFlash and elsewhere. Of particular interest are tools that generate flash in various ways.
Viewers
- Adobe (Flash player download)
- Gnash (Wikipedia article) A project which aims to create a player and browser plugin for the Adobe Flash file format which is free software.
Authoring tools
- Adobe Flash CS5 Professional. The commercial authoring tool. Students: You can get huge discounts either through some stores or Adobe's education program (takes some times to fight through this web site and to find the appropriate page). In both cases you will have to send proof to Adobe before you will get a key. Teachers pay more, institutions can make deals that are more difficult to get.
Adobe Flash CS3 Professional was released in April 2007, CS4 Professional in October 2008 and CS5 in April 2010. CS4 adds inverse kinematics, easier motion tweening (i.e. object-based animation finally!) and some basic support for 3D animations of 2D objects. CS5 adds for example a physics engine.
- SWISH. An alternative set of commercial products to produce Flash. Much cheaper and somewhat easier it seems, but doesn't export to *.fla files (so you can't import to the Adobe authoring tool). See the Wikipedia article.
- Salasaga. An free (and OSS) Integrated Development Environment for producing animated swf files, similar to Adobe Captivate. Goal is to create a free, easy to use GUI authoring environment that helps you create visually impressive and actually useful learning material. Example swf output here.
Decompilers
A decompiler can translate an *.swf to *.fla. Useful if you want to learn (not steal) from examples on the web or if you lost by mistake your *.fla sources.
- Sothink decompiler: Flash Decompiler, SWF Decompiler, SWF to FLA
- Flash Decompiler Trillix
- See also Flash Decompiler Trillix (strange website without any documentation)
Translators and common formats
E.g. *.fla to *.html
- Wallaby "Wallaby" is the codename for an experimental technology that converts the artwork and animation contained in FLA files (retrieved Feb 2011).
- The *.fxp file format is used by Flash Catalyst to create a (compressed/zipped) Flex project archive that is understandable by Flash Builder. I.e. designers can create a project in Catalyst and then hand it over to a Flash/Flex programmer who will work with Flash Builder.
- Conversely, *.fxg enables cross communication among Creative Suite, Flash Catalyst and Flash Builder. “The FXG format is new to Flash Professional CS5. It allows Flash to exchange graphics with other Adobe applications such as Illustrator, Fireworks, and Photoshop with all of the complex graphic information preserved. Flash allows you to import FXG files (version 2.0 only) as well as save selections of objects on the Stage or the entire Stage in FXG format. FXG is based on a subset of MXML, the XML-based programming language used by the Flex framework.” (Flash glossary: FXG, retrieved March 7 2011).
Special purpose authoring tools
There is an increasing variety of tools and for a wide range of people, covering casual users to programmers.
- Adobe Captivate. An authoring environment to create simulations, scenario-based training, and robust quizzes. Can import/export to Flash *.fla documents.
- Adobe Acrobat Connect (formerly called Breeze) is a flash-based videoconferencing software.
- Adobe Flex is a software development kit and an IDE for a group of technologies to make rich internet applications with Flash, HTML, JavaScript etc.).
- Toufee, an online tool to make Flash presentations (movies). Free in a basic version. Drag and drop pictures or special elements to a stage, add special effects, buttons, etc. Also saves in other formats.
- OpenOffice Impress (the power point clone) can produce *.swf
- Some capturing tools (see screen capture, photo gallery makers, and video editing software can export to Flash.
Server technology
- Silex is free open-source CMS with a Flash Interface (and AS API). Source Forge project of the month June 2009.
- red 5 is an open source Flash Server. I supports Streaming Audio/Video (FLV and MP3, Recording Client Streams (FLV only), Shared Objects, Live Stream Publishing and Remoting (AMF) (nov/2008)
- Adobe has a global Flash framework that includes e.g. a Flash Media Server Family.
Generating Flash
- Ming Ming is a C library for generating SWF ("Flash") format movies, plus a set of wrappers for using the library from C++ and popular scripting languages like PHP, Perl, Python, and Ruby.
- SWFMill xml2swf and swf2xml processor that can be used to create (non interactive) multiframe SWF animations.
- HaXe. Programming language very similar to actionscript that can compile a SWF file for Flash Players 6 to 9. Free to use.
In addition, you also should know that you can import several vector graphics formats. e.g. Windows Metafile formats into Flash CS3 (speeds up drawing).
Programming Editors for ActionScript
- Flashdevelop. Free and open source tool that provides syntax support and an interface with the Flex compilers.
- Some multi-purpose editors (like emacs also may support Actionscript 3 programming
- Adobe Flex Builder - a commercial Eclipse plugin from Adobe, but that is free for education upon request.
Media for building your own scenes
Extra Resources
- Flash and AS3 links - general
- Flash and AS3 links - tutorials
- Flash and AS3 links - documentation (Flash and AS3 Books, Reference Manuals and Cheatsheets)
- Flash and AS3 links - toolkits (AS 3 Toolkits, Libraries, Flash reusable components, AS 3 reusable code, etc.)
