SVG-SMIL animation tutorial
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
Important WARNING: This page was machine translated from the french version. Some code or some sentences may be garbled as a result. Also, the SVG code may include some comments in french - Will be fixed sometimes soon. Daniel K. Schneider 22:26, 2 April 2012 (CEST)
Introduction
This short tutorial provides an introduction to dynamic SVG, ie. animations. We introduce some elements of the SMIL ("Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language") tags that are embedded in the SVG specification. Aims:
- Know various SMIL animation types
- Understand the principle of "linking" animation tags to attributes of SVG elements
Prerequisites:
See also:
Attention: You must use a recent HTML5 compliant browser (issued 2011 or later), e.g. FireFox, Chrome, Opera or Safari. These examples will not work with Internet Explorer 9.
The principle of animation is simple: Animating means changing attributes of SVG elements over time.
There are two methods:
(1) SMIL animation using special animation tags
- We can animate virtually every SVG attribute with these animation elements
- SVG / SMIL animation extends the SMIL standard with some extensions.
(2) Animation via the SVG DOM with a script
- Each attribute and "style sheet setting" is available through the standard DOM 1 & 2. In addition, there is a set of additional SVG DOM interfaces.
- Basically, you will have to write an ECMAScript program that changes the attributes of items or that adds / remove elements and/or attributes in the DOM.
- This second method is not covered in this tutorial.
The principle of "time-based" animation:
- Time-based (as opposed to "frame-based" as in Flash) defines the start and duration of an animation in terms of a time unit, e.g. seconds.
- We can animate attributes independently in parallel animations
- In addition, an animation can be triggered though a user action (e.g. a mouse event), or by the ending of another animation.
Animation basics
The elements of this section on animation principles are based on the french version of the SMIL Animation W3C Recommendation 4 September 2001.
Definition: Animation is the time-based manipulation of an attribute of a target element.
Animations define a beginning and a simple duration that can be repeated. Each animation defines an animation function that produces a value for the target attribute at any time in the simple duration. The author can specify how long and how often the animation function should repeat itself. The simple duration combined with a repeat behavior defines the active duration.
The target attribute is the name of a characteristic of a target element. It can be either an XML attribute contained in the element or a CSS property applied to the element. By default, the target element of an animation will be the parent of the animation element.
Below is a simple example of an SVG animation. A rectangle changes its dimensions from thin elongated to wide and flattened. The rectangle animation starts with a width of 10 pixels and is increasing to 100 pixels for a duration of 10 seconds. During the same ten seconds, the height of the rectangle will change from 100 pixels to 10 pixels.
<rect x="50" y="50" width="10" height="100" style="fill:#CCCCFF;stroke:#000099">
<animate attributeName="width" from="10px" to="100px"
begin="0s" dur="10s" />
<animate attributeName="height" from="100px" to="10px"
begin="0s" dur="10s" />
</rect>
Instead of animating the parent element, one also can define an animation that refers to another element. In other words, the animation target can be any element in the document identified with an XLink locator, i.e. the equivalent of the HTML "href".
<rect id="TAG" .....> <animate xlink:href="#TAG"
The following example shows the principle:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<title>Simple animate example avec une référence xLink</title>
<desc>Rectangle shape will change</desc>
<rect id="monRect" x="50" y="50" width="10" height="100" style="fill:#CCCCFF;stroke:#000099"/>
<animate xlink:href="#monRect" attributeName="width"
from="10px" to="100px" begin="0s" dur="10s" />
<animate xlink:href="#monRect" attributeName="height"
from="100px" to="10px" begin="0s" dur="10s" />
<text x="50" y="170" style="stroke:#000099;fill:#000099;font-size:14;">
Hello. Admire the dynamic rectangle. Animation defined with targetElement.</text>
</svg>
This example also shows that one also can define an SVG DocType. This facilitates editing with an XML editor. It also shows that we must define a XML namespace for the href, e.g. use code like this:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
When the animation runs, it will not really change the attribute values in the object model DOM or CSS Object Model. In other words, animations only manipulate the presentation value and should not affect what is called the base value defined by the DOM or the CSS DOM. When an animation completes, the effect of the animation ceases to apply and the presentation value defaults to the base value. That being said, we can "extend" the animation effect and freeze the last value for the rest of the document duration.
In an animation, one can either replace' or add a value to the base value of the attribute. In this context, the base value may be the value of the DOM or the result of other activities aimed at the same attribute. This broader concept of value is called the basic underlying value. The animations that add to the underlying value are called additive. Animations that override the underlying value are called non-additive.
Overview of SMIL animation markup
There are five animation elements (tags):
- animate: used to animate over time a single attribute or a single CSS property
- Set: provides a simple way for setting a single attribute value for a specified duration.
- animateMotion: causes the displacement of an element along a path of movement (called motion tweening in Flash).
- animateColor: specifies a color transformation over time.
- animateTransform: animates a transformation attribute on a target element, thereby allowing animations to control translation, scaling, rotation and / or inclination.
For each of these animation tags you can use certain types of attributes / values. We first will introduce some of these attributes through examples. For those who can read a DTD we have included a partial formal definition that was mainly taken from the SMIL Animation W3C Recommendation 04-September-2001
A more systematic discussion of the common attributes is provided at the end.
Introductory example
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/translation.svg
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/ (directory)
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect x="50" y="50" width="200" height="100" style="fill:#CCCCFF;stroke:#000099">
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML"
begin="0s" dur="5s" from="50" to="300" fill="freeze"/>
</rect>
<text x="55" y="90" style="stroke:#000099;fill:#000099;fontsize:24;">
Hello. Let’s show a crawling rectangle ! </text>
</svg>
- The <animate /> element is simply placed inside the element we want to animate
- In this case, it animates the horizontal position ("x") of a rectangle (rect)
- attributeName - we animate the attribute "x" of parent "rect"
- begin = "0s" - animation starts after 0 seconds
- dur = "5s" - duration is 5 seconds
- from = "50" - starting point for x
- to = "300" - end point of X
- fill = "freeze" - the animation will freeze at the end (ie. the rectangle stays where it is)
Animation of an attribute with the animate element
The animate element can animate a single attribute.
The following example shows first how to create a definition for a gradient circle: yellow on the inside (255,255,0) and green on the outside (0,256,0). This gradient is then used in the fill of the ellipse.
Then we create an animation to enlarge / shrink an ellipse. For this, we animate attributes rx and ry (x and y radius) with a set of values that express: min, max, min values.
attributeName = "rx" values = "0% 50% 0%" dur = "2s" attributeName = "ry" values = "0% 50% 0%" dur = "2s"
As you can see, this time we are not using the "to" and the "from" attribute, but the "values" attribute allowing to enter a series of key values from start to end. The SVG engine will then interpolate all the values in between.
<svg version="1.1"
width="320" height="320"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<defs>
<radialGradient id="circleGrad">
<stop offset="0%" stop-color="rgb(255, 255, 0)" />
<stop offset="100%" stop-color="rgb( 0, 255, 0)" />
</radialGradient>
</defs>
<ellipse fill="url(#circleGrad)" stroke="#000"
cx="50%" cy="50%" rx="50%" ry="50%">
<animate attributeName="rx" values="0%;50%;0%" dur="2s"
repeatCount="indefinite" />
<animate attributeName="ry" values="0%;50%;0%" dur="2s"
repeatCount="indefinite" />
</ellipse>
</svg>
- File: http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/ellipse-growth.svg
- Original: Сhoosing Between the Two (Feb 2010).
Partial formal definition of the animate tag
- The animate element (SMIL Animation, W3C Recommendation 04-September-2001)
<!ELEMENT animate EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST animate
calcMode (discrete | linear | paced | spline ) "linear"
values CDATA #IMPLIED
keyTimes CDATA #IMPLIED
keySplines CDATA #IMPLIED
from CDATA #IMPLIED
to CDATA #IMPLIED
by CDATA #IMPLIED
<!-- Timing attributes -->
begin CDATA #IMPLIED
dur CDATA #IMPLIED
end CDATA #IMPLIED
restart (always | never | whenNotActive) "always"
repeatCount CDATA #IMPLIED
repeatDur CDATA #IMPLIED
fill (remove | freeze) "remove"
<!-- Common animation attributes -->
attributeName CDATA #REQUIRED
attributeType CDATA (CSS | XML | auto) "auto"
additive (replace | sum) "replace"
accumulate (none | sum) "none"
<!-- Common event attributes -->
onbegin CDATA #IMPLIED
onend CDATA #IMPLIED
onrepeat CDATA #IMPLIED
>
Transform a drawing with the set element
The 'set' element provides a simple means for setting a single attribute value for a specified duration. It manages all types of attributes, including those that can not reasonably be interpolated, such as strings and Boolean values.
- The 'set' element is not additive. So the attributes that control event sequences will not work.
Example: Simple animation and animation set
The first rectangle (blue) below appears after 4 seconds. Visibility is first hidden and then visible. The second one (yellow) is animated through the "opacity" attribute, i.e. from 0 (invisible/total see through) to 1 (totally opaque).
<rect x="50" y="50" width="200" height="100" style="fill:#CCCCFF;stroke:#000099"
visibility ="hidden" >
<set attributeName="visibility" attributeType="XML"
begin="4s" dur="5s" to="visible"/>
</rect>
<rect style="fill:yellow;stroke:#000099" x="250" y="50" width="200" height="100" opacity="0" >
<animate attributeName="opacity" attributeType="XML"
begin="1s" dur="5s" from="0" to="1" fill="freeze"/>
</rect>
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/simple-set.svg
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/ (directory)
Partial formal definition
<!ELEMENT set EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST set
attributeName CDATA #REQUIRED
attributeType CDATA (CSS | XML | auto) "auto"
to CDATA #IMPLIED
<!-- Timing attributes -->
begin CDATA #IMPLIED
dur CDATA #IMPLIED
end CDATA #IMPLIED
restart (always | never | whenNotActive) "always"
repeatCount CDATA #IMPLIED
repeatDur CDATA #IMPLIED
fill (remove | freeze) "remove"
>
Color animation with AnimateColor
Example: Animating a color
<svg height="900" width="900">
<!-- un gros rectangle qui remplit l’écran -->
<rect style="fill:#000000;" height="900" width="900" y="0" x="0">
<animate fill="freeze" dur="5s" begin="0.1s"
to="#FFFFFF" from="#000000" calMode="linear" attributeName="fill"/>
</rect>
<!-- représentation d’une tige (rectangle haut et fin) -->
<rect style="fill:#CC9933;stroke:#CC9933" width="20" height="500"
ry="5" rx="5" y="100" x="400">
<animate dur="5s" begin="1s" to="#000000"
from="#CC9933" calMode="linear" attributeName="fill"/>
<animate dur="5s" begin="6s" from="#000000"
to="#CC9933" calMode="linear" attributeName="fill"/>
</rect>
The principle is quite simple: the animation "moves" from one color to another. It includes two animations
- Background goes white to black (from = "# 000000") to (to = "# FFFFFF")
- The rod will go from = "#CC9933" to "#000000" (after 1s and during 4sec) and then from #000000 to "#CC9933".
Partial formal definition
<!ELEMENT animateColor EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST animateColor
<!-- Timing attributes -->
begin CDATA #IMPLIED
dur CDATA #IMPLIED
end CDATA #IMPLIED
restart (always | never | whenNotActive) "always"
repeatCount CDATA #IMPLIED
repeatDur CDATA #IMPLIED
fill (remove | freeze) "remove"
<!-- Common animation attributes -->
attributeName CDATA #REQUIRED
attributeType CDATA (CSS | XML | auto) "auto"
additive (replace | sum) "replace"
accumulate (none | sum) "none"
calcMode (discrete | linear | paced | spline ) "linear"
values CDATA #IMPLIED
from CDATA #IMPLIED
to CDATA #IMPLIED
by CDATA #IMPLIED
keyTimes CDATA #IMPLIED
keySplines CDATA #IMPLIED
>
Shape transformation with AnimateTransform
Example: Simple rotation
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.0//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/2001/PR-SVG-20010719/DTD/svg10.dtd">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<title>Simple rotation example</title>
<desc> Rotation with a grouping node </desc>
<g>
<rect x="50" y="50" rx="5" ry="5" width="200" height="100"
style="fill:#CCCCFF;stroke:#000099"/>
<text x="55" y="90" style="stroke:#000099;fill:#000099;font-size:18;">
Hello. Let's rotate</text>
<animateTransform attributeName="transform" type="rotate"
values="0 150 100; 360 150 100"
begin="0s" dur="5s" />
</g>
</svg>
This ugly rotation example
- Animates the attribute "rotate" attribute of <g> (which initially is without rotation)
- We give SVG just two degree values for the rotation (0 for departing and 360 for the end). The rest is interpolated by the machine.
This example also shows that one can animate any attribute that is implicitly defined. In the source code, we did not specify any initial rotation. By default it is just zero (0).
Partial formal definition
<!ELEMENT animateTransform EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST animateTransform
type (translate | scale | rotate | skewX | skewY)
<!-- qqs. attributs en plus -->
values CDATA #IMPLIED
from CDATA #IMPLIED
to CDATA #IMPLIED
by CDATA #IMPLIED
begin CDATA #IMPLIED
dur CDATA #IMPLIED
end CDATA #IMPLIED
>
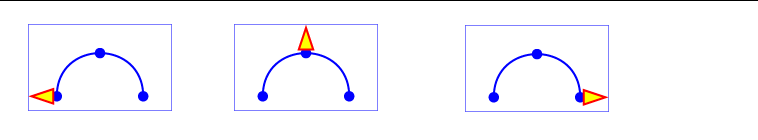
Interpolation of movement with animateMotion
Example: Animating a movement along a path
- http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG/animate.html (original)
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/svg-w3c/animMotion01-en.svg (copy)
- The 'animateMotion' causes the displacement of an element along a motion path.
- Not to be confused with simple translations, rotations etc.. that we do with animate or animateTransform.
Definition of a triangle and its animation along a path
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
<svg width="5cm" height="3cm" viewBox="0 0 500 300" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink">
<desc>Example animMotion01 - demonstrate motion animation computations</desc>
<rect x="1" y="1" width="498" height="298" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2"/>
<!-- Draw the outline of the motion path in blue, along
with three small circles at the start, middle and end. -->
<path id="path1" d="M100,250 C 100,50 400,50 400,250" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="7.06"/>
<circle cx="100" cy="250" r="17.64" fill="blue"/>
<circle cx="250" cy="100" r="17.64" fill="blue"/>
<circle cx="400" cy="250" r="17.64" fill="blue"/>
<!-- Here is a triangle which will be moved about the motion path.
It is defined with an upright orientation with the base of
the triangle centered horizontally just above the origin. -->
<path d="M-25,-12.5 L25,-12.5 L 0,-87.5 z" fill="yellow" stroke="red" stroke-width="7.06">
<!-- Define the motion path animation -->
<animateMotion dur="6s" repeatCount="indefinite" rotate="auto">
<mpath xlink:href="#path1"/>
</animateMotion>
</path>
</svg>
Note: The definition of the painter line and of the motion path follows exactly the same path. Also note that if you wanted to move an object that had an initial position, such as the first blue circle, then you should define all points of the motion path depending on the initial position of the object!
<circle cx="100" cy="250" r="17.64" fill="blue" />
Here the circle is x = y = 100 and 250. If you want to move the circle to the right of 100 and 100 upwards, you must enter as a point 100.100, that is to say, just moving this amount and not moving to !
Representation of a path
The notion of Path or path is special in SVG: it serves to produce complex figures with a set of coordinates and commands that specify the relations between the points (lines, curves ...). Here are the available commands:
- M: move (Move);
- L: creation of a line
- H: creating a horizontal line
- V: Creating a vertical line
- C: Creating a curve
- S: creation of a smooth curve
- Q: Creating a bezier curve;
- T: Creating a smoothed bezier curve
- A: creation of an arc;
- Z: termination of the road or path.
Partial formal definition
<!ELEMENT animateMotion EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST animateMotion
<!-- Timing attributes -->
begin CDATA #IMPLIED
dur CDATA #IMPLIED
end CDATA #IMPLIED
restart (always | never | whenNotActive) "always"
repeatCount CDATA #IMPLIED
repeatDur CDATA #IMPLIED
fill (remove | freeze) "remove"
additive (replace | sum) "replace"
accumulate (none | sum) "none"
calcMode (discrete | linear | paced | spline) "paced"
values CDATA #IMPLIED
from CDATA #IMPLIED
to CDATA #IMPLIED
by CDATA #IMPLIED
keyTimes CDATA #IMPLIED
keySplines CDATA #IMPLIED
path CDATA #IMPLIED
origin (default) "default"
/>
Animations combined
It is quite difficult to synchronize a complicated script. On the other hand, creating sequences of animations or animations in parrallel is quite simple.
Example: animation combined
Instead of defining the animation according to the time, it is possible to define sequences of events, ie. starting an event at the end of the previous event. Use the construction:
begin = "previous_event.end"
</ source>
The following example uses time-based seconds (not very useful for creating complicated suites)
<source lang="xml">
<rect id="carre" height="67" width="67" stroke-width="5" stroke="#000000" fill="#ffffff">
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="6s"
fill="freeze" from="300" to="0"/>
<animate attributeName="y" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="6s"
fill="freeze" from="100" to="0"/>
<animateColor attributeName="fill" attributeType="CSS" from="#ffffff" to="red"
begin="2s" dur="4s" fill="freeze" />
</rect>
The next example implements a true sequence where an animation starts when the first has finished.
<rect id="carre" height="67" width="67" stroke-width="5" stroke="#000000" fill="#ffffff">
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="6s"
fill="freeze" from="300" to="0"/>
</rect>
<rect id="carre2" height="80" width="23" stroke-width="5" stroke="#000000" fill="#ffffff">
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML" begin="carre.end"
dur="6s" fill="freeze" from="300" to="0"/>
</rect>
This way you can make loops of complex events.
Example: animation combined
This example is taken from the SVG 1.1 specification
It contains several animations:
- width / height of the yellow rectangle
- displacement of the origin of the yellow rectangle (up left)
- animation color for text
- movement along a path of the text
- rotation of the text
- expansion of the text
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd">
<svg width="8cm" height="3cm" viewBox="0 0 800 300" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<desc>Example anim01 - demonstrate animation elements</desc>
<rect x="1" y="1" width="798" height="298" fill="none" stroke="blue" stroke-width="2"/>
<!-- The following illustrates the use of the 'animate' element
to animate a rectangles x, y, and width attributes so that
the rectangle grows to ultimately fill the viewport. -->
<rect id="RectElement" x="300" y="100" width="300" height="100" fill="rgb(255,255,0)">
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="300" to="0"/>
<animate attributeName="y" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="100" to="0"/>
<animate attributeName="width" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="300" to="800"/>
<animate attributeName="height" attributeType="XML" begin="0s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="100" to="300"/>
</rect>
<!-- Set up a new user coordinate system so that
the text string's origin is at (0,0), allowing
rotation and scale relative to the new origin -->
<g transform="translate(100,100)">
<!-- The following illustrates the use of the 'set', 'animateMotion',
'animateColor' and 'animateTransform' elements. The 'text' element
below starts off hidden (i.e., invisible). At 3 seconds, it:
* becomes visible
* continuously moves diagonally across the viewport
* changes color from blue to dark red
* rotates from -30 to zero degrees
* scales by a factor of three. -->
<text id="TextElement" x="0" y="0" font-family="Verdana" font-size="35.27" visibility="hidden">
It's alive!
<set attributeName="visibility" attributeType="CSS" to="visible" begin="3s" dur="6s" fill="freeze"/>
<animateMotion path="M 0 0 L 100 100" begin="3s" dur="6s" fill="freeze"/>
<animateColor attributeName="fill" attributeType="CSS" from="rgb(0,0,255)" to="rgb(128,0,0)" begin="3s" dur="6s" fill="freeze"/>
<animateTransform attributeName="transform" attributeType="XML" type="rotate" from="-30" to="0" begin="3s" dur="6s" fill="freeze"/>
<animateTransform attributeName="transform" attributeType="XML" type="scale" from="1" to="3" additive="sum" begin="3s" dur="6s" fill="freeze"/>
</text>
</g>
</svg>
Online example:
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/svg-w3c/anim01-en.svg
- Original: http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG/animate.html#AnimateMotionElement
The common attributes for tags animation
Here's a quick summary of the most common attributes, without going into details, to use as a guide and then look at a manual if necessary.
xlink:href = "uri"
- SVG can use the XLink language for identifying the animation target. In other words, this is a URI reference (external or internal) to the element that is the target of this animation and whose attribute will be changed. Put more simply: An xlink:href creates a link to the id of the element to animate
- Alternatively, one can animation tags within an element. In this case, we refer to the attributes of the parent element.
When using xlink, one must declare the "xlink" namespace in a parent element. We suggest to do this in the root element (<svg>). Some SVG code that you can find on the Internet and even in published books does not and it must be added to make it work in a modern browser.
<svg width="8cm" height="3cm" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
attributeName = "name"
Specifies the name of the attribute must be animate, for example x
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML"
begin="0s" dur="5s" from="50" to="300" fill="freeze"/>
attributType = "type"
Indicates the attribute type that should animate, for example:
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML"
begin="0s" dur="5s" from="50" to="300" fill="freeze"/>
Below, it animates the attribute "x" (x position) of a rectangle and it is of type XML (SMIL):
<rect x="300">
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML"
begin="0s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="300" to="100" />
</rect>
begin = begin-value-list
Defines when the element should begin (ie become active).
The definition of begin-value-list is complicated, you can define multiple start and end timing as needed (see specification). In simple cases we tell just a beginning. The following example says "10 seconds" (see below for other "clock-value" simple:
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML"
begin="10s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="300" to="100" />
Later, we'll see you can also use the interaction with a user event (eg click) to trigger an animation.
dur = Clock-value | "media" | "indefinite"
defines the duration of the animation
- Clock-value specifies the length of a presentation time. The value must be greater than 0.
- "Indefinite" specifies the simple duration as indefinite (this is the default if you do not specify a duration or "media")
- Typically indicates one second, eg. 10s = 10 seconds
<animate attributeName="x" attributeType="XML"
begin="0s" dur="9s" fill="freeze" from="300" to="100" />
There are several ways to define a "clock-value". Here qqs. examples that work:
- Values clock (Clock-value) complete:
02:30:03 = 2 hours, 30 minutes and 3 seconds 50:00:10.25 = 50 hours, 10 seconds and 250 milliseconds
- Partial clock value:
02:33 = 2 minutes and 33 seconds 00:10.5 = 10.5 seconds = 10 seconds and 500 milliseconds
- Timecount values:
3.2h = 3.2 hours = 3 hours and 12 minutes 45min = 45 minutes 30s = 30 seconds 5ms = 5 milliseconds 12467 = 12 seconds and 467 milliseconds
end = end-value-list
defines when animation ends
min = Clock-value | "media"
defines the minimum animation time
max = Clock-value | "media"
Defines the maximum value of the active duration of the animation.
The following three attributes are used less often and can constrain the active duration. You may define an end, a minimum or maximum duration.
restart = "always" | "whenNotActive" | "never"
- always: The animation can be restarted at any moment. This is the default.
- whenNotActive: The animation can be restarted when it is not active
repeatCount : numeric value | "indefinite"
Specifies the number of iterations of the animation function. The attribute value can be one of the following:
- numeric value = numeric "decimal" which specifies the number of iterations.
- "Indefinite" = The animation is defined to repeat indefinitely (ie until the user moves away from the document).
repeatDur : Clock-value | "indefinite"
Defines the total time for the repetition.
- Clock-value = specifies the duration
- "Indefinite" = animation is defined to repeat indefinitely (ie until the end of the document).
fill : "freeze" | "remove"
- = freeze the animation effect F (t) is defined to freeze at the end of the active duration. The animation effect is "frozen" for the rest of the document duration (or until the animation is restarted)
- remove = the effect of animation is stopped (no longer applicable) when the active duration of the animation is complete. (Unless it is restarted)
Attributes for animation values interpolated
Here's a quick summary without going into details
- The basic principle of this type of language (as in VRML) is to let the designer the possibility to simply define at least two values (start / end) and let the machine handle the transition between these values (interpolation)
Definition of interpolation:
- In animation, computing intermediate images between two polynomial forms or between two positions on the screen.
- For color, calculation of intermediate colors between two colors
calcMode = "discrete | linear | paced | spline"
Specifies the interpolation mode for animation.
- discrete = animation function will jump from one value to another without any interpolation.
- linear = a simple linear interpolation between the values is used for the calculation of the animation function. Except for 'animateMotion' this is the default for calcMode.
- paced = to produce an even pace of change during the animation.
- spline = interpolates from a value of the attribute list and the following values, according to a time function defined by a cubic Bezier curve (spline). The points of the spline are defined in the keyTimes and control points for each interval are defined in the keySplines.
values = "list"
- A list of one or more values, separated by semicolons.
- The values you can specify, depend on the type of animation
keyTimes = "list"
- A list of time values, separated by semicolons, used to control the speed of the animation.
- Each time value in the list of keyTimes is defined as decimal value between 0 and 1 (inclusive), representing a proportional offset of the duration of the animation
keySplines = "list"
- A set of Bezier control points associated with the list of keyTimes, defining a cubic Bezier function that controls the speed of the scrolling intervals.
Attributes that control the sequence of events
additive = replace | sum
- This tag is used when performing only one processing at the same time.
- sum = the animation will add to the underlying value of the attribute and other lower priority animations.
- replace = the animation will override the underlying value of the attribute and other lower priority animations. This is the default
- If a simple "grow" animation can increase the width of an object 10 pixels ....
<rect width="20px" ...>
<animate attributeName="width" from="0px" to="10px" dur="10s"
additive="sum"/>
</rect>
... it is frequently useful for repeated animations to build it on the basis of previous results that accumulate with each iteration. The following example is the rectangle continues to grow as and when the repetition of the animation:
<rect width="20px" ...>
<animate attributeName="width" from="0px" to="10px" dur="10s"
additive="sum" accumulate="sum" repeatCount="5"/>
</rect>
At the end of the first repetition, the rectangle has a width of 30 pixels, at the end of the second a width of 40 pixels and the end of the fifth a width of 70 pixels.
accumulate = "none | sum"
- See the specification
Example: Deltas of an animation
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/inc-growth.svg
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/svg/ex/anim-trans/
- At the end of the first repetition, the rectangle has a width of 40 pixels, at the end of the second a width of 60 pixels and the end of the fifth a width of 120 pixels.
- The total animation lasts 5 * 5 s = 25 seconds
- We build on previous results, accumulating with each iteration:
<rect x="50" y="50" width="20px" height="20px"
style="fill:yellow;stroke:black">
<animate attributeName="width" dur="5s" repeatCount="5"
fill="freeze"
from="0px" to="20px"
additive="sum" accumulate="sum"/>
</rect>
<text x="55" y="90" style="stroke:#000099;fill:#000099;fontsize:24;">
Hello. Let’s show a growing rectangle ! </text>
Resources
- Specification
- W3C Recommendation SVG1 in French. JJ Solari translator. http://www.yoyodesign.org/doc/w3c/svg1/
- Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) 1.1 (Second Edition), W3C Working Draft 22 June 2010, W3C Working Draft 22 June 2010, http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/
- The animation modules of SMIL 2.0 Chapter of the French translation.
- Tutorials and examples used
- Tricks of Javascript, SVG and SMIL (tested with FF 4)
See also
Acknowledgments
Thanks to JJSolari (the translator of the W3C recommendation SVG1 in French). I "pumped" a lot of this text.
The section on principles of animation has been widely copied from the translation of SMIL Animation W3C Recommendation 4 September 2001 . This translation was made by Patrick Schmitz and Aaron Cohen and we thank them also. The reason why I went from the french translation back to English was that I did the french version first - DKS March 2012