Computer colors tutorial: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
RGB colors can be encoded in various ways. For Internet formats such as HTML, CSS or Flash, most often a ''hex triplet'' is used, i.e. a hexadecimal 6 digit number. With 2 hexadecimal digits you can represent numbers in the range of 0 to 255, i.e. the number hex ''FF'' corresponds to the normal ''255'' number. | RGB colors can be encoded in various ways. For Internet formats such as HTML, CSS or Flash, most often a ''hex triplet'' is used, i.e. a hexadecimal 6 digit number. With 2 hexadecimal digits you can represent numbers in the range of 0 to 255, i.e. the number hex ''FF'' corresponds to the normal ''255'' number. | ||
According to [http://www.htmlpedia.org/wiki/CSS_Color_Values HTMLPedia], retrieved 14: | According to [http://www.htmlpedia.org/wiki/CSS_Color_Values HTMLPedia], retrieved 14:22, 11 September 2009 (UTC), {{quotation|Hexadecimal values specify the three colors of the transmitted spectrum using base 16. In base ten, there are only ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. In base sixteen, there are sixteen digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, A, B, C, D, E, and F. Hexadecimal and octal (base 8) are commonly used in computer programs because it is easy to convert them into binary numbers (base 2). In terms of color, it is common to represent a given color value as consisting of three parts : red, green, and blue, which are mixed together in the specified proportion to produce the final color. A typical color expressed in hexadecimal looks like this: #FFFFFF. [...] A common shorthand version reduces each color to 1 hexadecimal digit instead: #FFF. This allows for 4,096 unique colors.}}. Each single digit represents its "double", e.g. #F04 gives #FF0044. | ||
With ordinary numbers you would represent a full red like this: | With ordinary numbers you would represent a full red like this: | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
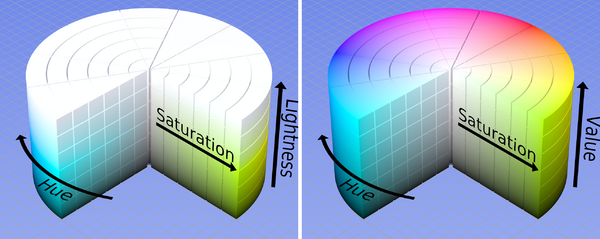
The HSL (Hue-saturation-lightness) model, also known as HSI (hue-saturation-intensity) model is similar to the HSV model described above. | The HSL (Hue-saturation-lightness) model, also known as HSI (hue-saturation-intensity) model is similar to the HSV model described above. | ||
[[image:HSL_HSV_cylinder_color_solid_comparison.png|thumb|600px|none|Comparison of the HSL (left) and HSV (right) color models. Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:HSL_HSV_cylinder_color_solid_comparison.png Wikipedia], retrieved 14: | [[image:HSL_HSV_cylinder_color_solid_comparison.png|thumb|600px|none|Comparison of the HSL (left) and HSV (right) color models. Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:HSL_HSV_cylinder_color_solid_comparison.png Wikipedia], retrieved 14:22, 11 September 2009 (UTC)]] | ||
According to the [http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-color/#hsl-color CSS specification], retrieved 14: | According to the [http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-color/#hsl-color CSS specification], retrieved 14:22, 11 September 2009 (UTC) | ||
{{quotationbox|CSS3 adds numerical hue-saturation-lightness (HSL) colors as a complement to numerical RGB colors. It has been observed that RGB colors have the following limitations: | {{quotationbox|CSS3 adds numerical hue-saturation-lightness (HSL) colors as a complement to numerical RGB colors. It has been observed that RGB colors have the following limitations: | ||
* RGB is hardware-oriented: it reflects the use of CRTs. | * RGB is hardware-oriented: it reflects the use of CRTs. | ||
| Line 299: | Line 299: | ||
* [[Sound Assets]] | * [[Sound Assets]] | ||
{{copyrightalso|[http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License]. Parts of this article are based on various Wikipedia articles, in particular we reuse some pictures. If you reuse these pictures from Wikipedia you should reproduce this license or equivalent.}} | |||
[[Category: Multimedia]] | [[Category: Multimedia]] | ||
Revision as of 15:22, 11 September 2009
This article or section is currently under construction
In principle, someone is working on it and there should be a better version in a not so distant future.
If you want to modify this page, please discuss it with the person working on it (see the "history")
Introduction
- Learning goals
- Understand principles underlying color models used in (simple) computer graphics
- Be able to specify a color for a web page
- Prerequisites
- Some HTML
- Moving on
- Level and target population
- Beginners
- Remarks
- This is a first draft version. The flash colors tutorial (for now) includes somewhat the same information.
See also: Color, Flash colors tutorial, CSS tutorial and
In various webtechnologies (such as HTML, CSS or Flash one could distinguish tow kinds of colors, in particular
- Normal colors, called solid colors
- All sorts of computer generated bitmap images that simulate special effects, like linear and radial gradients, bevel (3D) effects, shades, etc.
This article concerns (for now) solid colors.
Several solid color models exist, the most popular one is the RGB (read-green-blue) model, followed by the HSL/HSI (Hue-saturation-lightness, hue-saturation-intensity) and HSV/HSB (Hue-saturation-value, Hue-saturation-brightness) models.
Solid colors
Solid colors can be defined in various ways (and there is a whole science behind it). Let's just recall a few principles. For more information, please see the Wikipedia links in the color article.
Let's define a few terms first:
- Hue
- means "color"
- Saturation
- means amount of a color you apply, i.e. the intensity.
- Brightness
- How much light you apply. A lot of light makes a the color washed out and very little light makes it very dark.
- Transparency
- How much you can see trough
- See alpha channel below
- Tint and Shade
According to Wikipedia, “In color theory, a tint is the mixture of a color with white, and a shade is the mixture of a color with black. Mixing with white increases value or lightness, while mixing with black reduces chroma. Mixing with any neutral color, including black and white, reduces chroma or colorfulness. The intensity does not change.”
RGB colors
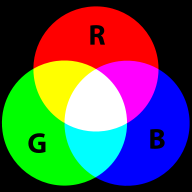
RGB colors are the most popular ones used in computing applications. A color is defined by the amount of Red - Green - Blue.
RGB is the way computer monitors work. E.g. to get a nice yellow you need 100% Red + 100% Green + 0% Blue. RGB is a so-called additive color mixing model. “Projection of primary color lights on a screen shows secondary colors where two overlap; the combination of all three of red, green, and blue in appropriate intensities makes white.” (Wikipedia). Now if you project each of these primary colors with different intensity, overlapping colors will change.
This model is not how colors work when you mix real paint. Then you'd rather work with a red-yellow-blue model. Color printers yet work with another model, i.e. magenta, cyan and yellow (or more).
RGB colors can be encoded in various ways. For Internet formats such as HTML, CSS or Flash, most often a hex triplet is used, i.e. a hexadecimal 6 digit number. With 2 hexadecimal digits you can represent numbers in the range of 0 to 255, i.e. the number hex FF corresponds to the normal 255 number. According to HTMLPedia, retrieved 14:22, 11 September 2009 (UTC), “Hexadecimal values specify the three colors of the transmitted spectrum using base 16. In base ten, there are only ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. In base sixteen, there are sixteen digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, A, B, C, D, E, and F. Hexadecimal and octal (base 8) are commonly used in computer programs because it is easy to convert them into binary numbers (base 2). In terms of color, it is common to represent a given color value as consisting of three parts : red, green, and blue, which are mixed together in the specified proportion to produce the final color. A typical color expressed in hexadecimal looks like this: #FFFFFF. [...] A common shorthand version reduces each color to 1 hexadecimal digit instead: #FFF. This allows for 4,096 unique colors.”. Each single digit represents its "double", e.g. #F04 gives #FF0044.
With ordinary numbers you would represent a full red like this:
- (255,0,0) - meaning full red, no green, no blue
The corresponding hex triplet is FF 00 00:
- #FF0000
In terms of percentage of colors you get:
- (100%, 0% , 0%), i.e. 100% red, 0% of green and 0% of blue
Let's now have a look at a few colors in a diagram we copied from Wikipedia on sept 8 2007: It represents "Truecolor", i.e. RGB values in 24 bits per pixel (bpp). In Truecolor, colors can be defined using three integers between 0 and 255, each representing red, green and blue intensities. For example, the following image shows the three "fully saturated" faces of the RGB cube, unfolded into a plane:
| yellow (255,255,0) |
green (0,255,0) |
cyan (0,255,255) | |
| red (255,0,0) |
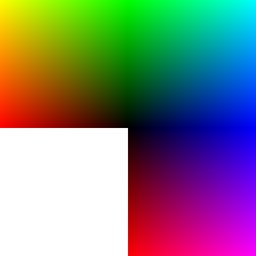
|
blue (0,0,255) | |
| red (255,0,0) |
magenta (255,0,255) |
For more information about colors see links in the color article. Have a look at Wikipedia's great list of colors if you need to find a number for your favorite color name. (If you speak french, get this one. You also may read the Wikipedia Web colors article. It also includes a list of colors and explains what a hex triplet is.
The HSV/HSB model
The HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) model also known as HSB (Hue, Saturation, Brightness) defines a color in terms of three components:
- Hue, the color: Represented as a position in the 360 degrees of a color circle.
- Saturation, the intensity or "purity" of the color: Ranges from 0-100%. 0 means no color, i.e., a shade of grey between black and white. 100 means intense color.
- Value or Brightness of the color: Ranges from 0-100%. 0 is always black. Depending on the saturation, 100 may be white or a more or less saturated color.
The Hue scale from 0 to 360 degrees is the following:
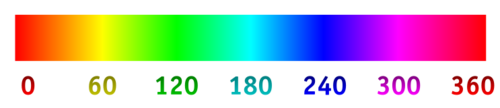
In many graphics tools (not in Flash) you get a HSV color wheel that looks like this:
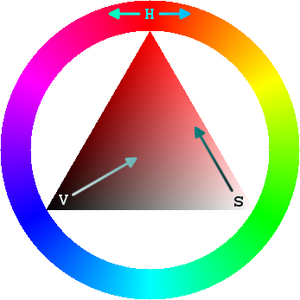
On the outside you can select a color (H), then on the inside you can select V and S.
For more information about HSV, read Wikipedia'sHSL and HSV article.
The HSL/HSI model
The HSL (Hue-saturation-lightness) model, also known as HSI (hue-saturation-intensity) model is similar to the HSV model described above.
According to the CSS specification, retrieved 14:22, 11 September 2009 (UTC)
CSS3 adds numerical hue-saturation-lightness (HSL) colors as a complement to numerical RGB colors. It has been observed that RGB colors have the following limitations:
- RGB is hardware-oriented: it reflects the use of CRTs.
- RGB is non-intuitive. People can learn how to use RGB, but actually by internalizing how to translate hue, saturation and lightness, or something similar, to RGB.
In CSS, the hsl value is defined by the position in the color wheel, e.g. red = 0, red = 360, blue=240. Saturation and lightness are represented by percentages. Here are a few examples:
{ color: hsl(0, 100%, 50%) } /* red */
{ color: hsl(120, 100%, 50%) } /* green */
{ color: hsl(120, 100%, 25%) } /* dark green */
{ color: hsl(120, 100%, 75%) } /* light green */
{ color: hsl(120, 75%, 75%) } /* pastel green, and so on */
E.g. The following HSL CSS code
<p style="color: hsl(240,75%,75%);"> Kind of not so blue</p>
would show like this (your browser may not support this):
Kind of not so blue
For more information about HSL (and HSV), we point again to Wikipedia's HSL and HSV article.
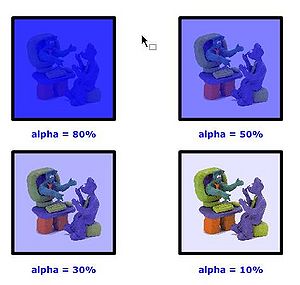
The alpha channel
In computer graphics, alpha compositing is the process of combining an image with a background to create the appearance of partial transparency (Wikipedia)
In more simple terms, you can set the alpha to some percentage:
- 100% can't see through
- 80% bad see trough
- 50% in between
- 30% good see through
- 10% good see through, but very little color
- 0% no color left
Hint: With the alpha channel you can create other effects than see-through "windows". E.g. you can overlay textures with color or the other way round.
Color names and transformations
In this section will firstly look at color names. Several technical formats define shorter list of predefined color names. Other than that, there exist hundreds of color names whose physical definition differ in various cultural contexts.
We also introduce some transformations, where a program or an author with the help of some graphics software creates "colors" with special effects.
HTML/CSS 2 colors
According to the CSS3 color model, HTML4/CSS 2 includes the following color keywords: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, and yellow.
Below is a table:
| ______ | Black = #000000 | ______ | Green = #008000 |
| ______ | Silver = #C0C0C0 | ______ | Lime = #00FF00 |
| ______ | Gray = #808080 | ______ | Olive = #808000 |
| ______ | White = #FFFFFF | ______ | Yellow = #FFFF00 |
| ______ | Maroon = #800000 | ______ | Navy = #000080 |
| ______ | Red = #FF0000 | ______ | Blue = #0000FF |
| ______ | Purple = #800080 | ______ | Teal = #008080 |
| ______ | Fuchsia = #FF00FF | ______ | Aqua = #00FFFF |
SVG 1.1 and CSS 3 color keywords
CSS 3 color keywords refer to the SVG standard tha defines many more colors. The model is actually taken from X11 (the graphical user interface display protocol for Unix)
You may have a look at the CSS3 color table that we made from the one in the CSS 3 spec and that relies on the SVG 1.1 specification
Alpha compositing in CSS
In CSS (if your browser supports it), you may use so-called RGBA values using the %% notation, i.e. The following RGBA CSS code
<p style="color: rgba(0,0,255,0.3);"> Kind of blue</p>
would show like this (your browser may not support this):
Kind of blue
Use as background color. The following code
<div style="background-color: rgba(0,0,255,0.2);">
<p> Kind of blue</p>
</div>
would show like this (your browser may not support this):
Kind of blue
The CSS 3 specification actually refers to the SVG 1.1. standard, i.e. the chapter on Clipping, Masking and Compositing.
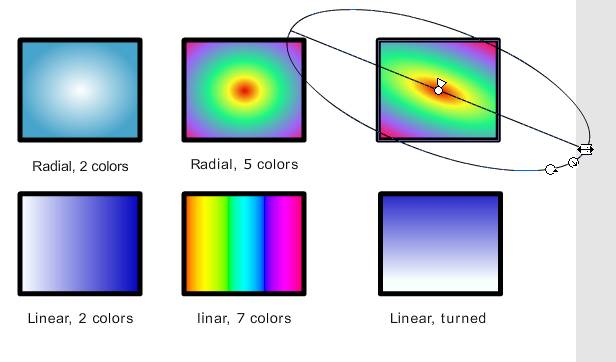
Gradients
Color gradients are transitions from one color to another (according to a color space model, typicall sRGB, a ). Authors will have to define at least to color bands. E.g. a gradient from white to blue would show all sorts of tinted blues. The most commonly use gradients are either linear or radial
- Linear gradients: color changing in one direction
- Radial gradients: color changing from a center to outside
Below is picture we made for the Flash colors tutorial
Colors in 3D graphics
3D graphics languages and tools usually offer a much richer palette of composed color types as well as sophisticated textures that one can lay over the colors.
E.g. in VRML/X3D (a Web standard) you get color types like this:
- Diffuse color is a color that reflects light depending on the angle of the surface. The object appears brighter (more lit) when its surface is directly exposed to light as you would expect. That's your "normal color".
- Emissive color defines "glowing objects". E.g. you would use this to build a visible lamp.
- Specular color defines extra reflection has when the angle from the light is close to the angle you are looking at. It is used together with shininess. You can experiment this effect in real life by holding a (new apple) or a photograph between you and a window (or a lamp).
Use of color in web pages
(to be written)
Links
- General color
- See also the color article. It includes links to good Wikipedia articles
- Specifications
- CSS Color Module Level 3 (W3C Working Draft 21 July 2008)
- Interesting Browser extensions
- ColorZilla includes an Eyedropper (you can "steal a color from a web page), a ColorPicker (i.e. you can select a color from color selection tool), a Page Zoomer and other colorful goodies.
- HTML colors
Note: Avoid using any kinds of HTML tags for styling, use CSS to specify colors, the CSS tutorial brievly explains how to do this.
- CSS Color Values (Note: CSS 2 system default settings seem to haved changed in CSS3)
- RGB color tables with color names
- HTML color codes and names (from computer hope.com) Actually these are not just for HTML. Anyhow, the list can be useful :)
- Other kinds of assets