CSS color and background tutorial
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
- Learning goals
- Understand CSS 2 and CSS color models
- Be able to user background and font colors
- Concurrent
- Moving on
- Level and target population
- Beginners
- Teaching materials
- ....
- Remarks
- This tutorial is intended for students in educational technology or any other field that is technology intensive. For people who need less, there exist many easy CSS tutorials on the web. This text is intended for students who also must learn principles and who are willing to learn CSS by doing a project, looking at CSS code and online reference manuals.
- Ideally, a teacher also should assign a text formatting task, during or before assigning this tutorial for reading).
Introduction
CSS 2 colors
In CSS 2.1 (support by nearly all browsers on the market, i.e. also back two older generations), there exist several properties for which a color can be set.
Let's have a look at some example code that demontrates two of the most popular color properties and the typical RGB hex notation for color values:
The following inline CSS code
<p> <span style="background-color: #0000ff; color: #ffffff;"> Blue background and white foreground</span> demo </p>
would show like this:
Blue background and white foreground demo
We shall explain more details below, but befor we shall present an overview of CSS 2 color properties and introduce the color model used in CSS 2.
Setting the font color
- color
- defines the foreground color for text content
- Example: color: #ff0000;
Setting the background color “Authors may specify the background of an element (i.e., its rendering surface) as either a color or an image. In terms of the box model, "background" refers to the background of the content, padding and border areas. Border colors and styles are set with the border properties. Margins are always transparent.” (CSS 2 spec.)
- background-color
- defines the background’s color of an element
- Example: background-color: red;
- background-image
- sets the background image for an element. An image is not really a color, but can be used for the same purpose
- background-repeat
- defines the tiling (and tiling direction) of a background-image
- background-position
- defines the position of a background image
- background-attachment
- defines whether the background image scrolls with the containing block or stays fixed with respect to the viewport (i.e. what is displayed)
- background
- is a short hand notation that allows to define all background definitions
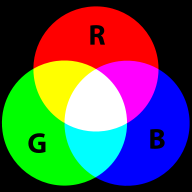
The RGB color model
RGB colors are the most popular ones used in computing applications. A color is defined by the amount of Red - Green - Blue.
RGB is the way computer monitors work. E.g. to get a nice yellow you need 100% Red + 100% Green + 0% Blue. RGB is a so-called additive color mixing model. “Projection of primary color lights on a screen shows secondary colors where two overlap; the combination of all three of red, green, and blue in appropriate intensities makes white.” (Wikipedia). Now if you project each of these primary colors with different intensity, overlapping colors will change.
This model is not how colors work when you mix real paint. Then you'd rather work with a red-yellow-blue model. Color printers yet work with another model, i.e. magenta, cyan and yellow (or more).
RGB colors can be encoded in various ways. For Internet formats such as HTML, CSS or Flash, most often a hex triplet is used, i.e. a hexadecimal 6 digit number. With 2 hexadecimal digits you can represent numbers in the range of 0 to 255, i.e. the number hex FF corresponds to the normal 255 number.
CSS 2 color models
There are two way of defining CSS 2 colors. Either by its name (but the official list only includes 17 colors) or by a so-called RGB value. The latter can be specified in four different ways as we shall show in the example below. The 17 pre-defined color names in CSS 2.1 are the following, according to the CSS 2.1 specification from which we made a screen shot:
Otherwise, you may choose from several RGB numerical colors specifications as the following example shows. The following example will set the color of a text:
em { color: #f00 } /* #rgb = Red-Green-Blue shortcut for rrggbb*/
em { color: #ff0000 } /* #rrggbb */
em { color: rgb(255,0,0) }
em { color: rgb(100%, 0%, 0%) }
In order to set the background-color use something like:
em { background-color: #f00 } /* #rgb = Red-Green-Blue shortcut for rrggbb*/
em { background-color: #ff0000 } /* #rrggbb */
em { background-color: rgb(255,0,0) }
em { background-color: rgb(100%, 0%, 0%) }
CSS 3 colors
CSS 3 implements (of course) all CSS 2 features. In addition it implements a whole range of new color related properties and values.
HSL colors
In CSS, the hsl value is defined by the position in the color wheel, e.g. red = 0, red = 360, blue=240. Saturation and lightness are represented by percentages. Here are a few examples:
{ color: hsl(0, 100%, 50%) } /* red */
{ color: hsl(120, 100%, 75%) } /* light green */
{ color: hsl(120, 75%, 75%) } /* pastel green, and so on */
E.g. The following HSL CSS code
<p style="color: hsl(240,75%,75%);"> Kind of not so blue</p>
would show like this (your browser may not support this):
Kind of not so blue
Alpha channel
In CSS (if your browser supports it), you also can define the alpha channel. You may use so-called RGBA values using the % notation, i.e.
p { background-color: rgba(0,0,255,0.5) } /* semi-transparent solid blue */
The following RGBA CSS inline code
<p style="float:right; background-color: rgba(0,0,255,0.3);"> Kind of blue</p>
would show like the "Kind of blue" box to the right (your browser may not support this):
Kind of blue
Alternatively you can use the opacity property that does the same, e.g.
background: rgb(255, 0, 0) ; opacity: 0.2;">
Finally, in CSS 3, you also may use HSL with an alpha channel
/* HSL model with alpha channel */
p { color: hsla(120, 100%, 50%, 1) } /* green */
p { color: hsla(120, 100%, 50%, 0.5) } /* semi-transparent green */
p { color: hsla(120, 100%, 50%, 0.1) } /* very transparent green */