Learning object
Definition
- Learning objects are supposed to be reusable learning objects (RLO)
- Small (relative to the size of an entire course) instructional components that can be reused a number of times in different learning contexts.
- “digital entities deliverable over the internet” (Wiley, 2000, p.3)
See also: the learning object repository article and the list of learning objects repositories
What is a learning object ?
Size
“The purpose of learning objects and their reality seem to be at odds with one another. On the one hand, the smaller designers create their learning objects, the more reusable those objects will be. On the other hand, the smaller learning objects are, the more likely it is that only humans will be able to assemble them into meaningful instruction. From the traditional instruction point of view, the higher-level reusability of small objects does not scale well to large numbers of students (i.e., it requires teachers or instructional designers to intervene), meaning that the supposed economic advantage of reusable learning objects has evaporated.” ([1])
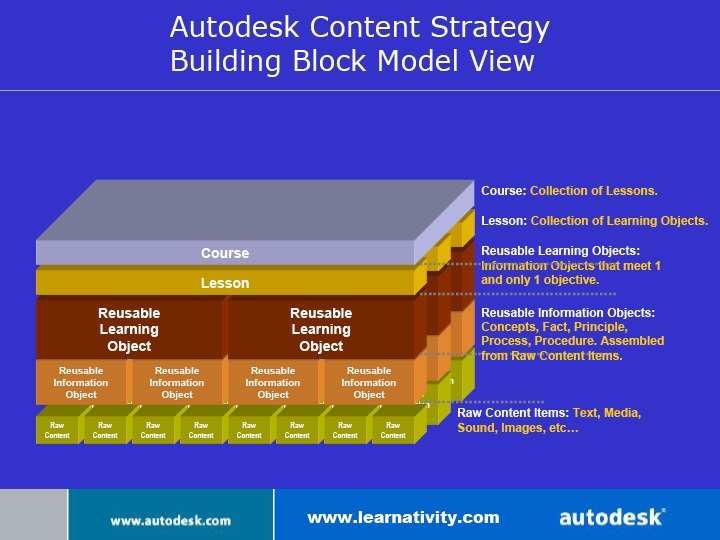
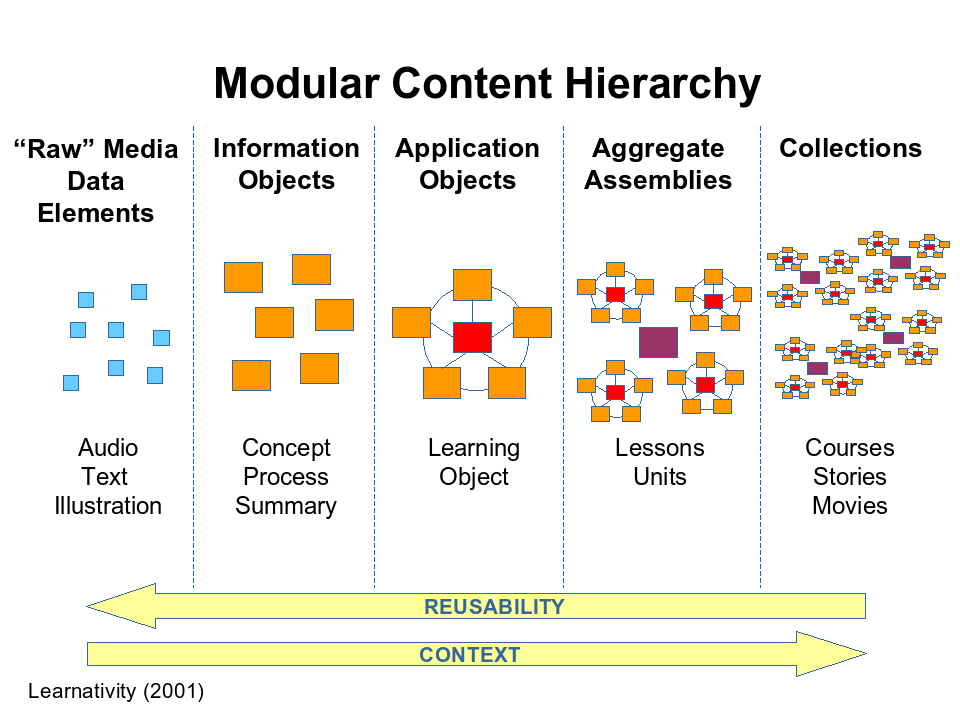
According to Hodgins (2000) as described in MODWiki, the hierarchy of modular content can be divided into 5 levels:
- Raw Content
- The most fine-granular level consists of raw media elements including media types like text, audio, illustration, animation and others.
- Reusable Information Object
- From raw media elements, information objects are formed. They describe a certain procedure, process or structure, define a concept, present a fact, or provide an overview on some subject.
- Reusable Learning Object
- The third aggregation layer combines information objects circumscribed by a learning objective. The objects at this level are called learning objects.
- Lesson
- The fourth layer groups learning objects around a more encompassing outcome or terminal objective to create aggregates like lessons, chapters, learning units etc.
- Course
- The top layer includes collections of lower level aggregate assemblies to form thematic courses, books, stories or whole movies.
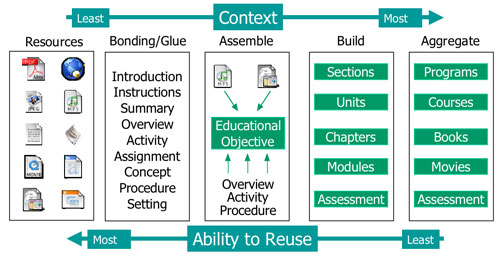
In the A Short Course on Structured Course Development, Learning Objects, and E-Learning Standards we can find the following diagram that illustrates the relationship between context and reusability (adapted from Hodgins, 2002 ??).
Krull and Mallinson, also based on Hodgins made this slide that expresses the same principle:
E-learning objects vs any teaching materials
Most commonly used learning objects are teaching materials that can be found in teacher-centered repositories. There are several categories, e.g.
- Simple Contents for learners (e.g. Web Pages, Word documents)
- Multimedia presentations and multimedia animations
- Interactive learning software (e.g. interactive multimedia)
- Microworlds
However, it is debatable whether these are learning objects in a more strict sense. Clearly some of these are not just "raw contents", but non-standardized reusable contents at any level of granularity.
Gerry Paille defines the characteristics of Learning Objects in a more narrow sense as follows:
- Learning objects are digital
- Learning objects can be stored in a database or repository
- Learning objects can be described using a metadata standard or specification
- Learning objects are discoverable through searching a database
- Learning objects are interoperable in that they are independent of hardware, operating system and browser type
- Learning objects tend to be, but are not necessarily, small or granular in nature
- Learning objects tend to be, but are not necessarily, disassociated from context
- Learning objects are reusable
- Learning objects can be repurposed for different educational contexts
- Learning objects have an explicit educational purpose
Daniel K. Schneider thinks that in the world of e-learning, learning objects mostly refer to a set of interactive web pages, in particular standards-based IMS Content Packaging that can be imported into a LMS.
The SCORM 2004 3rd Edition Overview (p 1-6) defines “ilities,” that should caracterize a learning objects "economy":
- Accessibility: The ability to locate and access instructional components from one remote location and deliver them to many other locations.
- Adaptability: The ability to tailor instruction to individual and organizational needs.
- Affordability: The ability to increase efficiency and productivity by reducing the time and costs involved in delivering instruction.
- Durability: The ability to withstand technology evolution and changes without costly redesign, reconfiguration or recoding.
- Interoperability: The ability to take instructional components developed in one location with one set of tools or platform and use them in another location with a different set of tools or platform.
- Reusability: The flexibility to incorporate instructional components in multiple applications and contexts.
See also:
- educational modelling languages e.g. other IMS standards like the IMS Simple Sequencing or IMS Learning Design that deal with the sequencing part of a learning object
- metadata standards to describe objects or its compontents
Constructionist learning objects
The constructionist Oren Zuckerman (2006, in preparation) defines a learning object as {{quotation | specifically designed to promote learning through hands-on interaction. They are popular materials in early childhood education, at school and at home.
See constructionist learning object
Formal definition of learning objects
- See the standards article for an overview and the Learning object standard article for a technical overview table
- See educational modeling languages and IMS Content Packaging for the most important faces of pedagogical e-learning standards.
Pedagogical design and learning objects
Learning objects play different roles in given instructional design models / pedagogic strategies. Ip and Morrison (2001) argue that one should clearly distinguish three main types of educational technology uses cases and that emphasize different kinds of resources:
- Learn from a computer (CBT, e-instruction, etc.): Learning objects, i.e. learning objects in a narrow sense.
- Learn with a computer (cognitive tool, writing-to-learn, etc.): Software tools
- Learn via a computer (CSCL, etc.): Communication (peer learners)
Conference, August 2002, pp. 76�%Gâ�%@82.
| Pedagogical Design | Nature of the resources | Need special rendering software | Resources are specifically designed for educational use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tutorial, Drill and Practice | Test or drill items, (may be structured to meet interoperability standards such as IMS QTI) | Yes – directly or indirectly. Some learning objects may have embedded content and some may not. | Yes |
| Case Study Method | Teaching cases | No - cases are normally hardcopy but online cases can include video – but hard-wired to the learning scenario (see GBL) | Yes |
| Goal-based learning | Stories, or video clips, provided mainly ‘ondemand’ | No | Yes |
| Learning by designing | The requirement for an artifact | No | Yes |
| Web-based role-play, simulation | A scenario & associated design of the role play, simulation resources | No, but the environment itself may be a specialist engine (Ip & Linser, 1999) | Scenario etc: yes, Resources: no |
| Distributed problem based learning | Problem for solving during the learning | No | Yes |
| Critical incident-based computer supported learning | Opportunities for learning - incidence | No | No |
| Rule-based simulation | Embedded in the software | Yes, most componentbased approaches to creating rule-based simulation will have embedded content in the components which roughly map to learning objects in this paper | Yes |
| Cognitive tool | Structured content to work with some tools, generic tools may not need any content | N/A | N/A |
| Resource-based Learning Environment | Resources | Search tool and resource discovery mechanism, e.g. in the form of support from subject gateways | No |
Learning Objects Repositories
In the case of digital learning resources, there are many problems to be overcome before we can expect widespread reuse and sharing. Learning tends to be highly contextual, and context is not as easy to disseminate as data alone. (Learning )
See the learning object repository article and the list of Learning objects repositories
Links
- Learning Objects, MODWiki
- http://www.reusability.org/read/ (on line book)
- http://ijklo.org/ (This is an open content on-line journal)
- http://learningobjects.org/ (Portal with advice, good links Krull & Mallinsonfor articles, etc.)
- Learning Objects
- Get R.E.A.L. -- Relevant Effective Adaptive Learning, Wayne Hodgins PPT Talk.
References
Standards and Manuals
- Advanced Distributed Learning (2006): SCORM 2004 3rd Edition Overview Version 1.0, Available from http://www.adlnet.gov/.
Tutorials
- A Short Course on Structured Course Development, Learning Objects, and E-Learning Standards Gerry Paille
Papers
- Ip, Albert, Iain Morrison and Mike Currie (2001). What is a learning object, technically?, WebNet2001 conference, Orlando, USA. PDF
- Ip, Albert and Iain Morrison (2001), Learning Objects in Different Pedagogical Paradigms, ASCILITE 2001. PDF
- Hodgins, H. W. (2000). The future of learning objects. In D. A. Wiley (Ed.), The Instructional Use of Learning Objects. WORD Reprint
- Hodgins, Wayne (2002). The future of learning objects, Proc. of the 2002 eTEE Conference, August 2002, pp. 76-82. PDF (full proceedings, retrieved 16:12, 30 May 2007 (MEST))
- Wiley, David A. (2000). Connecting learning objects to instructional design theory: A definition, a metaphor, and a taxonomy. In D.A. Wiley (Ed.). The Instructional Use of Learning Objects [on-line]. Available: [2].
- Wiley, Gibbons, & Recker. (2000). A reformulation of the issue of learning object granularity and its implications for the design of learning objects PDF
- Williams, Roy (2003) Context, Content and Commodities: e-Learning Objects, Electronic Journal of e-Learning (EJEL) 2 (2). Abstract (PDF/HTML open access)