3D printing
Introduction
According to Wikipedia, retrieved 14:48, 14 October 2011 (CEST), “3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing technology where a three dimensional object is created by laying down successive layers of material. 3D printers are generally faster, more affordable and easier to use than other additive manufacturing technologies. 3D printers offer product developers the ability to print parts and assemblies made of several materials with different mechanical and physical properties in a single build process. Advanced 3D printing technologies yield models that can serve as product prototypes.”
See also:
- 3D printer
- Other articles in the 3D printing category
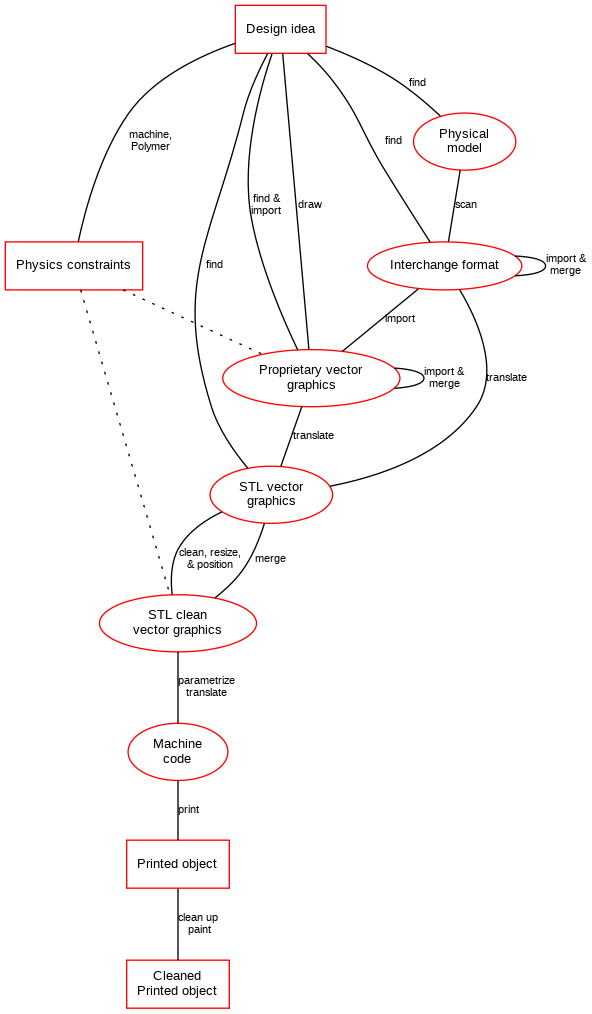
A workflow model
The following figure summarizes typical workflows. There a three fundamental design stages:
- Model an object with any kind for modeling program, e.g. a 3D modeler, a CAD drawing program, a CAD programming tool like OpenScad or through 3D scanning.
- If the modeler can't export to STL, export to a popular exchange format like OBJ, then translate the OBJ with a program like Meshlab.
- Translate the model to a format that is appropriate for 3D printing, typically .STL, a stereolithography CAD format created 3D Systems. This file format is supported by many other software packages. STL basically describes an object with triangles using an x,y,z coordinate system. A similar format that can be used by some "cleaning/positioning/to-machine-code" programs is OBJ.
- Repair the STL file and (if necessary) make simple changes to size, position, etc.). Either use a specific STL Editor or some integrated 3D printing tool that offers this functionality.
- Translate STL to machine code with a slicer, typically into so-called G-code
As you can see, there are several paths that lead from a design idea to a printed object. Absolute beginners can start simply by downloading STL files from a repository such as Thingiverse, positioning it, maybe re-sizing and then printing it. Intermediate users can merge existing objects together at any level, e.g. at STL level with a tool like Meshlab (free) or Netfabb (commercial).
Some low level "how to print an STL file" is described in the First steps with the RapMan V3.1 3D printer article.
Also take note that respecting physical constraints is important ! For example, you can't print bigger than your print area, you can't print designs that have a large footprint with ABS, you can't print large overhangs with a printer that doesn't allow printing support structures, etc.
Links and bibliography
Textbooks
- General
As of oct. 2014, there exist several books, some of which are available as e-books from on-line sellers like Amazon or Kobo
- Made for education
- E. Canessa, C. Fonda & M. Zennaro (2014). Low-cost 3D Printing for Science, Education and Sustainable Development, ICTP—The Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics, Free and open book, http://sdu.ictp.it/3d/book.html (First International Workshop on "Low-cost 3D Printing for Science, Education and Sustainable Development)
- Thornburg,David, Norma Thornburg, and Sara Armstrong (2014). The Invent To Learn Guide to 3D Printing in the Classroom: Recipes for Success. CMK Press.
- Sylvia Libow Martinez and Gary S. Stager (2013). Invent To Learn: Making, Tinkering, and Engineering the Classrooom, Constructing Modern Knowledge Press, ISBN: Print 978-0-9891511-0-8, http://www.inventtolearn.com/