DialogPlus Toolkit: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{Stub}} | {{Stub}} | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
=== Concepts === | === Concepts === | ||
At the heart of this [[instructional design method]] are '''nuggets''', i.e. [[learning activities]] or [[pedagogical scenario]]s. Nuggets embody both learning activities and resources. | At the heart of this [[instructional design method]] are '''nuggets''', i.e. [[learning activity | learning activities]] or [[pedagogical scenario]]s. Nuggets embody both learning activities and resources. Nuggets are activity-based [[learning object]]s. | ||
{{quotation | Nuggets range in size (from a single file, to a mini-website), formats (word documents, powerpoint slides, html, flash etc), media (text, images, animations) and educational styles (learning material, assessments, activities, resources).}} ([http://www.dialogplus.soton.ac.uk/nuggets.php]), retrieved 10: | {{quotation | Nuggets range in size (from a single file, to a mini-website), formats (word documents, powerpoint slides, html, flash etc), media (text, images, animations) and educational styles (learning material, assessments, activities, resources).}} ([http://www.dialogplus.soton.ac.uk/nuggets.php]), retrieved 10:46, 23 November 2006 (MET)). | ||
The software uses a '''nugget taxonomy''' as a language to to specifify the nugget and its components. | The software uses a '''nugget taxonomy''' as a language to to specifify the nugget and its components. | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 23 November 2006
Definition
The DialogPLUS Toolkit is to guide and support teachers as they create, modify, and share learning activities and resources.
DialogPLUS is an online browser-based application (free access on 19:19, 22 November 2006 (MET)) and it is sponsored by the British JISC/NSF funded DialogPlus project.
Purpose
This tool is partly insprired by IMS Learning Design and somewhat related toolkits like LAMS and MOT.
According to Conole and Fill (2005: 1), “despite the plethora of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) tools and resources available, practitioners are still not making effective use of e-learning to enrich the student experience”. The DialogPLUS learning design toolkit should guide practitioners through the process of creating pedagogically informed learning activities which make effective use of appropriate tools and resources.
The learning design toolkit described can be used for three main purposes:
- As step-by-step guidance to help practitioners make theoretically informed decisions about the development of learning activities and choice of appropriate tools and resources to undertake them.
- As a database of existing learning activities and examples of good practice which can then be adapted and reused for different purposes.
- As a mechanism for abstracting good practice and metamodels for e-learning
The tool
Concepts
At the heart of this instructional design method are nuggets, i.e. learning activities or pedagogical scenarios. Nuggets embody both learning activities and resources. Nuggets are activity-based learning objects. “Nuggets range in size (from a single file, to a mini-website), formats (word documents, powerpoint slides, html, flash etc), media (text, images, animations) and educational styles (learning material, assessments, activities, resources).” ([1]), retrieved 10:46, 23 November 2006 (MET)).
The software uses a nugget taxonomy as a language to to specifify the nugget and its components. Below we reproduce some concept maps produced by the authors that illustrate a few selections a teacher/designer has to make when he designs a "nugget". These concept maps probably do not reflect the current state of the system, but they give an idea of the kind of design decisions that are being modeled. Also, please note that we don't show all expanded "nodes" of the model.
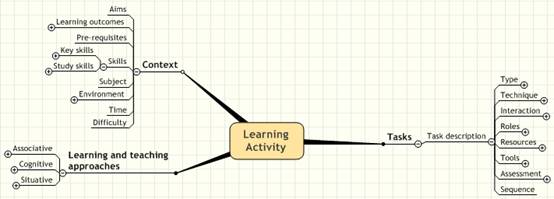
- The learning activity
The notion of a learning activity (LA) is at the heart of the tool and it is composed of three elements:
- The context of the activity: e.g. subject, level of difficulty, intended learning outcomes and the environment within which the activity takes place.
- The learning and teaching approaches: including theories and models.
- The learning tasks: This includes type of task, techniques used, associated tools and resources, interaction and roles of those involved and learner assessment.
- Learning and teaching approaches
The tool supports a variety of [[instructional design model]s. DSchneider thinks that it definitely fits a modern activity-based instructional design perspective, e.g. as an alternative to more traditional lesson planners and more in the spirit of more poweful tools like MOT+, but being much easier to learn.
With the tool, the teacher can explicitly state a given pedagogical approach, but the design itself is then defined through tasks.
- Assessment types
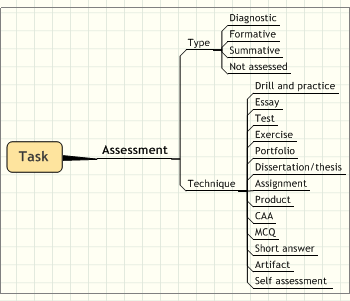
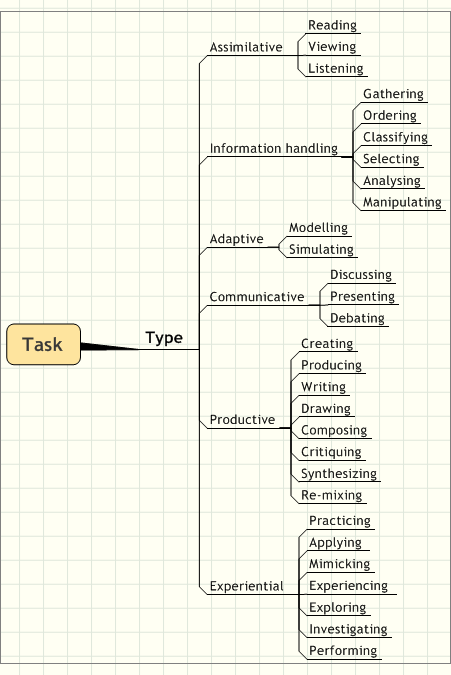
- Task types and resources
Task techniques include brainstorming, exercise, field work, role play, reflection and syndicates. The authors “identified almost thirty techniques to be stored in the toolkit such that advice can be offered to practitioners. Interactions required are likely to be individual, one to many, student to student, student to tutor, group or class base”.
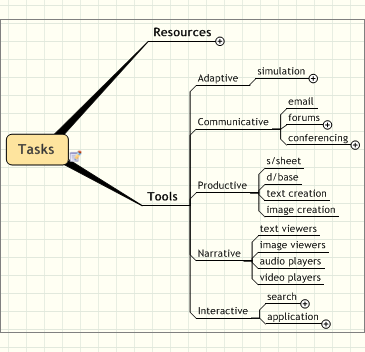
Available resources and tools are based on the Laurillard conversational framework five principal media forms (Narrative, Communicative, Adaptive, Productive, and Interactive) (Laurillard, 2002, p.90).
The tool
The tool is available as on-line Web application. External users may create an account (checked on 20:24, 22 November 2006 (MET)).
(needs some description and evaluation here - DSchneider)
Current status
As of Nov 2006, the DialogPlus toolkit is being further evaluated, together with LAMS, as tools for teacher development as learning activity designers in the JISC funded EDIT4L project, part of the Design for Learning programme.
Links
- DialogPLUS On-line Application
- Project websites and related
- DialogPlus Home Page (Note: The old http://www.dialogplus.org/ website is no longer supported)
- EDIT4L, Evaluation of Design and Implementation Tools for Learning
- JISC Design for learning. A larger British project (2006 - 2088) for projects in developing, implementing and evaluating tools and systems that support design for learning.
- Other
- Fill, K., Bailey, C., Conole, G. & Davis, H. (2004). "Supporting teachers: the development and evaluation of a learning design toolkit." ALT-C 2004, Exeter, UK. Abstract (and PPT)
References
- Gráinne Conole and Karen Fill (2005). A learning design toolkit to create pedagogically effective learning activities. Journal of Interactive Media in Education (Advances in Learning Design. Special Issue, eds. Colin Tattersall, Rob Koper), 2005/08. ISSN:1365-893X Abstract (PDF/HTML open access)
- Conole, G. & Fill, K. "Designing a Learning Activity Toolkit." Ed-Media 2004 Poster, Lugano, Switzerland PPT
- Laurillard, D. (2002). Rethinking University Teaching. A conversational framework for the effective use of learning technologies. London: Routledge ISBN 0415256798 .
- Other publications to sort out ...
Conole, G. (2002). 'Systematising Learning and Research Information', Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 7. Abstract (HTML/PDF).
Conole, G. (2004). 'Report on the effectiveness of tools for e-learning', report for the JISC commissioned Research Study on the Effectiveness of Resources, Tools and Support Services used by Practitioners in Designing and Delivering E-Learning Activities. [cited] [cited]
Conole, G. and Dyke, M. (2004). 'What are the affordances of Information and Communication Technologies', ALT-J, 12.2,113-124.
Conole, G., Dyke, M., Oliver, M. and Seale, J. (2004). 'Mapping pedagogy and tools for effective learning design', Computers and Education, 43 (1-2), 17-33
Conole, G. and Oliver, M. (2002). 'Embedding Theory into Learning Technology Practice with Toolkits, Journal of Interactive Media in Education, Special issue on learning technology theory', Open University, 2002(8), http://jime.open.ac.uk/.