Learning objective: Difference between revisions
m (→Links) |
m (→Definition) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Also known as : Instructional objectives, learning outcomes, learning goals. | Also known as : Instructional objectives, learning outcomes, learning goals. | ||
See also: *[[Learning_level#Blooms_taxonomy | Bloom's taxonomy]] | See also: | ||
*[[Learning_level#Blooms_taxonomy | Bloom's taxonomy]] | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
Revision as of 15:01, 7 March 2019
Definition
Learning objectives are statements that define the expected goal of a curriculum, course, lesson or activity interms of demonstrable skills or knowledge that will be acquired by a student as a result of instruction. Also known as : Instructional objectives, learning outcomes, learning goals.
See also:
Introduction
The definition of learning objectives is (or should be) the foundation of any instructional design. They are integral determining factor of strategies and Instructional design model and methods, pedagocial scenarios and lesson plans.
Problems defining learning objectives
Learning objectives when attained should be observable behaviours or actions. Words used to define learning objectives are often teacher centered and ambiguous.
E.g. Students will know the seven original member countries of the European Union and their capitals.
Formulations such as "Student will understand, comprehend, know" are problematic in that one cannot observe knowing or comprehension. Learning objectives should be formulated in a way that specifies how learning will be observed or measured and are thus intertwined with evaluation methods. Words that describe what the student will do to show that he or she understands are more useful.
E.g. Students will be able to list 5 countries in Europe and their capitals.
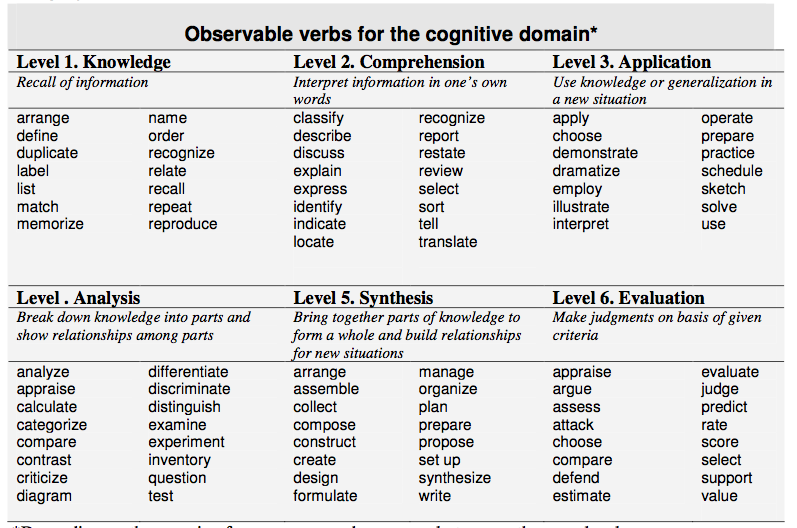
Verbs for defining learning objectives
Verbs presented in the following table are lists of verbs that correspond to the cognitive domains within Bloom's Taxonomy from CyberCampus's Tips for writing performance-based objectives.
Source:Kemp, J.E., Morrison, G.R., & Ross, S.M. (1998). Designing effective instruction, 2nd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill
Tools
- Radio James Objectives Builder (link fixed 3/2013).
Links
Introductions for "Bloom"-type definitions
All of the following links offer similar advice. That doesn't mean that there are no alternatives. For example, in some pedagogies, the learning objectives also could be described in terms of a product that implicitly defines skills to be learned.
- See also: learning level and learning type
- Articulate Your Learning Objectives, Teaching Excellence & Educational Innovation, Carnegie Mellon University, (3/2013).
- Learning Objectives, TIPS AND TACS COURSES, niversity of Nottingham (consulted 3/2013).
- Mager's Tips on Instructional Objectives - overview of Mager's Preparing instructional objectives provided in a course at Georgia State University
- Effective Use Of Performance Objectives For Learning And Assessment (PDF), ©Teacher & Educational Development, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, 2005
- Bloom's Taxonomy (Wikipedia)
- Educational aims and objectives (Wikipedia)
- Intended Learning Outcomes, Teaching and Learning Laboratory, MIT. (consulted 3/3013)
- Developing Learning Outcomes: A Guide for Faculty UToronto (consulted 3/3013)
- Writing Quality Learning Objectives, Park University (consulted 3/3013)
- Writing learning objectives, Schreyer Institute for Teaching Excellence, Penn State.
Examples
- Swiss Catalogue of Learning Objectives for Undergraduate Medical Training (consulted 3/2013).
References
- Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., Airasian, R. W., Cruikshank, K. A., Mayer, R. E., Pintrich, P. R., Raths, J. & Wittrock, M. C. (2001). A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing. New York, NY: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
- Bloom, B.S. (Ed.) (1956) Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The classification of educational goals: Handbook I, Cognitive Domain. New York ; Toronto: Longmans, Green.
- Mager, R.F. (1984). Preparing instructional objectives. (2nd ed.). Belmont, CA: David S. Lake.
- Cybercampus, Golden Gate University, Tips for writing performance-based objectives, accessed November 16, 2009.
- Kraiger, K., Ford, J. K., & Salas, E. (1993). "Application of cognitive, skill-based, and affective theories of learning outcomes to new methods of training evaluation." Journal of Applied Psychology, 78, 311-328.
- McKeachie, W. J. (1999). Teaching Tips: Strategies, Research, and Theory for College and University Teachers (10thEdition). Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Company.