Learning level
Definition
- From a learning psychological perspective, Levels of learning refer to competencies a learner can achieve.
- Taking into account learning levels is a key issue in instructional design
- Instructional design also has to clearly identify the level of instruction a design is aiming at.
See also Learning type, concept learning
Taxonomies of learning levels
Bruner's
- Bruner (1966) distinguishes between passive and active learning, between what we know and what we do with what we know.
- He also presented a three stage learning model “which he calls enactive, iconic and symbolic and are solidly based on the developmental psychology of Jean Piaget. The first, the enactive level, is where the child manipulate materials directly. Then he proceed to the iconic level, where he deals with mental images of objects but does not manipulate them directly. At last he moves to the symbolic level, where he is strictly manipulating symbols and no longer mental images or objects. The optimum learning process should according to Bruner go through these stages.” (J.Bruner, retrieved 11:12, 26 June 2007 (MEST)).
Blooms taxonomy
In education, Blooms taxonomy of educational objectives is still the reference regarding detailed competencies that can be achieved through learning, i.e. that can be related to demonstrated skills (outcome-illustrating verbs). Firstly he distinguished among 3 broad categories:
- the Cognitive Domain
- the Affective Domain
- the Psychomotor Domain
Within the Cognitive Domain, Bloom defines 6 levels of intellectual behavior that are important for learning.
- Knowledge:
- Recall data or information
- Verbs: describe, identify, recall, arrange, define, duplicate, label, list, memorize, name, order, recognize, reproduce state.
- Comprehension:
- Understand the meaning of a problem, be able to translate into own words.
- Verbs: comprehend, give example, classify, describe, discuss, explain, express, identify, indicate, locate, recognize, report, restate, review, select, translate,
- Application:
- Use a concept in a new situation
- Verbs: apply, change, construct, compute, choose, demonstrate, dramatize, employ, illustrate, interpret, operate, practice, schedule, sketch, solve, use, write.
- Analysis:
- Can split concepts into parts and understands the structure
- Verbs: analyze, break down, relate, appraise, calculate, categorize, compare, contrast, criticize, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, examine, experiment, question, make inferences, find evidence, test.
- Synthesis:
- Produce something from different elements (e.g a report).
- Verbs: summarize, arrange, combine, categorize, assemble, collect, compose, construct, create, design, develop, formulate, manage, organize, plan, prepare, propose, set up, write.
- Evaluation:
- Make judgments, justify a solution, etc.
- Verbs: appraise, interpret, argue, assess, attach, compare, defend, estimate, judge, predict, rate, core, select, support, value, evaluate, prove, deduct.
This taxonomy allows to defined the desired learning level of a target audience and then to develop an appropriate design that will help the learner achieve this desired learning goal.
In addition, this taxonomy (not just this short summary) is useful to build behavioral assessment instruments. The "verbs" in the above tell give a hint on what an evaluator should observe.
- Example in use: Bloom's Taxonomy for Corrosion Training. This page shows how to apply Bloom's taxonomy to training levels in an engineering program.
Krathwohl's revised Taxonomy
Krathwohl (2002) (Access restricted), based on his original work with Bloom makes a distinction between the Knowledge Dimension and the cognitive process dimension.
The knowledge dimension (Krathwohl, 2002: 214)
- A. Factual Knowledge – The basic elements that students must know to be acquainted with a discipline or solve problems in it.
- Aa. Knowledge of terminology
- Ab. Knowledge of specific details and elements
- B. Conceptual Knowledge – The interrelationships among the basic elements within a larger structure that enable them to function together.
- Ba. Knowledge of classifications and categories
- Bb. Knowledge of principles and generalizations
- Bc. Knowledge of theories, models, and structures
- C. Procedural Knowledge – How to do something; methods of inquiry, and criteria for using skills, algorithms, techniques, and methods.
- Ca. Knowledge of subject-specific skills and algorithms
- Cb. Knowledge of subject-specific techniques and methods
- Cc. Knowledge of criteria for determining when to use appropriate procedures
- D. Metacognitive Knowledge – Knowledge of cognition in general as well as awareness and knowledge of one’s own cognition.
- Da. Strategic knowledge
- Db. Knowledge about cognitive tasks, including appropriate contextual and conditional knowledge
- Dc. Self-knowledge
The cognitive process dimension (Krathwohl, 2002: 215)
- 1.0 Remember – Retrieving relevant knowledge from long-term memory.
- 1.1 Recognizing
- 1.2 Recalling
- 2.0 Understand – Determining the meaning of instructional messages, including oral, written, and graphic communication.
- 2.1 Interpreting
- 2.2 Exemplifying
- 2.3 Classifying
- 2.4 Summarizing
- 2.5 Inferring
- 2.6 Comparing
- 2.7 Explaining
- 3.0 Apply – Carrying out or using a procedure in a given situation.
- 3.1 Executing
- 3.2 Implementing
- 4.0 Analyze – Breaking material into its constituent parts and detecting how the parts relate to one another and to an overall structure or purpose.
- 4.1 Differentiating
- 4.2 Organizing
- 4.3 Attributing
- 5.0 Evaluate – Making judgments based on criteria and standards.
- 5.1 Checking
- 5.2 Critiquing
- 6.0 Create – Putting elements together to form a novel, coherent whole or make an original product.
- 6.1 Generating
- 6.2 Planning
- 6.3 Producing
Filling in the following table allows to “classify objectives, activities, and assessments provides a clear, concise, visual representation of a particular course or unit.” (Krathwohl, 2002: 218)
| Cognitive process dimension | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge dimension | Remember | Understand | Apply | Analyze | Evaluate | Create |
| Factual | ||||||
| Conceptual | ||||||
| Procedural | ||||||
| Metacognitive | ||||||
Gagne's hierarchy
Gagne (1965 ?) also postulated a hierarchy of eight different learning types:
- signal learning
- learn how to respond to a signal, like Pavlov's dog
- stimulus-response learning
- learn precise responses to precise signals
- chaining
- learn to follow procedures
- be able to chain 2 or more stimulus-response
- verbal association
- use terminology in verbal chains
- discrimination learning
- learn how to distinguish between similar stimuli
- concept learning
- singular response to an entire class of stimuli
- principle learning
- learn to apply rules
- problem solving
On the basis of Bloom's taxonomy of learning, these levels were later, in the Conditions of Learning and Theory of Instruction (Gagné, 1985) reformulated as taxonomy of learning outcomes:
- Verbal information: reciting something from memory, e.g. recall a definition, tell a poem.
- Intellectual skills:
- Discrimination: Recognizing that two classes of things differ, e.g. be able to identify objects, features, symbols, etc. as not being the same.
- Concrete concept: Classifying things by their physical features alone, e.g. identify blue paintings, a symbol.
- Defined concept: Classifying new examples by their abstract (and possibly physical) features, e.g. a identify an assignement in a computer program.
- Rule: Applying a simple procedure (a single relationship) to solve a problem or accomplish a task, e.g. add two numbers.
- Higher-order rule: Applying a complex procedure (multiple rules) to solve a problem or accomplish a task, e.g. write a computer program
- Cognitive strategies: Inventing or selecting a particular mental process to solve a problem or accomplish a task
- Attitudes: Choosing to behave in a way that reflects a newly-acquired value or belief
- Motor skills: Performing a physical task to some specified standard
Within the intellectual skills group there is a learning hierarchy, e.g. rules can not be learned without mastering a defined concept. To prepare an instructional design for a given learning objective, one has to construct a learning hierarchy (sometimes called a task analysis) and ask "what are the intellectual skills one needs to have mastered in order to achieve an outcome ?" Since Gagne is also an instructional designer he formulated the "nine events of instruction" lesson design model that draws both from behaviorism (lower levels) and cognitivism (higher levels). An idea that has been taking up by many modern instructional design models is that teaching should transition from simple to complex skills. It should also be noted that outcomes can build on various components, e.g. a defined concept can build on facts (verbal information) and appropriate attitudes.
Deutscher Bildungsrat
Quoted in Mankel (2008, cited by Stary and Wichhart (2012):
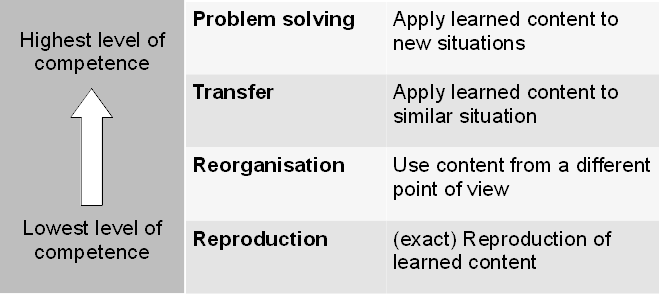
Levels of instruction
Mayes and Fowler model
In the context of usability of educational software, Mayes and Fowler (1999), present a simple three stage model that is popular in e-learning.
(1) Conceptualization
- refers to the users initial contact with other peoples concepts. This involves an interaction between the learner's pre-existing framework of understanding and a new exposition.
(2) Construction
- refers to the process of building and combining concepts through their use in the performance of meaningful tasks. Traditionally these were tasks like laboratory work, writing, preparing presentations etc. The results of such a process are products like essays, notes, handouts, laboratory reports and so on.
(3) Application
- the testing and tuning of conceptualizations through use in applied contexts. In education, however, as Laurillard (1993) has pointed out, the goal is testing of understanding, often of abstract concepts. This stage is best characterized in education, then, as dialogue. The conceptualizations are tested and further developed during conversation with both tutors and fellow learners and in the reflection on these. ([1])
This leads to the distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary courseware.
Merrill's Levels of Instructional Strategy
See Merrill's first principles of instruction for background information or Merrill (in press, 2006).
Critical variables are learning efficiency, effectiveness and engagement
- Level 0 Instructional Strategy -- Information Only
- Presentation of information.
- with or without accompanying recall questions
- Level 1 Instructiroviders need to be aware that a certain content and
problem solving structure correspondonal Strategy -- Information-only plus demonstration
- adds consistent demonstrations (portrayals) of scaled complex tasks.
- This will add some effectiveness and engagement under the condition that demonstrations use relevant contents and media (e.g. appropriate multimedia presentations).
- Level 2 Instructional Strategy -- Information-only plus demonstration plus application
- adds consistent application of scaled complex tasks with corrective feedback.
- In addition, application coaching should diminish gradually over time.
- Level 3 Instructional Strategy -- Task-centered with demonstration and application
- includes consistent demonstrations, application of all component skills.
- In addition, task progression will increase effectiveness, efficiency and engagement.
Jonassen's meaningful learning
For Jonassen (2007), the most meaningful kind of learning outcome, is problem-solving of which he distinguishes four kinds: planning problems, diagnosis-solution problems, policy analysis problems, and design problems (that latter include all the former).
Links
- Kearsley's TIP Explorations in Learning & Instruction: The Theory Into Practice Database
- This is one of the best sources on Learning Theory.
- Bloom's Taxonomy
- Learning Domains or Bloom's Taxonomy
- Major Categories in the Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (Bloom 1956)
- Robert Gagne
- Applying Learning Theories to Online Instructional Design
- The Taxonomy Of Educational Objectives
- Bloom's Taxonomy (Wikibooks)
Links
- Bloom's Taxonomy Visualizations Cheat Sheet (edVibes / G. Alex Ambrose, 2009)
- Gagne's Outcomes of Learning, part of Edward Vockell's Educational Psychology: A Practical Approach on-line book, retrieved 21:12, 3 October 2006 (MEST).
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, part of Edward Vockell's Educational Psychology: A Practical Approach on-line book, retrieved 21:12, 3 October 2006 (MEST).
- Bloom's Taxonomy and Critical Thinking, Barbara Fowler, Critical Thinking Accross the Curriculum Project.
- A., Dirks, C., & Wenderoth, M. (2008). Biology in bloom: implementing Bloom's taxonomy to enhance student learning in biology. Life Sciences Education, 7(4), 368. Traduction française de la [[Taxonomie_de_Bloom_adapt%C3%A9e_%C3%A0_la_Biologie Table 3 Traduction de la Table 1]
References
- Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (2001). A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: A revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of educational objectives. New York: Longman.
- Bloom Benjamin S. and David R. Krathwohl. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals, by a committee of college and university examiners. Handbook I: Cognitive Domain. New York, Longmans, Green, 1956. ISBN 0582280109
- Bruner, J. S. (1966). Toward a theory of instruction. Cambridge MA: The Belnap Press of Harvard University Press.
- Driscoll, M. (1991, 1994) Psychology of Learning for Instruction: Allyn and Bacon.
- Gagne, Robert M. (1975). Essentials of Learning for Instruction. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Gagne, Robert M. (1985). The Conditions of Learning and Theory of Instruction, Harcourt, ISBN 0030636884
- Gagne, Robert M., Briggs, Leslie, J., Wager, Walter, F. (1985). Principles of Instructional Design, Wadsworth, ISBN 0030347572
- Jonassen, D. H. (2007). A Taxonomy of Meaningful Learning. Educational Technology, 47(5), 30–35. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/44429440?seq=1#metadata_info_tab_contents
- Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). “A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy: An overview.” Theory into Practice 41(Autumn): 212–218.
- Leonard, W. Patrick (1975), Essay Review - Instructional Design: An Essay Review of Three Books, American Educational Research Journal, Vol. 12, No. 4. (Autumn, 1975), pp. 507-511. Abstract /PDF
- Laurillard, D (1993) Rethinking University Teaching. A framework for the effective use of educational technology, Routledge, London.
- Mayes, J.T. & Fowler, C.J.H. ( 1999) Learning Technology and Usability: a framework for understanding courseware. Interacting with Computers 11, 485-497doi:10.1016/S0953-5438(98)00065-4
- Merrill, M. D. (In Press). Levels of Instructional Strategy. Educational Technology (2006) [PDF Preprint]
- Merriënboer, Jeroen (1997). Training Complex Cognitive Skills: A Four-Component Instructional Design Model for Technical Training. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications.
- Wilson, Brent, G. (1997) Reflections on Constructivism and Instructional Design, Preprint for (C. R. Dills and A. A. Romiszowski (Eds.), Instructional Development Paradigms Englewood Cliffs NJ: Educational Technology Publications. HTML
- Stary, C., & Weichhart, G. (2012). An e-learning approach to informed problem solving. Knowledge Management & E-Learning: An International Journal (KM&EL), 4(2), 195-216. http://www.kmel-journal.org/ojs/index.php/online-publication/article/viewArticle/184
- Vockell, Edward, Educational Psychology: A Practical Approach, on-line book, HTML, retrieved 21:12, 3 October 2006 (MEST).
- Vockell, Edward, Educational Psychology: A Practical Approach Workbook, on-line bookHTML,retrieved 21:12, 3 October 2006 (MEST).