PHP tutorial - basics: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (→Links) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* Beginners | * Beginners | ||
; Remarks | ; Remarks | ||
* This is a first version ... | * This is a first version '''made from slides'''. Lot's of missing prose - [[User:Daniel K. Schneider|Daniel K. Schneider]] 19:24, 9 February 2010 (UTC). | ||
* '''Warning''': There may be mistakes in the code that you can copy/paste. Slides to wiki translation isn't working very well and needs manual fixing. Try using the associated files instead. | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 75: | ||
PHP code is defined within an XML processing instruction | PHP code is defined within an XML processing instruction | ||
< | <source lang="php"> | ||
<?php ..... ?> | |||
</source> | |||
For example: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
<?php | <?php | ||
| Line 139: | Line 143: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
== Elements of programming == | |||
: <center>'''Program= algorithm + data structures'''</center> | : <center>'''Program= algorithm + data structures'''</center> | ||
| Line 153: | Line 154: | ||
: Each instruction is ended with a ";" | : Each instruction is ended with a ";" | ||
: Comments // or #, or included within /* ... */ | : Comments // or #, or included within /* ... */ | ||
== Variables, data structures and assignments == | |||
=== Variables and assignments === | === Variables and assignments === | ||
| Line 258: | Line 261: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Summary - variables === | |||
You should, but don’t need to initialize varibales | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
$a = 1234; # decimal number | $a = 1234; # decimal number | ||
| Line 270: | Line 273: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Constants === | |||
Constants are "variables" with information that cannot change. | |||
: By convention, use capital letters. | |||
: '''Syntax''': | |||
define(<NAME>, <value>); | |||
: Do not use "$". | : Do not use "$". | ||
Examples: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
define("PI", 3.14); | define("PI", 3.14); | ||
| Line 288: | Line 294: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Result: | |||
Thanx for using our program | Thanx for using our program | ||
| Line 294: | Line 300: | ||
Je vous prie d’agréer, Madame, Monsieur, l’expression de nos sentiments dévoués. | Je vous prie d’agréer, Madame, Monsieur, l’expression de nos sentiments dévoués. | ||
== Simple expressions and operators == | |||
=== Arithmetic operators === | |||
Like normal math ... | |||
{| class="prettytable" | {| class="prettytable" | ||
| Line 330: | Line 337: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Example: | |||
: '''Application''' [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.php /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.php] | |||
:'''Source''' [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.phps /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.phps] | |||
:'''To copy''' [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.text /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.text] | |||
: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 364: | Line 355: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Assignment + addition in one step: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 371: | Line 362: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Operators for strings === | |||
'''concatenation of strings''' | For '''concatenation of strings''' use the "." operator | ||
Example: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 384: | Line 373: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Note: There are dozens of string manipulation functions in PHP !! | |||
Assignment + concatenation in one step: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 394: | Line 383: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Logical operators === | |||
| Line 401: | Line 390: | ||
| <center>'''name'''</center> | | <center>'''name'''</center> | ||
| <center>'''result'''</center> | | <center>'''result'''</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>$a and $b</center> | | <center>$a and $b</center> | ||
| <center>"and"</center> | | <center>"and"</center> | ||
| <center>result true, if $a et $b are true</center> | | <center>result true, if $a et $b are true</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>$a && $b</center> | | <center>$a && $b</center> | ||
| <center>"and"</center> | | <center>"and"</center> | ||
| <center>"</center> | | <center>"</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>$a or $b</center> | | <center>$a or $b</center> | ||
| <center>"or"</center> | | <center>"or"</center> | ||
| <center>result true, if $a or $b or both are true</center> | | <center>result true, if $a or $b or both are true</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>$a || $b</center> | | <center>$a <nowiki>||</nowiki> $b</center> | ||
| <center>"or"</center> | | <center>"or"</center> | ||
| <center> | | <center>(same)</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>$a xor $b</center> | | <center>$a xor $b</center> | ||
| <center>Or exclusive</center> | | <center>Or exclusive</center> | ||
| <center>result true, if $a or $b are true, but not both</center> | | <center>result true, if $a or $b are true, but not both</center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <center>! $a</center> | | <center>! $a</center> | ||
| <center>"not"</center> | | <center>"not"</center> | ||
| <center>result true, if $a is false(</center> | | <center>result true, if $a is false(</center> | ||
|} | |||
=== comparison === | |||
| Line 483: | Line 466: | ||
|} | |} | ||
: | : | ||
You can use parenthesis if you like to group operators ! | |||
: | |||
: [/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-compare.php | Some simple comparisons: | ||
: [/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-compare.phps | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-compare.php simple-compare.php] | ||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-compare.phps simple-compare.phps] | |||
: Note: in PHP each number equal or small than 0 is FALSE, each superior is TRUE | : Note: in PHP each number equal or small than 0 is FALSE, each superior is TRUE | ||
| Line 498: | Line 482: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
== Selection == | |||
(Conditions and tests) | |||
Principle (several typical situations): | Principle (several typical situations): | ||
| Line 506: | Line 492: | ||
: If a condition is true then do ... , else if an other condition is true do ... , else ...... | : If a condition is true then do ... , else if an other condition is true do ... , else ...... | ||
'''"IF" (several variants)''' | |||
: '''if''' (expr) statements | |||
: '''if''' (expr) ''statements'' '''else''' ''statements'' | |||
: '''if''' (''expr'') ''statements'' '''elseif''' (''expr'') ''statements'' else ... | |||
: '''if''' (expr) statements '''elseif''' (expr) statements [ '''elseif '''(expr) ... ] | |||
: | explanations: | ||
: <tt>''expr''</tt> = Expression must return TRUE or FALSE | : <tt>''expr''</tt> = Expression must return TRUE or FALSE | ||
: <tt>''statements ''</tt>= simple instructions or a block or instructions | : <tt>''statements ''</tt>= simple instructions or a block or instructions | ||
: simple: $a = 10; | : simple: $a = 10; | ||
: block: { $a =12; echo "salut"; ..... } | : block: { $a =12; echo "salut"; ..... } | ||
Execution model: | |||
: If expression = TRUE then execute statement(s) | : If expression = TRUE then execute statement(s) | ||
: If expression = FALSE then go to the next clause | : If expression = FALSE then go to the next clause | ||
'''Simple "if" example (comparison)''' | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-if.php simple-if.php] | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-if.phps simple-if.phps] '''(source)''' | |||
Compares two numbers: $a and $b, and displays a message. | |||
[[image:php-decision-tree.png|frame|none|Simple decision tree]] | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 545: | Line 535: | ||
See also the following: | See also the following contructs: | ||
: switch | : switch | ||
| Line 551: | Line 541: | ||
: do ... while | : do ... while | ||
: break and continue | : break and continue | ||
== PHP functions == | |||
Like all programming languages PHP allows to define procedures/functions. | |||
A function is a a mini program that has a name and that you can "call" (invoke). | |||
<center>[[Image:]]</center> | '''Principle''': "Hey, take that information, do something and (maybe) return the result" | ||
Usually, you will find function definition in the beginning of a program (or within include files) | |||
<center>[[Image:php-colormix-metaphor.png]]</center> | |||
'''Color mixing for paint example''' | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/ http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/] (files color-mix.*)''' | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/ http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/] (files color-mix.*)''' | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 591: | Line 583: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
'''HTML generation with functions example''': | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.php /guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.php] | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.php /guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.php] | ||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.phps /guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.phps] | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.phps /guides/php/examples/simple/function-demo.phps] | ||
| Line 599: | Line 591: | ||
// html formats a data element | // html formats a data element | ||
function pretty_print ($output) { | |||
separator (); | separator (); | ||
echo "<p align='center'> <strong>ELEMENT:</strong> $output </p>"; | echo "<p align='center'> <strong>ELEMENT:</strong> $output </p>"; | ||
} | } | ||
// outputs a separator | // outputs a separator | ||
function separator () { | |||
echo "<hr size=4 width=70%>"; | echo "<hr size=4 width=70%>"; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 612: | Line 604: | ||
$el3 = "A yellow sky"; | $el3 = "A yellow sky"; | ||
// dump the data | // dump the data | ||
pretty_print($el1); | |||
pretty_print($el2); | |||
pretty_print($el3); | |||
separator (); | |||
echo "<hr>"; | echo "<hr>"; | ||
?> | ?> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
== Loops (iterations) == | |||
'''The "for loop" syntax''' | '''The "for loop" syntax''' | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
FOR (expr1; expr2; expr3) statement | FOR (expr1; expr2; expr3) statement | ||
| Line 632: | Line 625: | ||
: expr3 is evaluated at the end of each loop, | : expr3 is evaluated at the end of each loop, | ||
: statement is executed for each loop. | : statement is executed for each loop. | ||
: ''' | |||
: | : <tt>'''$i'''</tt> is used as so-called iteration variable. At start $i = 1 or 2. | ||
Love generation example: | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.php /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.php] (program) | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.phps /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.phps] (source) | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 641: | Line 637: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Result: | |||
I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! ...... | |||
Here is a slightly more complex one: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
echo "Je t’aime plus que toi.<br> | echo "Je t’aime plus que toi.<br> | ||
| Line 650: | Line 649: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Result: | |||
Je t’aime plus que moi. | Je t’aime plus que moi. | ||
Non, je t’aime 2 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 3 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 4 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 5 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 6 ..... | |||
Non, je t’aime 2 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 3 fois plus que moi ! Non, | |||
je t’aime 4 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 5 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 6 | |||
..... | |||
Other PHP elements: | Other PHP elements: | ||
: <tt>echo</tt> | : <tt>echo</tt> | ||
: <tt>print</tt> works like print. | : <tt>print</tt> works like print. | ||
'''Generation of html tables example''' | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.php /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.php] | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.phps /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.phps] | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.text /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.text] | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
$love_list = array ("a lot", "a bit", "somewhat", "à mourir", "forever", "until notice", "more than I love my dog"); | |||
<table border align="center"> | <table border align="center"> | ||
<? | <? | ||
// define a function to generate a table | // define a function to generate a table | ||
function build_table($list) { | function build_table($list) { | ||
for ($i=0; $i < sizeof($list); $i++) { | |||
$love_text = $list[$i]; | $love_text = $list[$i]; | ||
echo "<tr> <td> ... I love you</td> <td>$love_text</td>"; | echo "<tr> <td> ... I love you</td> <td>$love_text</td>"; | ||
| Line 678: | Line 679: | ||
// call the function, generate the table | // call the function, generate the table | ||
build_table($love_list); | build_table($love_list); | ||
?> | ?> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 684: | Line 685: | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
: PHP is used | : PHP is used within the HTML <nowiki><table></nowiki> element | ||
: The <tt>'''build_table'''</tt> function is called with an array | : The <tt>'''build_table'''</tt> function is called with an array | ||
: There exist more looping constructs in PHP (like while or for-each) ! | : There exist more looping constructs in PHP (like while or for-each) ! | ||
== Practical advice == | |||
=== Debugging === | |||
(1) Look at the generated HTML code "View Source") | |||
(2) Insert ''phpinfo()'' in your PHP file (will give you lots of information, e.g. about PHP installation, its environment, variables passed to script from the server, etc.) | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 696: | Line 701: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
(3) Insert print statements! | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 703: | Line 708: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
(4) Raise "error reporting" to its maximum ! Insert this on top: | |||
<source lang="php"> | |||
error_reporting(E_ALL); | |||
</source> | |||
(5) Know where your server / php log files are | |||
In some configurations, php error messages and notices are not displayed on the rendered web page. You will have to find these in the log files or the server. Check the settings of the ''php.ini'' file to find out. | |||
(6) Portals | |||
Warning: NEVER insert blank lines at start or end of a file ! Most files should stop like this (no line feed !!) | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
?> | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
: ... because PHP starts producing HMTL headers as soon as it sees a little blank space before or after php code <nowiki><?php .... ?></nowiki> | |||
== HTML forms processing with PHP == | |||
=== Forms processing with PHP I === | |||
'''Simple quiz and POST to a php file''' | |||
:[http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire.html /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire.html] | |||
:Source: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire.text /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire.text] | |||
This example shows: | |||
* how to treat and HTML form | |||
* how to compute and display a result. | |||
[[image:html-form-php-script.png|frame|none|HTML form and a php script]] | |||
'''Part of the HTML form:''' | '''Part of the HTML form:''' | ||
<source lang=" | <source lang="html4strict"> | ||
<form | <form action="calcul.php" method="post"> | ||
Quelles sont vos connaissances de HTML ? | Quelles sont vos connaissances de HTML ? | ||
<input type="radio" | <input type="radio" name="choice" value="1" checked>faibles | ||
<input type="radio" name="choice" value="2">moyennes | <input type="radio" name="choice" value="2">moyennes | ||
<input type="radio" name="choice" value="3">bonnes | <input type="radio" name="choice" value="3">bonnes | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Indiquez votre expertise en programmation: | Indiquez votre expertise en programmation: | ||
<input type="radio" | <input type="radio" name="choice2" value="1" checked>absente | ||
<input type="radio" name="choice2" value="2">moyenne | <input type="radio" name="choice2" value="2">moyenne | ||
<input type="radio" name="choice2" value="3">bonne | <input type="radio" name="choice2" value="3">bonne | ||
| Line 749: | Line 762: | ||
<center>[[Image:]]</center> | <center>[[Image:]]</center> | ||
'''Retrieve values of an HTML form''' | |||
Data from a form a stored by the server in a so-called super global variables | |||
: POST: values are | |||
Use $_POST to deal with POST variables | |||
: POST: values are attached to the HTML request (and not visible to the user) | |||
Use $_GET for GET variables | |||
: GET: values are handed over in the URL string (user can see these) | : GET: values are handed over in the URL string (user can see these) | ||
You can use the "name" attribute of the form to retrieve values | |||
In our example, we use $_POST: | In our example, we use $_POST: | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
$choice = $_POST[ | $choice = $_POST['choice']; | ||
$choice2 = $_POST[ | $choice2 = $_POST['choice2']; | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
We now have two PHP variables: $choice and $choice2 | |||
'''Computing and display of results''' | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/calcul.phps /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/calcul.phps] | |||
We add the the two values and compute a summary result with an if clause. | |||
<source lang="php"> | |||
<?php | |||
// Get values from the form | // Get values from the form | ||
$choice = $_POST[ | $choice = $_POST['choice']; | ||
$choice2 = $_POST[ | $choice2 = $_POST['choice2']; | ||
// Compute score | // Compute score | ||
| Line 788: | Line 805: | ||
} | } | ||
?> | ?> | ||
</source> | |||
'''Inhibit direct access to PHP (without data)''' | |||
: (1) if (isset($_POST['choice'])) then { ..... } else { echo "sorry ......."; } | |||
: (2) Alternative: if (!isset($_POST['choice'])) {echo "sorry"; exit; } | |||
=== Forms processing with PHP II === | |||
(Checkboxes with PHP - arrays) | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.text /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.text] | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.html /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.html] | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.text /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.text] | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.html /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.html] | |||
'''Part of the HTML code:''' | '''Part of the HTML code:''' | ||
<source lang=" | <source lang="html4strict"> | ||
<form action=" | <form action="calcul4.php" method=post> | ||
Quels sont vos couleurs préféres? | Quels sont vos couleurs préféres? | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<input type=" | <input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Red">Red | ||
<table bgcolor="red" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | <table bgcolor="red" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | ||
<input type="checkbox" | <input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Blue">Blue | ||
<table bgcolor="blue" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | <table bgcolor="blue" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | ||
<input type="checkbox" | <input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Green">Green | ||
<table bgcolor="green" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | <table bgcolor="green" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | ||
..... | ..... | ||
<input type="checkbox" | <input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Black">Black | ||
<table bgcolor="black" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | <table bgcolor="black" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table> | ||
| Line 822: | Line 844: | ||
'''PHP code:''' | '''PHP code:''' | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
<?php | <?php | ||
$choice = $_POST[ | $choice = $_POST['choice']; | ||
echo("<h3>Vos couleurs préférées sont </h3>"); | echo("<h3>Vos couleurs préférées sont </h3>"); | ||
for ($i=0;$i<sizeof($choice);$i++) { | for ($i=0;$i<sizeof($choice);$i++) { | ||
if (isset( | if (isset($choice[$i])) { | ||
echo(" | echo("$choice[$i] - "); | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 838: | Line 859: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== All in one solution === | |||
You can put both the form and the processing code in a single php page. In this case, test if the file is called with data from a form or through a link/a navigator. See the variable''$process'' below | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
<?php | <?php | ||
if (!isset($_POST[ | if (!isset($_POST['process'])) { | ||
?> | ?> | ||
//... lets display the form) | //... lets display the form) | ||
<FORM METHOD="POST" ACTION="<? echo $PHP_SELF ?>"> | |||
</FORM> | |||
<?php | |||
} else {''' | } else {''' | ||
//... we got data, so let’s process | //... we got data, so let’s process | ||
} | |||
?> | ?> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== Polishing === | |||
To test if we have all the POST/GET variables, we may use two methods to see what we have in $_POST or $_GET: | |||
: | : array_key_exists() | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
if (array_key_exists( | if (array_key_exists('first', $_POST)) { .... do something ...}; | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
: | : isset() | ||
: to see if a variable exists: | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
if (isset($POST[ | if (isset($POST['first']) ) { .... do ....} | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
The difference is that: | |||
: array_key_exists returns TRUE if value is NULL | : array_key_exists returns TRUE if value is NULL | ||
: isset returns FALSE if value is NULL. | : isset returns FALSE if value is NULL. | ||
| Line 882: | Line 903: | ||
'''ATTENTION, to test <input type="text"> you also may want to test if there is an empty string.''' | '''ATTENTION, to test <input type="text"> you also may want to test if there is an empty string.''' | ||
: | : empty() | ||
: to decide if user filled in a text field | : to decide if the user filled in a text field | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 890: | Line 911: | ||
: empty() returns TRUE if a value is: "", 0, "0", NULL, FALSE, array(), .... | : empty() returns TRUE if a value is: "", 0, "0", NULL, FALSE, array(), .... | ||
=== Session management === | |||
PHP has session support (can keep variables over a whole user session). | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/sessions/ http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/sessions/] | * Each visitor gets an identifier (a "sessions id"). It is stored in a cookie (in the www client) or within the URL. | ||
* This information is available in super global: $_SESSION | |||
'''Restrict repetitive access to a page example:''' | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/sessions/ http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/sessions/] | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
session_start(); | session_start(); | ||
if (!isset($_SESSION[ | if (!isset($_SESSION['count'])) { | ||
$_SESSION[ | $_SESSION['count'] = 0; | ||
} else { | } else { | ||
$_SESSION[ | $_SESSION['count']++; | ||
} | } | ||
if ($_SESSION[ | if ($_SESSION['count'] > 2) { | ||
echo | echo '<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">'; | ||
echo "<html> <body>"; | echo "<html> <body>"; | ||
echo "Sorry | echo "Sorry it's over you can't do it twice"; | ||
echo "</body> </html>"; | echo "</body> </html>"; | ||
exit; | exit; | ||
| Line 914: | Line 940: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
=== On-line surveys and file-based storage === | |||
This is a simple code that shows how to collect survey data. | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/form-file-demo/ http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/form-file-demo/] | |||
: new-entry.php contains the form and code | : new-entry.php contains the form and code | ||
: dump_results.php shows file contents | : dump_results.php shows file contents | ||
'''The HTML form''': | |||
This time we use PHP to generate the HTML code | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 957: | Line 986: | ||
$try = touch($file_name); | $try = touch($file_name); | ||
if (!$try) { | if (!$try) { | ||
echo "<p>Sorry I | echo "<p>Sorry I can't open a file, something is wrong"; | ||
exit; | exit; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 967: | Line 996: | ||
// note that we add a \n (line break) to the end of the string. | // note that we add a \n (line break) to the end of the string. | ||
$output_line = implode ($input, " ")."\n"; | $output_line = implode ($input, " ")."\n"; | ||
// Now open the file (get a file pointer) | // Now open the file (get a file pointer) | ||
| Line 989: | Line 1,015: | ||
<? | <? | ||
// EXIT here ... we | // EXIT here ... we don't want to see the form again. If you do, kill the exit | ||
exit; | exit; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 1,000: | Line 1,026: | ||
fopn (<file name>, "a") | fopn (<file name>, "a") | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
: to open a file and then append. | : to open a file and then append. | ||
| Line 1,006: | Line 1,031: | ||
fputs(<handle>, “string”) | fputs(<handle>, “string”) | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
: to write to a file | : to write to a file | ||
: WARNING: This will attract spammers !! | : WARNING: This will attract spammers !! | ||
'''Dump contents of a file''' | |||
.... we just insert it a <pre> with an “include” | .... we just insert it a <pre> with an “include” | ||
<source lang="html4strict"> | |||
<source lang=" | |||
<BODY> | <BODY> | ||
<H1>PHP/MySQL Demo - Dump Database Contents</H1> | <H1>PHP/MySQL Demo - Dump Database Contents</H1> | ||
<? | <? | ||
/* Daniel.Schneider@tecfa.unige.ch | /* Daniel.Schneider@tecfa.unige.ch | ||
| Line 1,033: | Line 1,055: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
'''Important:''' | |||
''' | : Use "readfile", and not "include" or "require", '''else you will get hacked '''!! | ||
=== Other formats than HTML === | |||
PHP supports any other format. By default a PHP script starts creating an HTML script as soon as it encounters and HTML section or an echo/print/etc. instruction. | |||
: | Principle: Before '''any other output in your program''', you have to define the content-type (e.g. put this into the first line). | ||
'''Example binary pictures''' | |||
<source lang="php"> | |||
Header("Content-type: image/gif"); | |||
</source> | |||
'''Example XML''' | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
| Line 1,049: | Line 1,077: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
'''Example SVG''' | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
Header("Content-type: image/svg+xml"); | Header("Content-type: image/svg+xml"); | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
'''Example RDF''' | |||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
Header("Content-type: application/rdf+xml"); | Header("Content-type: application/rdf+xml"); | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
'''Generate some simple XML example ''' | |||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.php http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.php] | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.php http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.php] | ||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.phps http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.phps] | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.phps http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.phps] | ||
: [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.css http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.css] | : [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.css http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.css] | ||
<source lang="php"> | <source lang="php"> | ||
<?php | <?php | ||
header("Content-type: text/xml"); | |||
print('<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>' . "\n"); | |||
print('<?xml-stylesheet href="simple-calcul-xml.css" type="text/css" ?>'); | |||
$leisure_satisfaction = 5; $work_satisfaction = 7; $family_satisfaction = 8; | $leisure_satisfaction = 5; $work_satisfaction = 7; $family_satisfaction = 8; | ||
$index = ($leisure_satisfaction + $work_satisfaction + $family_satisfaction) / 3 ; | $index = ($leisure_satisfaction + $work_satisfaction + $family_satisfaction) / 3 ; | ||
echo " | echo "<resultat> Satisfaction Index = $index </resultat>"; | ||
?> | ?> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
== Links == | |||
* [https://websitesetup.org/php-cheat-sheet/ PHP Cheat sheet] at websitesetup.org (retrieved July 2020) | |||
[[category: PHP]] | |||
Latest revision as of 23:14, 30 June 2020
Introduction
- Learning goals
- Be able to make modifications in a PHP file (in particular configuration files)
- Prerequisites
- Some HTML and XHTML, i.e. HTML and XHTML elements and attributes
- Moving on
- Level and target population
- Beginners
- Remarks
- This is a first version made from slides. Lot's of missing prose - Daniel K. Schneider 19:24, 9 February 2010 (UTC).
- Warning: There may be mistakes in the code that you can copy/paste. Slides to wiki translation isn't working very well and needs manual fixing. Try using the associated files instead.
PHP standards for Hypertext Preprocessor
History:
- Personal Home Page Generator (Php2/FI) in the mid-nineties
- PHP 3 since 1997,
- PHP 4 since 1999,
- PHP 5 since 2004/2005
Since PHP 3.0, the language is used to write larger web applications. PHP Version 3.0 was defined as HTML-embedded scripting language. Much of its syntax is borrowed from C, Java and Perl with a couple of unique PHP-specific features thrown in. The goal of the language is to allow web developers to write dynamically generated pages quickly. This definition remains the same in the PHP 5 FAQ.
Principle:
- Analogy with JavaScript: PHP code can be mixed with HTML
- BUT: The server reads the files and computes it (and end-user never can see the code)
- Servers are configured to read *.php files as PHP (sometimes also *.php3, *.php4 etc.)
Purpose:
- Create dynamic web pages (small applications) or program larger web applications
Links:
- See PHP links
PHP features
Availability:
- Free and open source (GPL)
- cross-platform (Unix, Linux, BSD, MacOS X, Win32, etc.)
Installation:
- can run as CGI program (external to a web server)
- can run as web server module (this is the standard case, e.g. with the Apache server)
- can be used as command-line scripting engine
Highlights:
- good database support (Oracle, Sybase, Microsoft, MySQL, Postgres, ODBC, etc.)
- good system integration (files)
- complete programming language, including OO support
- easy to learn
- made for internet application (cookies, authentication, sessions, redirection...)
- dozens of integrated libraries (LDAP, PDF, XML, GIF,...)
- support for object-oriented programming since PHP 4 (PHP 5 introduced a new model)
Alternatives to PHP:
- ASP (Microsoft)
- JSP (Java)
- Cold Fusion (Adobe)
HTML and PHP integration
PHP code is defined within an XML processing instruction
<?php ..... ?>
For example:
<?php
echo("if you want to serve XML documents, do like this\n");
?>
File inclusion
Let's now introduce our first PHP code. PHP code can be spread over many files (hundreds or thousands in some larger applications).
Include:
inserts content of file when this expression is evaluated
- include ("file name");
include("style.php");
Require:
inserts content of file when the php file is loaded
- require ("file name");
require("my_functions.inc");
Variant (recommended):
include_once() and require_once().
Only include once, will make your application faster.
File inclusion example
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Simple Include Demo (21-Apr-1998)</TITLE>
<?php include("style.text"); ?>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1>Simple Include Demo</H1>
In this file we include a <A HREF="style.text">style sheet</A> and
a <A HREF="footer.text">footer</A>.
<P>
Look at <A HREF="include1.phps">the formatted source</A>
or the <A HREF="include1.source">unformatted one</A>
if you want to know how this is done.
<H1>Yet another styled title</H1>
<UL>
<LI> bullet item </LI>
<LI> bullet item </LI>
</UL>
<?php
/* A footer */
include("footer.text");
?>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Elements of programming
Program= algorithm + data structures
PHP syntax overview:
PHP looks like "C" (C, C++, Java, Perl, etc.)
- Each instruction is ended with a ";"
- Comments // or #, or included within /* ... */
Variables, data structures and assignments
Variables and assignments
Variables are “containers” for information.
- Each identifier with a $ in front is a variable
- Variables don’t need to be declared
- Assignment operator: =
Principle:
$variable = "content" ;
Illustrations:
$a = 10; $name = "Patrick Ott"; $sum = 123.456;
Using variables with content strings example:
- /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-echo.php (application)
- /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-echo.phps (pretty source)
- /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-echo.text (source)
<BODY>
<H1>Simple Echo of variables with PHP</H1>
<?php
$a = 10;
$nom = "Patrick Ott";
$somme = 123.456;
echo "Le nommé $nom a $somme francs dans la poche, mais il voudrait $a fois plus.";
?>
<p><hr>
</BODY>
- echo is an “instruction” to display a string (chain of characters)
- Note: all the $xxx are replaced by their contents !
Simple arrays
- Arrays are a sort of lists (several values within the same variable)
Array creation - method 1:
$numbers[] =1; $numbers[] =2; $numbers[] =3; $numbers[] =4;
Array creation - method 2:
$numbers = array (1, 2, 3, 4);
$names = array ("Pat", "Dave", "Surf", "K");
Use of simple arrays:
$array[index]
Index starts at 0 ! (zero). Example:
echo "Second element of $names is: $names[1];
Example: Simple variables and some HTML generation
<?php
// Some simple HTML
echo"<h1>Simple arrays</h1>";
$utilisateur = "cher étudiant";
$no_utilisateur = 3;
$numbers = array (1, 2, 3, 4);
$names = array ("Pat", "Dave", "Surf", "K");
$names[] = "Zorro";
// Note html <br> tag
echo "Salut $utilisateur. Vous êtes le numéro $no_utilisateur.<br>";
// echo with concatenation, use it to print complex things
echo "La quatrième personne s’appelle " . $names[3] ." ";
// simple echo
echo "et la cinquième personne s’appelle $names[4].<p>";
$n = sizeof($numbers);
// note that we have to use \ in order to print a $ !
echo "We have $n numbers in array \$numbers.";
?>
Associative arrays and multi-dimensional tables
$fruits = array(
"fruits" => array("a"=>"orange","b"=>"banana","c"=>"apple"),
"numbers" => array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
"holes" => array("first", 5 => "second", "third")
);
Summary - variables
You should, but don’t need to initialize varibales
$a = 1234; # decimal number
$a = -123; # a negative number
$a = 1.234; $a = 1.2e3; # floating point number
$str = "This is a string"; # string
$a[0] = "abc"; # element zero of un array
$a[1] = "def"; # element 1 of an array
$b["foo"] = 13; # element "foo" of an array
Constants
Constants are "variables" with information that cannot change.
- By convention, use capital letters.
- Syntax:
define(<NAME>, <value>);
- Do not use "$".
Examples:
define("PI", 3.14);
define("REMERCIEMENTS", "Thanx for using our program<br>");
define("SALUTATIONS", "Je vous prie d’agréer, Madame, Monsieur, l’expression de nos sentiments dévoués");
$radius = 12;
$perimeter = 2 * $radius * PI;
echo REMERCIEMENTS;
echo "le périmètre du cercle is de " . $perimeter . "<br>";
echo SALUTATIONS;
Result:
Thanx for using our program le périmètre du cercle is de 77.76 Je vous prie d’agréer, Madame, Monsieur, l’expression de nos sentiments dévoués.
Simple expressions and operators
Arithmetic operators
Like normal math ...
Example:
- Application /guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul.php
$leisure_satisfaction = 5;
$work_satisfaction = 7;
$family_satisfaction = 8;
$index = ($leisure_satisfaction + $work_satisfaction + $family_satisfaction)
/ 3 ;
echo "<p align=center> Satisfaction Index = $index <b>";
Assignment + addition in one step:
// sets $a to 8, as if we had said: $a = $a + 5;
$a += 5;
Operators for strings
For concatenation of strings use the "." operator
Example:
$a = "Hello ";
$b = $a . "World!"; // now $b = "Hello World!"
Note: There are dozens of string manipulation functions in PHP !!
Assignment + concatenation in one step:
$b = "Hello ";
// sets $b to "Hello There!", just like $b = $b . "There!";
$b .= "There!";
Logical operators
comparison
You can use parenthesis if you like to group operators !
Some simple comparisons:
- simple-compare.php
- simple-compare.phps
- Note: in PHP each number equal or small than 0 is FALSE, each superior is TRUE
$a = "Migros";
$b = "Coop";
$result = $a==$b;
$result2 = $a > $b;
$result3 = $result==TRUE;
echo "Result One = $result. Result TWO = $result2. Result THREE = $result3.";
Selection
(Conditions and tests)
Principle (several typical situations):
- If a condition is true then do ...
- If a condition is true then do ... , else do .....
- If a condition is true then do ... , else if an other condition is true do ... , else ......
"IF" (several variants)
- if (expr) statements
- if (expr) statements else statements
- if (expr) statements elseif (expr) statements else ...
- if (expr) statements elseif (expr) statements [ elseif (expr) ... ]
explanations:
- expr = Expression must return TRUE or FALSE
- statements = simple instructions or a block or instructions
- simple: $a = 10;
- block: { $a =12; echo "salut"; ..... }
Execution model:
- If expression = TRUE then execute statement(s)
- If expression = FALSE then go to the next clause
Simple "if" example (comparison)
- simple-if.php
- simple-if.phps (source)
Compares two numbers: $a and $b, and displays a message.
<?php
$a = 10; $b = 11;
print "a was $a, b was $b. ";
if ($a > $b) {
print "a is bigger than b";
} elseif ($a == $b) {
print "a is equal to b";
} else {
print "==> a is smaller than b.";
}
?>
See also the following contructs:
- switch
- foreach
- do ... while
- break and continue
PHP functions
Like all programming languages PHP allows to define procedures/functions. A function is a a mini program that has a name and that you can "call" (invoke).
Principle: "Hey, take that information, do something and (maybe) return the result"
Usually, you will find function definition in the beginning of a program (or within include files)
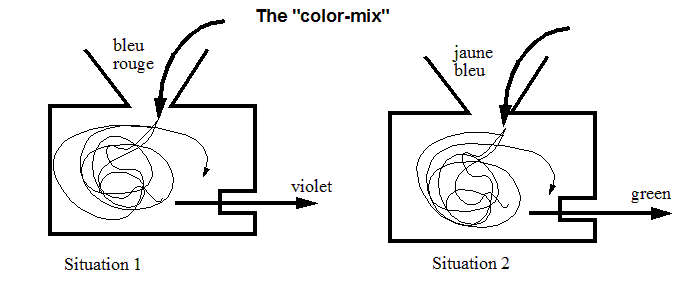
Color mixing for paint example
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/ (files color-mix.*)
function color_mix($color1,$color2) {
$result= "unknown";
if ($color1 == "bleu" and $color2 == "rouge") {
$result = "violet"; }
elseif ($color1 == "jaune" and $color2 == "bleu") {
$result = "green"; }
elseif ($color1 == "noire" and $color2 == "blanc") {
$result = "gris"; }
else {
$result = "orange"; }
return $result;
}
// Two calls to this function, results saved in variables
$situation1 = color_mix ("bleu", "rouge") ;
$situation2 = color_mix ("jaune", "bleu") ;
// Print
echo "Bleu et rouge donne $situation1 <br>";
echo "Jaune et bleu donne $situation2";
HTML generation with functions example:
<?php
// html formats a data element
function pretty_print ($output) {
separator ();
echo "<p align='center'> <strong>ELEMENT:</strong> $output </p>";
}
// outputs a separator
function separator () {
echo "<hr size=4 width=70%>";
}
// data we have
$el1 = "Un arbre jaune";
$el2 = "Ein gelber Hund";
$el3 = "A yellow sky";
// dump the data
pretty_print($el1);
pretty_print($el2);
pretty_print($el3);
separator ();
echo "<hr>";
?>
Loops (iterations)
The "for loop" syntax
FOR (expr1; expr2; expr3) statement
- expr1 is evaluated at start
- expr2 is evaluated at start of each loop,if result = TRUE the loop will continue, else it will stop
- expr3 is evaluated at the end of each loop,
- statement is executed for each loop.
- $i is used as so-called iteration variable. At start $i = 1 or 2.
Love generation example:
- /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.php (program)
- /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.phps (source)
for ($i=1; $i<=10; $i++) {
print "I love you so ! "; }
Result:
I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! I love you so ! ......
Here is a slightly more complex one:
echo "Je t’aime plus que toi.<br>
for ($i=2; $i<=10; $i++) {
echo "Non, je t’aime $i fois plus que toi ! ";
}
Result:
Je t’aime plus que moi.
Non, je t’aime 2 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 3 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 4 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 5 fois plus que moi ! Non, je t’aime 6 .....
Other PHP elements:
- echo
- print works like print.
Generation of html tables example
- /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.php
- /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.phps
- /guides/php/examples/html-generate/love.text
$love_list = array ("a lot", "a bit", "somewhat", "à mourir", "forever", "until notice", "more than I love my dog");
<table border align="center">
<?
// define a function to generate a table
function build_table($list) {
for ($i=0; $i < sizeof($list); $i++) {
$love_text = $list[$i];
echo "<tr> <td> ... I love you</td> <td>$love_text</td>";
}
}
// call the function, generate the table
build_table($love_list);
?>
</table>
Note:
- PHP is used within the HTML <table> element
- The build_table function is called with an array
- There exist more looping constructs in PHP (like while or for-each) !
Practical advice
Debugging
(1) Look at the generated HTML code "View Source")
(2) Insert phpinfo() in your PHP file (will give you lots of information, e.g. about PHP installation, its environment, variables passed to script from the server, etc.)
phpinfo();
(3) Insert print statements!
echo "DEBUG: \$var = $var";
echo "TEST: var = $var";
(4) Raise "error reporting" to its maximum ! Insert this on top:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
(5) Know where your server / php log files are
In some configurations, php error messages and notices are not displayed on the rendered web page. You will have to find these in the log files or the server. Check the settings of the php.ini file to find out.
(6) Portals
Warning: NEVER insert blank lines at start or end of a file ! Most files should stop like this (no line feed !!)
?>
- ... because PHP starts producing HMTL headers as soon as it sees a little blank space before or after php code <?php .... ?>
HTML forms processing with PHP
Forms processing with PHP I
Simple quiz and POST to a php file
- /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire.html
- Source: /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire.text
This example shows:
- how to treat and HTML form
- how to compute and display a result.
Part of the HTML form:
<form action="calcul.php" method="post">
Quelles sont vos connaissances de HTML ?
<input type="radio" name="choice" value="1" checked>faibles
<input type="radio" name="choice" value="2">moyennes
<input type="radio" name="choice" value="3">bonnes
<br>
Indiquez votre expertise en programmation:
<input type="radio" name="choice2" value="1" checked>absente
<input type="radio" name="choice2" value="2">moyenne
<input type="radio" name="choice2" value="3">bonne
<P>
<input type="submit" value="Voir le result!">
</form>
Retrieve values of an HTML form
Data from a form a stored by the server in a so-called super global variables
Use $_POST to deal with POST variables
- POST: values are attached to the HTML request (and not visible to the user)
Use $_GET for GET variables
- GET: values are handed over in the URL string (user can see these)
You can use the "name" attribute of the form to retrieve values
In our example, we use $_POST:
$choice = $_POST['choice'];
$choice2 = $_POST['choice2'];
We now have two PHP variables: $choice and $choice2
Computing and display of results
We add the the two values and compute a summary result with an if clause.
<?php
// Get values from the form
$choice = $_POST['choice'];
$choice2 = $_POST['choice2'];
// Compute score
$score = $choice + $choice2;
// Compute message as function of result
echo "<h3>Votre score is de " . $score . "</h3>";
if ($score < 3) {
echo "<p>Vous êtes un débutant</p>";
} elseif ($score < 5) {
echo "<p>Vous avez un niveau moyen</p>";
} else {
echo "<p>Vous êtes un expert !</p>";
}
?>
Inhibit direct access to PHP (without data)
- (1) if (isset($_POST['choice'])) then { ..... } else { echo "sorry ......."; }
- (2) Alternative: if (!isset($_POST['choice'])) {echo "sorry"; exit; }
Forms processing with PHP II
(Checkboxes with PHP - arrays)
- /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.text
- /guides/php/examples/simple-calculate/formulaire4.html
Part of the HTML code:
<form action="calcul4.php" method=post>
Quels sont vos couleurs préféres?
<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Red">Red
<table bgcolor="red" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table>
<input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Blue">Blue
<table bgcolor="blue" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table>
<input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Green">Green
<table bgcolor="green" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table>
.....
<input type="checkbox" name="choice[]" value="Black">Black
<table bgcolor="black" width="50"><tr><td> </td></tr></table>
<input type="submit" value="Voir le result!">
</form>
- Remember the syntax to put all values into an array: "choice[]"
PHP code:
<?php
$choice = $_POST['choice'];
echo("<h3>Vos couleurs préférées sont </h3>");
for ($i=0;$i<sizeof($choice);$i++) {
if (isset($choice[$i])) {
echo("$choice[$i] - ");
}
}
?>
All in one solution
You can put both the form and the processing code in a single php page. In this case, test if the file is called with data from a form or through a link/a navigator. See the variable$process below
<?php
if (!isset($_POST['process'])) {
?>
//... lets display the form)
<FORM METHOD="POST" ACTION="<? echo $PHP_SELF ?>">
</FORM>
<?php
} else {'''
//... we got data, so let’s process
}
?>
Polishing
To test if we have all the POST/GET variables, we may use two methods to see what we have in $_POST or $_GET:
- array_key_exists()
if (array_key_exists('first', $_POST)) { .... do something ...};
- isset()
- to see if a variable exists:
if (isset($POST['first']) ) { .... do ....}
The difference is that:
- array_key_exists returns TRUE if value is NULL
- isset returns FALSE if value is NULL.
ATTENTION, to test <input type="text"> you also may want to test if there is an empty string.
- empty()
- to decide if the user filled in a text field
if (empty ($input) ) { ... complain ... } else { ... do ...}
- empty() returns TRUE if a value is: "", 0, "0", NULL, FALSE, array(), ....
Session management
PHP has session support (can keep variables over a whole user session).
- Each visitor gets an identifier (a "sessions id"). It is stored in a cookie (in the www client) or within the URL.
- This information is available in super global: $_SESSION
Restrict repetitive access to a page example:
session_start();
if (!isset($_SESSION['count'])) {
$_SESSION['count'] = 0;
} else {
$_SESSION['count']++;
}
if ($_SESSION['count'] > 2) {
echo '<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">';
echo "<html> <body>";
echo "Sorry it's over you can't do it twice";
echo "</body> </html>";
exit;
}
// .... continue code with access time = 1 and 2
On-line surveys and file-based storage
This is a simple code that shows how to collect survey data.
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/form-file-demo/
- new-entry.php contains the form and code
- dump_results.php shows file contents
The HTML form:
This time we use PHP to generate the HTML code
$scales = array("food", "work", "love", "leisure", "sports");
function scale ($thing) {
echo "<TR> <TD align=right>Importance of <STRONG>$thing</STRONG>:</TD>";
echo "<TD><select name=$thing>";
echo "<option value=1>1 - totally unimportant";
echo "<option value=2>2 - not important";
echo "<option value=3 selected>3 - rather not important";
echo "<option value=4>4 - slightly important";
echo "<option value=5>5 - rather important";
echo "<option value=6>6 - very important";
echo "</select>";
echo "</TD></TR>";
}
function dump_scales () {
global $scales;
reset($scales);
do {
$scale = scale(current($scales));
echo "$scale\n";
}
while (next($scales));
} ?>
<form> <table>
......
dump_scales();
......
</table> </form>
Ecrire dans un fichier
// check existance of file (or try to create it)
// a better alternative to touch() would be is_file, is_writable and so on.
$try = touch($file_name);
if (!$try) {
echo "<p>Sorry I can't open a file, something is wrong";
exit;
}
// this is the stuff we get from the form, we insert it into an array
$input = array ($login, $password, $fullname, $url, $food, $work, $love, $leisure, $sports);
// so we can make a big string with tabs between the elements
// note that we add a \n (line break) to the end of the string.
$output_line = implode ($input, " ")."\n";
// Now open the file (get a file pointer)
// We will append to it and therefore use the "a" option
'''$output_stream = fopen($file_name, "a");'''
// and dump the string into the file
'''$result = fputs ($output_stream, $output_line);'''
// give feedback
if ($result) {
echo "<p>Your data have successfully been registered.";
}
else {
echo "<p>Too bad, the db did not want your data.";
}
// close the file pointer
fclose($output_stream);
?>
<?
// EXIT here ... we don't want to see the form again. If you do, kill the exit
exit;
}
?>
Remember
fopn (<file name>, "a")
- to open a file and then append.
fputs(<handle>, “string”)
- to write to a file
- WARNING: This will attract spammers !!
Dump contents of a file
.... we just insert it a
with an “include”
<source lang="html4strict">
<BODY>
<H1>PHP/MySQL Demo - Dump Database Contents</H1>
<?
/* Daniel.Schneider@tecfa.unige.ch
Will dump the contents of the results file
*/
?>
<strong>Results registered so far:</strong>
<pre>
<? readfile("results/result.text"); ?>
.......... </BODY>
</source>
Important:
- Use "readfile", and not "include" or "require", else you will get hacked !!
Other formats than HTML
PHP supports any other format. By default a PHP script starts creating an HTML script as soon as it encounters and HTML section or an echo/print/etc. instruction.
Principle: Before any other output in your program, you have to define the content-type (e.g. put this into the first line).
Example binary pictures
Header("Content-type: image/gif");
Example XML
Header("Content-type: text/xml);
Example SVG
Header("Content-type: image/svg+xml");
Example RDF
Header("Content-type: application/rdf+xml");
Generate some simple XML example
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.php
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.phps
- http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/php/examples/simple/simple-calcul-xml.css
<?php
header("Content-type: text/xml");
print('<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>' . "\n");
print('<?xml-stylesheet href="simple-calcul-xml.css" type="text/css" ?>');
$leisure_satisfaction = 5; $work_satisfaction = 7; $family_satisfaction = 8;
$index = ($leisure_satisfaction + $work_satisfaction + $family_satisfaction) / 3 ;
echo "<resultat> Satisfaction Index = $index </resultat>";
?>
Links
- PHP Cheat sheet at websitesetup.org (retrieved July 2020)


