Learning theory: Difference between revisions
(using an external editor) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
Learning | Learning theories make general statements about how people learn (at least for a given class of [[learning type]]s. Therefore learning theories are mostly ''descriptive''. | ||
As an example, [[situated learning]] claims that learning is strongly tied to the context and the activity in which it occurs. In order to learn a concept in a useful way it must be learned in the culture in which is has been developed and is used. Activity and perception are prior to conceptualization. The teaching and learning situation is characterized as cognitive apprenticeship. | As an example, [[situated learning]] claims that learning is strongly tied to the context and the activity in which it occurs. In order to learn a concept in a useful way it must be learned in the culture in which is has been developed and is used. Activity and perception are prior to conceptualization. The teaching and learning situation is characterized as cognitive apprenticeship. | ||
From that follows that the acitvity of learning must take place in an authentic situation. | From that follows that the acitvity of learning must take place in an authentic situation. | ||
Learning theories also can be prescriptive (tell how people should learn), but mostly prescription is the role of [[pedagogical theory]]. | |||
== Major schools of thought == | == Major schools of thought == | ||
Revision as of 13:14, 28 February 2006
Definition
Learning theories make general statements about how people learn (at least for a given class of learning types. Therefore learning theories are mostly descriptive.
As an example, situated learning claims that learning is strongly tied to the context and the activity in which it occurs. In order to learn a concept in a useful way it must be learned in the culture in which is has been developed and is used. Activity and perception are prior to conceptualization. The teaching and learning situation is characterized as cognitive apprenticeship. From that follows that the acitvity of learning must take place in an authentic situation.
Learning theories also can be prescriptive (tell how people should learn), but mostly prescription is the role of pedagogical theory.
Major schools of thought
In the literature related to education (in particular in educational technology, it is not always easy to separate learning theory from educational theory. Here is a provisional list of major schools of thought.
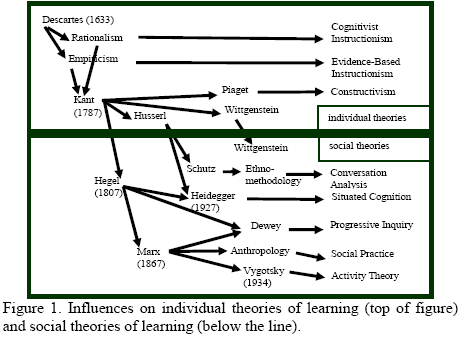
Gerry Stahl (2003: 6) provideded a graphical representation of how the influences mentioned here led to social versus individual theories of learning:
Links
- Learning Theories
- Explorations in Learning & Instruction: The Theory Into Practice Database, probably the best hypertext available
References
- Stahl, G. (2003) Building Collaborative Knowing: Elements Of A Social Theory Of CSCL, In J.W. Strijbos, P.Kirschner & R. Martins (ed.), What we know about CSCL in higher education, Amsterdam: Kluwer.