Design science: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* Pertti Järvinen: On Research Methods. Tampere: Opinpajan Kirja, ISBN 952-99233-1-7 . Note: | * Pertti Järvinen: On Research Methods. Tampere: Opinpajan Kirja, ISBN 952-99233-1-7 . | ||
** Note: This seems to be the only useful methdology book related to design-oriented research. Very dense reading, but worth to buy, directly from here (no other place sells it): http://www.uta.fi/taju ... a small and friendly university bookshop (tested by [[User:Dschneider|me]]). | |||
Revision as of 22:00, 25 February 2006
Definition
- Design sciences related to disciplines that build things.
- See also: Design methodology
Key elements of design-oriented approaches
(according to Pertti Järvinen, 2004)
- Technological rules
- tell you how to do things and are dependant on other theories (and beliefs)
- Bunge (quoted by Järvinen:99): "A technological rule: an instruction is defined as a chunk of general knowledge, linking an intervention or artifact with a desired outcome or performance in a certain field of application".
- Types of outcomes (artifacts, interventions):
- Constructs (or concept) form the " language " of a domain
- Models are sets of propositions expressing relationships among constructs
- Methods are a set of steps to perform a task (guidelines, algorithms)
- Instantiations are realizations of an artifact in its environment
- Types of research:
- Build: Demonstrate feasibility of an artifact or intervention
- Evaluate: Development of criteria, and assessment of both artifact building and artifact usage
What does this mean ?
- There are 4*2 ways to lead interesting design research.
- Usually, it's the not the program you build that is interesting, but something behind (constructs, models, methods) or around (usage).
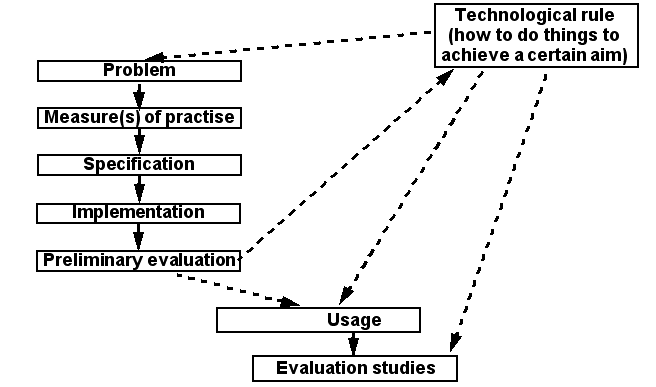
Here is picture that shows some of the relationsships between elements of a design process:
- A researcher can investigate at least on of the dotted lines
- A technological rule, i.e. a theory on how to do things can be input, output or both in a research project.
- See instructional design models and instructional design method for designs and methods related to education.
References
- Pertti Järvinen: On Research Methods. Tampere: Opinpajan Kirja, ISBN 952-99233-1-7 .
- Note: This seems to be the only useful methdology book related to design-oriented research. Very dense reading, but worth to buy, directly from here (no other place sells it): http://www.uta.fi/taju ... a small and friendly university bookshop (tested by me).