Semantic web
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Definition
- “The Semantic Web is a project that intends to create a universal medium for information exchange by putting documents with computer-processable meaning (semantics) on the World Wide Web.” Wikipedia: Semantic Web
Technology
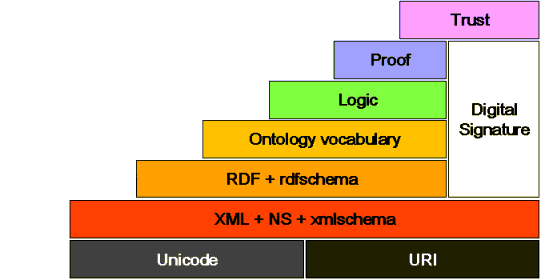
People who work on the Semantic Web base their work on the famous "semantic web tower". Its major components are:
A simplified picture of the Semantic web tower is:
Alternatively, there are initiatives outside the W3C RDF framework, like:
The relation to Web 2.0
Web 2.0 does incorporate some "semantics" but globally speaking it is much inspired by making it as simple as possible. E.g.
- Simple RSS (0.91, 2.0) instead of RSS 1.0 that was based on RDF
- Folksonomies instead of formal taxnomies metadata based on RDF semantics
- People-driven aggregation of knowledge (e.g. via syndication of the blogsphere) instead of smarter search engines. An exception are some of the best citation indexes that use both approaches.
Some examples
- FOAF ("Friends of a friend") is an RDF-based social software for social networks.
- Semantic Media Wiki] (At some DSchneider will make a test with this within this wiki)
Links
- Semantic Web. W3C home page. (includes links to all standards, groups, and some publications).
- The Semantic Web Made Easy, W3C page, retrieved 15:56, 23 November 2006 (MET).
- Short Tutorials etc.
- FAQs
References
- Hendler, James, Berners-Lee, Tim and Miller, Eric "Integrating Applications on the Semantic Web," Journal of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan, Vol 122(10), October, 2002, p. 676-680. HTML (Reprint).
- Horrocks, Ian; Bijan Parsia, Peter Patel-Schneider and James Hendler (2005). Semantic Web Architecture: Stack or Two Towers, in Francois Fages and Sylvain Soliman, editors, Principles and Practice of Semantic Web Reasoning (PPSWR 2005), number 3703 in LNCS, pages 37-41. SV, 2005.
Shadbolt, Nigel; Tim Berners-Lee and Wendy Hall (2006). The Semantic Web Revisited, by , IEEE Intelligent Systems 21(3) pp. 96-101, May/June 2006 PDF.