Methodology tutorial - finding a research subject
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
This is part of the methodology tutorial.
Introduction
Finding a research subject is trivial, if you have to pick it from a list that your professors define. On the other hand, if you have the liberty and the obligation to define your own, you may be surprised at how much time and effort it may take.
- Learning goals
- Understand the various parameters that you should look at
- Understand how to optimize the process
- Understand how important it is to be able to define a "big question"
- Learn that the big questions should then decline into a set of research objectives and research questions
- Prerequisites
- Moving on
- Level and target population
- Beginners
- Quality
- Should be ok (no more)
Choice of a research subject
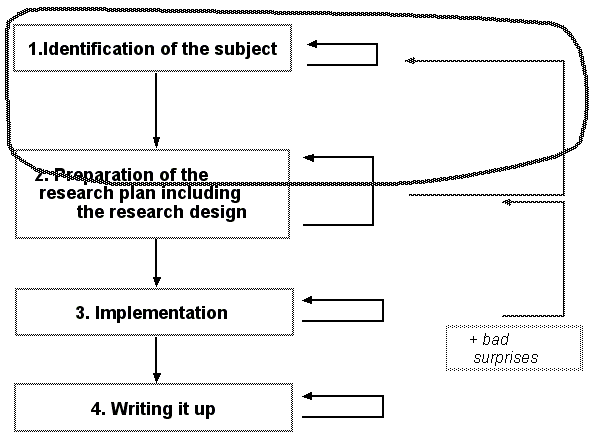
Finding a research subject is the first stage of a research project. This may seem obvious, but it is not. Students without tight advising often tend to identify just a research topic, but then fail to formulate a research subject in terms of precise research objects and research questions.
In other words: If you don't watch out, you are unlikely to know what you really are going to do and you will loose a few month...
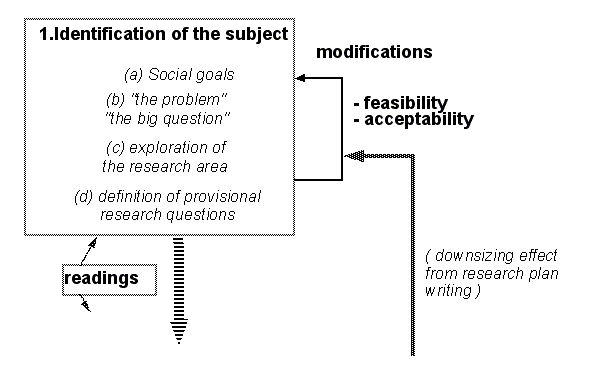
Identification of the subject: important elements
Finding a research subject is an iterative process and has to be done in several stages. The final formal step happens when you write the research plan and the final non-formal one happens when your really implement your research. E.g. you may find it necessary to add a new question or to downsize the initial project. Nevertheless, you really should aime to do plan as best as you can what you are going to do. This way you will get better advice and you will be done earlier.
There are several elements you should look at.
The identification process
The most important phases
- Identify a few topics / subjects and make a "short list"
- Make explicit each potential subject
- Discuss with your professors
- Explore the subjects (new short list), see: Readings and ideas
- Make a draft of the research plan and negotiate. See Anticipation of the research plan
- Make it official (consult your local procedure)
Identification of social goals
Learn something, institutional constraints, fun, ....
- What should your job be in 3-4 years ?
- A thesis is part of your "profile", a "visit card"
- A thesis will teach you a lot, what do you wish to learn ?
- And your employer ?
- Is he interested in your master thesis
- can you marry academic work with the goals of your organization ?
- What would you consider to be real "fun" ?
- are you intrinsically motivated ?
Identification of the central problem
- A research subject is not just a topic !!
- It must be of some academic interest, for example: explain a phenomenon, identify
processes, provide scientific arguments for an expertise, prove cognitive ergonomics of some software, demonstrate pedagogic effectiveness, invent new design rules, ...
The "big question"
- does not necessarily match the title of your project (which just can announce a topic)
La “grande question”
- is a summary of your research question
- .... may also imply practical goals
Example: E-learning
Bad: “E-learning” in vocational teacher training
Good (a): Efficiency of e-learning in ...
Good (b): Perception of e-learning ....
Maybe: Analysis of e-learning in ...
(all these variants need further precision)
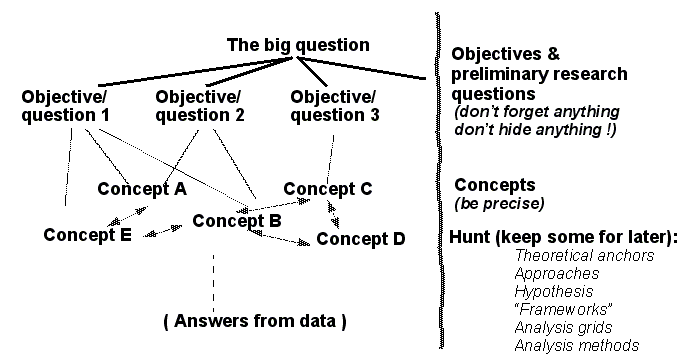
Objectives and research questions
- Even if you did manage to phrase a good "big question", your intentions will be too vague
- Therefore you must take your big question apart
- in the form of research questions and/or hypothesis
- You absolutely must make all your objectives explicit
(else you are looking
for conflicts and other problems).
- You then must formulate research questions that cover your objectives
- Formulate working hypotheses if you can and if it’s appropriate.
- You also may formulate scientific hypothesis (based on theoretical argumentation)
- It is much easier to deal with hypothesis than with more open research questions ....
- Finding the right research questions / hypothesis is an iterative process.
- Usually you only get them right after having written a draft of the literature review !!
- Therefore, don’t start field research, development etc. before you have done some theory !
Let's look at two examples (translation needed) now.
Example: Etude pilote sur la mise en oeuvre et les perceptions des TIC
(Luis Gonzalez, DESS thesis 2004)
Main goal: "Understand the factors that favor teacher’s use of ICT"
The author first defines 8 factors and then also postulates a few relationships among them
- The 8 factors were found through literature review.
Below we quote from the thesis (and not the research plan):
Sachant qu’une faible proportion d’enseignants utilise le matériel informatique dans leur pratique, je me suis demandé s’il était possible d’identifier des facteurs favorisant l’intégration des TIC.
Mon hypothèse principale postule l’existence d’une corrélation entre les facteurs suivants et la mise en œuvre des TIC par les enseignants :
- Le type support offert par le cadre institutionnel
- Leurs compétences pédagogiques
- Leurs compétences techniques
- La formation reçue, que se soit la formation de base ou la formation continue
- Leur sentiment d’auto-efficacité
- Leur perception des technologies
- Leur perception de l’usage pédagogique des TIC
- Leur rationalisation et digitalisation pédagogique
Engineering project: a system to support inquiry-based learning (IBL)
L'objectif de ce module est de donner une structure basique adaptable, aux enseignants qui désirent offrir une activité d’apprentissage par investigation à leurs élèves. Ils peuvent
ainsi aisément créer des supports informatisés pour des activités pédagogiques de ce type.The goals of this research have been defined implicitly by deriving the specification of the software module from a known inquiry framework:
- L'enseignant peut ainsi créer un type de fiche qui correspond à l'activité qu'il a en tête, [....]
- Cette fiche donne une structure qui permettra aux apprenants de répondre à des questions [...] (étape 1 : Questionner).
- L’enseignant soumet l’activité aux apprenants qui peuvent créer une instance de la fiche type afin de faire l’exercice. [...]. Dès lors, ils recherchent les informations susceptibles de les aider à remplir les différents éléments de la fiche (étape 2 :Questionner), [...]
- Une fois les informations trouvées, l’apprenant rempli son instance de fiche, [...] (étape 3 : Créer),
- puis, au moyen de la visualisation des instances des autres apprenants et de la possibilité des commenter, il peut débattre avec les différentes personnes ayant fait la même fiche que lui (étape 4 : Discuter). [....] Enfin, il soumet son instance de fiche au professeur et/ou à l’expert associé à l’activité.
- La 5e étape du modèle (Réfléchir) peut être incluse dans l’activité de différentes manières, [...]
This master thesis clearly lacked precise research questions
- the big questions was: how should we design a system for IBL support (and can I do it ?)
- the driving operational questions were a specification based on a popular IBL model
- but it was accepted that this development would lay the basis for further research,
since such a tool did not exist before
- ( only preliminary usability testing was required from the thesis advisor )
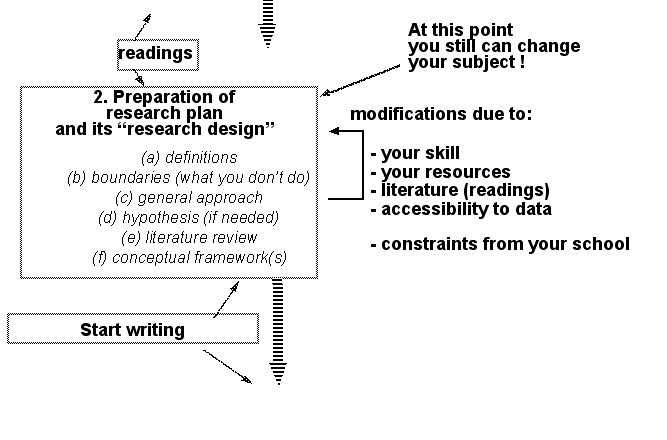
Anticipation of the research plan
Here is an idea of what will enter the research plan
Research plan = what + how
|
What ? |
A good question ! |
|
|
A (or more) good conceptual framework(s) |
| |
|
How? |
Consider that your research plan should be ... |
(and nothing else!)
questions. |
|
Be realistic !Prove that you have ... |
| |
|
A whole ! |
Integration ! |
|
Readings and ideas
Who/what can help you finding a good subject
- Examples (other thesis in the same area)
- Academic articles
- Academic web sites like this one :)
- Interviews with academic experts
- Interviews with domain experts
- Your librarian, your library, on-line journals
- http://scholar.google.com
Remarks
- Your research topic will be vague in the beginning
- Be sure to talk to other persons than just your advisor
- Engage discussion with a written list of precise questions
- and make sure that all questions have been covered at the end of your meeting
- don’t ask by mail, ask for an appointment (unless the teacher tells you otherwise)
- Don’t just think, start producing at some point
Initial readings
- start with 2-3 articles/standard works and that contain a survey of your topic or a related area.
- ask experts, use the library, use scholar.google.com, use on-line journals
- if you can’t find anything:
- hunt for articles that cover subjects with similar structural properties (e.g. concerning the approach, the “way to look at things”, etc.)
- start to occupy "islands" (and enlarge with ”circles”)
- look for further publications
- follow-up leads from you 2-3 initial articles
- go through specialized indexes
- systematically browse through specialized journals
- Go through the Internet pages of well know researchers in your field
- do not trust randomly found things (e.g. indirect quotes) on the Internet
- hunt down the home pages (a lot of researchers publish at least a few papers on their site)
- etc.
![]() Don’t read too much ! Stop when:
Don’t read too much ! Stop when:
- the same information comes back,
- you found a good central framework, the analysis grids for your concepts, experimental designs that provide you with a good example, etc. (details depend on your approach),
- you can relate your research questions to published work.
Exploitation of literature and draft of the theory part
- Don’t write “summary memos”, it takes to much time (IMHO)
Here is an advice:
Step 1: Read texts "diagonally", and just mark the most relevant concepts, theories, models, hypothesis, etc.
Step 2: Make a matrix of the most important concepts like this:
|
Concepts | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Articles |
Concept A |
Concept B |
Concept C |
Concept D |
.... |
|
1 |
x |
x |
|||
|
2 |
x |
x |
x |
||
|
... |
x | ||||
- you may add some small comments
Step 3: Sort concepts
- mark the most important ones
- look at relations
- throw away the ones you won’t need (the theory part must support the empirical part, nothing else)
Step 4: Write a draft
- Be synthetic and be critical (!)
- Do not align one mini-summary after each other (i.e. order by concepts and not authors !)
- End up with a conclusion that argues in favor of a central framework, that identifies major dimensions (elements) and corresponding analysis grids
- Look again at your research questions (revise them or add/remove things from your draft)
See also: the note taking and literature review entries.
Idea generation
brainstorming
Brainstorming is done in several stages:
- Write rapidly keywords (what you want investigate, know, etc.) on paper
- Take this list and do it again for each point
- Sort/clean and go to the next steps
Organize your ideas
make drawings, that contain major elements and relationships
- you may use mind mapping software, but don’t not overdo it !
- ... mind mapping may generate too much complexity
Alternatively, consider using a wiki (make sure to think about categories tagging and make links). Daniel K. Schneider used this wiki to prepare an introductory text on educational technology ... and it turned out to be a good strategy. See [and outcomes] of edutechwiki.
The outline
![]() Outlines are useful for your research plan, difficult chapters like the theory part, to:
Outlines are useful for your research plan, difficult chapters like the theory part, to:
- organize your ideas,
- produce a detailed plan of work to do (e.g. work packages),
- order your ideas in a linear way (your thesis will be linear).
![]() Have something to write on you (always)!
Have something to write on you (always)!
- good ideas sometimes pop out of nothing at odd times, and you should not forget them.
Summary of some exploration activities
- Discussions
- Talk to field experts, academic experts (in particular potential advisors)
- Also contact your "victims"
- Political feasibility
- Make sure that you will find "subjects", that organizations will cooperate, etc.
- Theoretical feasibility
- Have got a good enough overview ?
- E.g. theoretical frameworks, analysis grids, propositions (hypothesis)
- Methodological feasibility
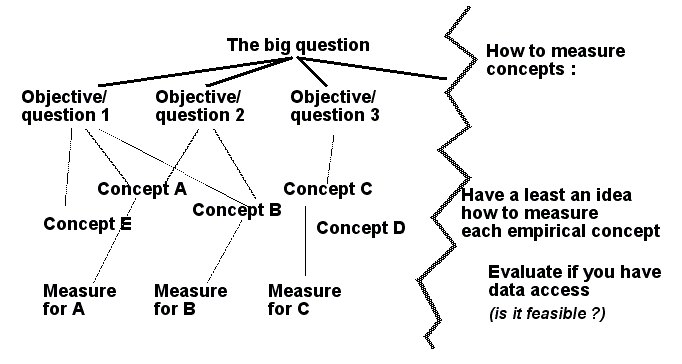
- Did you make a list of the concepts found in your research questions ?
- Do you have initial definitions for them ?
- Do you believe that you can measure each empirical concept ?
- Do you have an idea how to analyze relationships (to answer your research questions) ?
- Budgetary feasibility
- Time is your enemy
- keep your subject as small as possible (but make sure that you address an academic question ..)
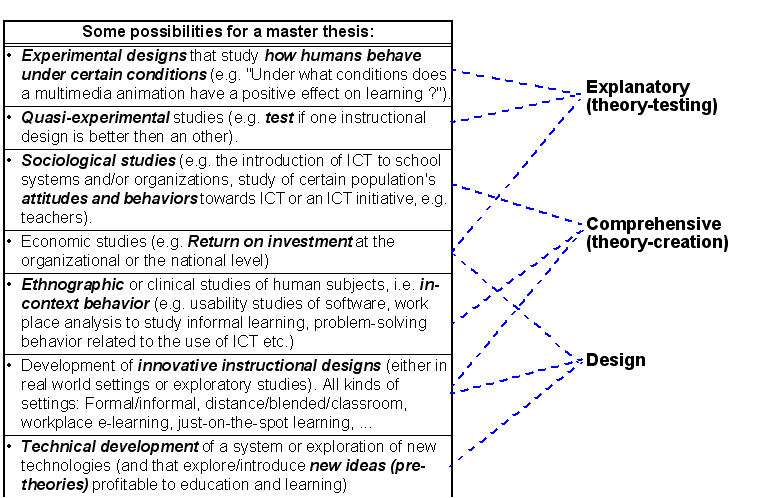
Try to identify a general thrust for your research
Think hard about the concepts you use
The theoretical face
The empirical face
See the modules on research design if you don’t understand this (and come back later)