Collaborative learning flow pattern
Definition
Collaborative Learning Flow Patterns (CLFP) allow identification and formalization of common practices in collaborative learning, i.e. they describe a kind of learning design for CSCL scripts.
“CLFPs describe well-accepted ways of arranging participants in collaborative learning sessions, sequencing types of collaborative learning activities, assigning contents to those activities, etc. CLFPs can be used to identify common types of collaborative learning activities that might potentially be mapped onto CSCL reusable functional blocks.” (Bote-Lorenzo et al. 2004).
Learning flows or learnflows refer to educational work-flows, i.e. what coordination of learner and teacher work within activities. CLFPs are design patterns that should allow to support creation of “effective, reusable, flexible and customizable collaborative learning activities designs.” (Hernández-Leo, 2005b:223).
Rationale
The advantages of using CLFPs to collect and formulate CSCL practices are according to (Hernández-Leo, 2005b:224):
- A way of communicating collaborative learning expertise to others (including novices). That's an often heard argument in learning design communities.
- A conceptual common ground among practicioners and software developers.
- Promotion of software reuse.
Therefore, it is necessary to develop CLFP-based collaborative learning design authoring tools like Collage.
Design formalism
CLFPs can be described with UML activity diagrams or with some summary table using natural language.
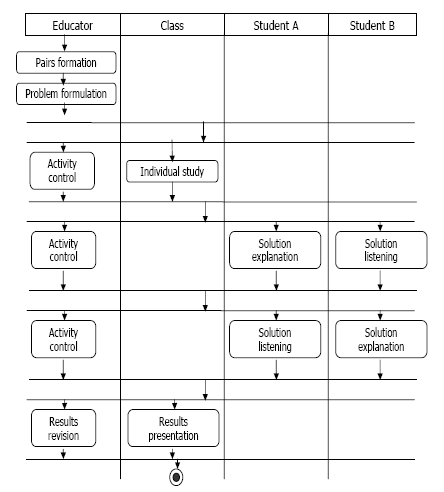
Here is an example from (Hernández-Leo, 2005b:224) that describes a Thinking Aloud Pair Problem Solving (TAPPS) CSCL Script with a diagram. In a TAPPS CLFP, students first study a problem individual in class. Then, they are paired and given a series of problems. The two students are assigned specific roles that switch with each problem: problem solver and listener. The problem solver explains her/his solution to the problem. The listener follows the explanation and catches any errors that occur. Finally all groups present results for class-room discussion.
This diagram just shows what different actors do at a given time (time flows from top to bottom). It doesn't include object flow, i.e. "products" made by learners.
Links
- Research Groups
- Software
- CLFPs have been implemented in the Collage editor
References
- Bote-Lorenzo, M.L., Hernández-Leo, D., Dimitriadis, Y., Asensio-Pérez, J.I., Gómez-Sánchez, E., Vega-Gorgojo, G., Vaquero-González, L.M. (2004). Towards Reusability and Tailorability in Collaborative Learning Systems Using IMS-LD and Grid Services Advanced Technology for Learning. 1(3):129-138.
- Hernández-Leo, D., Bote-Lorenzo, M.L., Asensio-Pérez, J.I., Gómez-Sánchez, E., Villasclaras-Fernández, E.D., Jorrín-Abellán, I.M., Dimitriadis, Y. (2007). Free- and Open Source Software for a Course on Network Management: Authoring and Enactment of Scripts based on Collaborative Learning Strategies. IEEE Transactions on Education. 50(4):292-301. http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/TE.2007.904589
- Hernández-Leo, D., Harrer, A., Dodero, J.M., Asensio-Pérez, J.I., Burgos, D. (2007). A Framework for the Conceptualization of Approaches to "Create-by-Reuse" of Learning Design Solutions. Journal of Universal Computer Science. 13(7):991-1001. http://www.jucs.org/jucs_13_7/a_framework_for_the
- Hernández-Leo, D., Villasclaras-Fernández, E.D., Jorrín-Abellán, I.M., Asensio-Pérez, J.I., Dimitriadis, Y., Ruiz-Requies, I., Rubia-Avi, B. (2006). Collage, a Collaborative Learning Design Editor Based on Patterns Special Issue on Learning Design, Educational Technology & Society. 9(1):58-71. http://www.ifets.info/issues.php?id=30
- Hernandez-Leo, D., Asensio-Perez, J. I. & Dimitriadis, Y. (2005a). Computational Representation of Collaborative Learning Flow Patterns using IMS Learning Design. Educational Technology & Society, 8 (4), 75-89. http://www.ifets.info/issues.php?id=29
- Hernández-Leo, D., Asensio-Pérez, J.I., Dimitriadis, Y., Bote-Lorenzo, M.L., Jorrín-Abellán, I.M., Villasclaras-Fernández, E.D. (2005b). Reusing IMS-LD Formalized Best Practices in Collaborative Learning Structuring. Advanced Technology for Learning 2(4):223-232. http://dx.doi.org/10.2316/Journal.208.2005.4.208-0865 - PDF