XSLT Tutorial - Basics
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
Introduction
This is a beginners tutorial for XSLT. It will teach you how to render XML contents in HTML.
Learning goals
- Understand the purpose of XSLT, i.e. be able to think of XSLT as a translation language.
- Do simple transformations from XML to HTML
- Be able to use simple XPath expressions (tag and attribute names) in template selectors and for element and attribute extraction.
- Prerequisites
- Editing XML (being able to use a simple DTD). Catch up with the Editing XML tutorial
- If you plan to create your own XML: DTD tutorial
- XML namespaces (some, have a look at the XML namespace article)
- HTML and CSS (some)
- Next steps
- XPath tutorial - basics
- XSLT to generate SVG tutorial
- XQuery tutorial - basics (if you have interest in XML databases)
- PHP - MySQL - XML tutorial - basics (shows how to display an XML result-set retrieved form MySQL with XSLT)
- Warning
XSLT is a rather complex transformation language. I believe that one could distinguish four levels of difficulty:
- This tutorial is introductory (level 1)
- Level 2 XSLT is more sophisticated template ordering, conditional expressions, loops, etc.
- Level 3 is advanced XPath expressions
- Level 4 is functional programming with templates
- Tools
There are many XSLT processors. www.online-xslt-processor.tk is an automatic As You Type Online XSLT Processor website that will help you test the XSLTs.
Introduction Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations
- Goals of XSLT
- XSLT is a transformation language for XML
- XSLT is a W3C XML language (the usual XML well-formedness criteria apply)
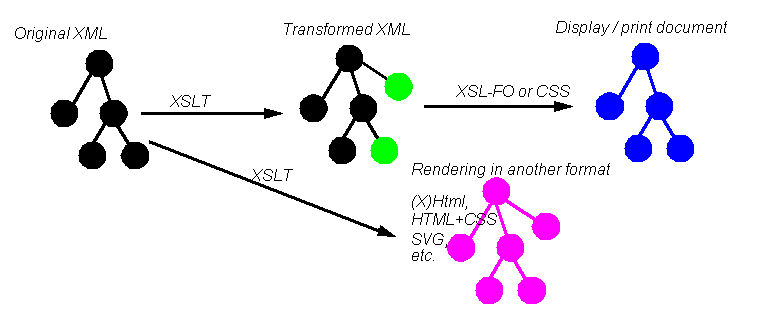
- XSLT can translate XML into almost anything , e.g.:
- wellfomed HTML (closed tags)
- any XML, e.g. yours or other XML languages like SVG, X3D
- non XML, e.g. RTF (this is a bit more complicated)
The picture below shows some use cases. In principle, the input data to be transformed is always XML. With XSLT we then can produce some "enriched" or otherwise transformed XML or directly some other format that is used to render the contents.
Keep in mind that XSLT doesn't understand HTML!. Frequently, beginners assume that XSLT knows about HTML, in particular that it can deal with links and pictures. All XSLT can do is translate XML elements into something else. Part of this confusion may stem from the fact that XSLT programs are called "stylesheets". There is no styling in XSLT, period.
XSL-FO, on the other hand was the initial target of the XSL project. It never was implemented in web browsers and this is the reason why we translate XML contents to HTML + CSS for web display. XSL-FO, however, is a very good solution for creating print documents from XML. This only can be done with server-side scripts or programs that you can install on your PC.
History and specifications
- Specification
- XSLT 1.0 was formalized as W3C Recommendation on 16/11/99: http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt
- Most modern web browser support most of it (even Safari)
- XSLT 2.0 is a W3C recommendation since 23 January 2007: http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt20/
- not implemented in current browsers, but in most good XSLT processors (e.g. Saxon)
- XSLT 3.0 is a W3C working draft: http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt-30/
- History
- Initially, XLS (XSL: eXtensible Stylesheet Language) was a project to replace CSS for both display and print media and to provide support for complex formatting and layout features (pagination, indexing, cross-referencing, recursive numbering, indexing, etc.
- XSLT ( Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations ) was originally intended as a small part of the larger specification for XSL
- However, when the XSL specification draft became very large and complex it was decided to split the project into XSLT for transformations (that were urgently needed) and XSL for the rest (W3C recommendation of 2001)
- Related languages
- XPath (XML Path language used by XSLT, XQuery, etc.), http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath. XPath identifies particular parts of an XML document. Read the XPath tutorial - basics
- XSL also called XSL/FO (the formatting language), http://www.w3.org/TR/xsl/
- XQuery (Query language for XML), http://www.w3.org/TR/xquery/. Read the XQuery tutorial - basics
A first glance at XSLT
Simple use of XSLT means creating program in a file (wrongly called a stylesheet). This file is associated with an XML file in the similar way that you would associate a CSS with HTML file. Since your web browser includes an XSLT processor, the browser will not display the XML (you can still look at the source), but it will execute the XSLT and display the result of the translation, e.g. HTML5.
Alternatively, you can use an XML editor or a XSLT processor to translate XML contents to files and then put these result files on the web or print them. Finally, you could install server-side software that does this. E.g. PHP5 includes an XSLT processor, but unfortunately it does support XSL-FO. To process the latter you likely need some Java-based software.
Root of an XSLT file stylesheet
An XSLT program is an XML document.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
....
</xsl:stylesheet>
Mandatory "elements"
- An XML declaration on top of the file
- A stylesheet root tag with the following version and namespace attributes (as seen above):
version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
Furthermore:
- Usually the "xsl" prefix is used for XSLT tags, but you also can find "xs" or none if you look at examples.
- XSLT must be wellformed and valid, e.g. obey the XSLT specification
- XSLT files usually have the *.xsl extension and should have the text/xsl or application/xml mime type when served by http (a web server). So make sure that your web server is configured correctly.
Association of XML and an XSLT file
You can directly associate a XSLT stylesheet with an XML file by using a so-called processing instruction (similar principle as CSS stylesheets)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="project.xsl" type="text/xsl" ?>
<yourxml>
....
</yourxml>
Basic XSLT
Basic (!) use of XSLT means:
- Translating XML to HTML
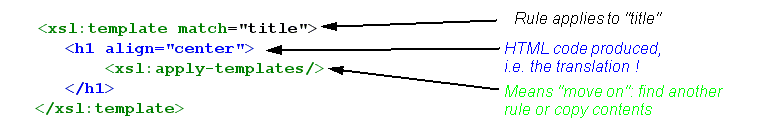
- Creating translation rules (aka templates) for each XML tag we want to translate. Basically, a template will tell how a given XML element should be translated. All text inside the template that is not XSLT, i.e. does not start with xsl: will be found in the output.
- A simple translation rule (called "template" in XSLT)
- Example Translation of a title tag into HTML centered H1
XML Source we want to translate:
<title>Hello friend</title>
Wanted result:
<h1>Hello friend</h1>
XSLT rule that does it
A complete XSLT example
Below is the complete code for a simple "Hello XSLT" example.
- XML file (source)
- hello.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="hello.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
<page>
<title>Hello</title>
<content>Here is some content</content>
<comment>Written by DKS.</comment>
</page>
- Wanted result document
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<h1 align="center">Hello</h1>
<p align="center"> Here is some content</p>
<hr><i>Written by DKS</i>
</body>
</html>
- The XSLT Stylesheet
- hello.xslt
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="page">
<html>
<head>
<title> <xsl:value-of select="title"/>
</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="title">
<h1 align="center"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </h1>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="content">
<p align="center"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="comment">
<hr/> <i><xsl:apply-templates/> </i>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
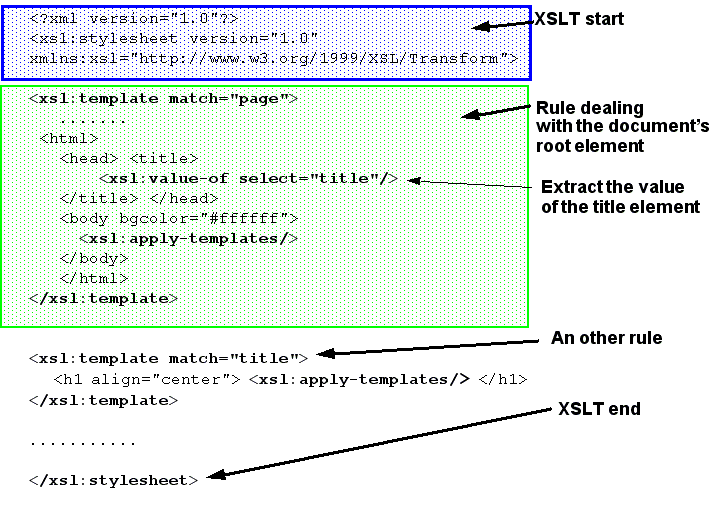
The picture below explains the anatomy of this simple stylesheet. We could distinguish between:
- some sort of prolog that would include the XML header and (optionally) as we shall see later some kind of output and input directives;
- the all important template that will triggered by the either the root of the file "/" or the XML root element, e.g. "page" in our case;
- additional templates.
Rule execution order
(1) The XSLT engine first looks at the XML file and tries to find a XLT rule that will match the root element
- E.g. in the above example it will find "page" and then the template for page
(2) The XSLT processor will then "move" inside the rule element and do further processing
- HTML elements (or any other tags) will be copied to the output document
- If an XSLT instruction is found, it will be executed
<xsl:apply-templates/> means: "go and look for other rules"
E.g. in the above example
- the processor dealing with root element "page" will first find a rule for "title" and execute it according to the same principle.
- once it is done with "title" and its children, it then will find the rule for "content" and execute it
(3) and so forth .... It is important to understand that the XSLT processor works within a given context. In our example, if the processor is within the "page" element, it then will recognize title, content and comment as child elements.
More information
- <xsl:value-of select="title"/> will retrieve contents of the "title" child element.
- In our example, it would only work in the template for "page", since only "page" has a "title" child
- You have to understand that XSLT works down "depth-first" the XML tree, i.e.
- it first deals with the rule for the root element,
- then with the first instruction within this rule.
- If the first instruction says "find other rules" it will then apply the first rule found for the first child element and so forth...
- The rule of the root element is also the last one be finished (since it must deal step-by-step with everything that is found inside) !!!
The procedure recapitulated
(1) Create a XSLT stylesheet file: xxx.xsl
(2) Copy/paste the XSLT header and root element below (decide encoding as you like)
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
</xsl:stylesheet>
(3) Write a rule that deals with your XML root element This rule must produce the root, head and body of the HTML (copy/paste this too, but replace "page ")
<xsl:template match="page">
<html>
<head>
<title> <xsl:value-of select="title"/> </title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
(4) Write rules for each (!!) of your XML elements,
- for each insert some HTML, sometimes some text, or sometimes nothing
- make sure to place a <xsl:apply-templates> inside each rule (usually between some HTML) ... unless you wish to censor contents.
A typical simple rule might look like this:
<xsl:template match="element_name">
<h1>Some kind of heading</h2>
<div class="element_name">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</div>
</xsl:template>
(5) Associate this stylesheet with your XML file using:
<xml-stylesheet href="xxx.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
Tuning output with xsl:output and CSS
Output declarations
So far, HTML output produced would display in a navigator, but is not fully HTML compliant.
xsl:output is an instruction that allows you to fine-tune XSLT translation output in an easy way. Its definition is the following:
<xsl:output method = "xml" | "html" | "text" version = nmtoken encoding = string omit-xml-declaration = "yes" | "no" standalone = "yes" | "no" doctype-public = string doctype-system = string indent = "yes" | "no" media-type = string />
Usually, this instruction is inserted in the beginning of the file (after xsl:stylesheet)
HTML 4 output
- Example - Output in HTML 4 UTF-8 encoded
<xsl:output method="html"
encoding="UTF-8"
doctype-public="-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"/>
- Example - Output in HTML 4 ISO-latin encoded
<xsl:output method="html"
encoding="ISO-8859-1"
doctype-public="-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"/>
XHTML 1 output
- Example - Output in XHTML 1 transitional with a namespace
- This is quite more complicated than producing simple HTML
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" >
<xsl:output
method="xml"
doctype-system="http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"
doctype-public="-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
indent="yes"
encoding="iso-8859-1" />
<xsl:template match="recipe">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" >
<head> ... </head> ... <body> ... </body>
</xsl:template>
HTML5 and XHTML5 output
Since HTML5 is neither SGML nor XML this is a bit more tricky, since HTML5 did not exist when XSLT was defined. You have to choose between elegant XSLT and perfect output. Can't have both ....
- Example - Output in HTML 5
<xsl:output
method="html"
doctype-system="about:legacy-compat"
encoding="UTF-8"
indent="yes" />
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>HTML5 + SVG example</title>
</head>
<body>
.....
</body>
</html>
Or output as XML, but you must remove the XML header using omit-xml-declartion="yes". In addition we show how to "print" out the DOCTYPE declaration if you don't like the SYSTEM "legacy-compat" bit. However, this solution does not seem to work with Firefox 19 (client-side). It would be the perfect server-side solution.
<xsl:output
method="xml"
omit-xml-declaration = "yes"
encoding="UTF-8"
indent="yes" />
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<xsl:text disable-output-escaping="yes">
<![CDATA[<!DOCTYPE html>]]>
</xsl:text>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>HTML5 + SVG example</title>
</head>
<body>
.....
</body>
</html>
- Example - XHTML5 serialisation of HTML5
Frankly, I don't really know how XHTML5 contents are to be served. In principle, since a navigator would have to parse XHTML differently (e.g. find non-HTML5 name spaces), there should be an XML declaration on top in addition to a correct mime-type sent by the server.
<xsl:output
method="xml"
omit-xml-declaration = "yes"
doctype-system="about:legacy-compat"
encoding="UTF-8"
indent="yes" />
or with an XML header:
<xsl:output
method="xml"
doctype-system="about:legacy-compat"
encoding="UTF-8"
indent="yes" />
Or maybe the following, but it won't work with Firefox 19, i.e. the doctype is printed into the body...
<xsl:output
method="xml"
encoding="UTF-8"
indent="yes" />
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:text disable-output-escaping="yes">
<![CDATA[<!DOCTYPE html>]]>
</xsl:text>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>...</head>
<body>.....</body>
</html>
Output in any XML language
- Example - Another XML language
<xsl:output
method="xml" indent="yes"
doctype-system="mydtd.dtd" />
- Example - Output in SVG 1.1
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
>
<xsl:output
method="xml"
indent="yes"
standalone="no"
doctype-public="-//W3C//DTD SVG 1.1//EN"
doctype-system="http://www.w3.org/Graphics/SVG/1.1/DTD/svg11.dtd"
media-type="image/svg" />
CSS styling of HTHML output
Associating a CSS stylesheet with HTML output is trivial, if you remember HTML ....
- add a link tag in the "head" produced by the template for the root element
- .... in the hello.css file you then have to define styles of HTML elements you generate
- cooking.xml
<xsl:template match="hello">
<html>
<head>
<link href="hello.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head>
......
</xsl:template match="hello">
- Example 3-5 - cooking
- cooking.xsl inserts cooking-html.css into the HTML output
<xsl:template match="recipe">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title> <xsl:value-of select="title"/> </title>
<link href="cooking-html.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
If things go wrong
Frequent problems and remediation
- Style-sheet error !
- Validate the style-sheet in your XML editor
- If it provides XSLT support, it will help you find the error spots
- XHTML doesn't display in Firefox !
- Firefox wants a namespace declaration in the XHMTL produced, do it (see above).
- HTML doesn't seem to be right !
- Transform the XML document within your XML editor and look at the HTML
In the Exchanger XML Editor (IMHO, the best free XML editor for XSLT), use Transform in the menu bar with the following parameters:
Transform->Execute Advanced XSLT Input = current document XSLT = Use Processing instructions
- You also may validate the output HTML !
- There is various unformatted text in the output !
- See the XSLT default rule (below)
- HTML still doesn't seem to be right !!
- Use a XSLT debugger/tracer to understand how your XSLT executes
The XSLT default rule
- When you test your first style sheet, it is likely that some of your contents will appear non-formatted.
- This is due to the fact that XSLT will apply two default rules to all XML elements for which it didn't find a rule.
- If you forget to write a rule for a tag (or misspell tag names) this will happen .....
- The XSLT default rules simply copy all contents to the output.
This rule applies to the document root element and all other elements. It will walk down the tree.
<xsl:template match="*|/">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
If text is available in a node or attributes, they are just copied.
<xsl:template match="text()|@*">
<xsl:value-of select="."/>
</xsl:template>
A modified default rule that will help you find missing pieces
- simply cut/paste this to your XSLT (but remove it later on)
<xsl:template match="*">
<dl><dt>Untranslated node:
<strong><xsl:value-of select="name()"/></strong></dt>
<dd>
<xsl:copy>
<xsl:apply-templates select="@*"/>
<xsl:apply-templates select="node()"/>
</xsl:copy>
</dd>
</dl>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="text()|@*">
Contents: <xsl:value-of select="."/>
</xsl:template>
A short glance at XPath
XPath is a very powerful language for extracting information from XML. The XPath specification was published at the same time as XSLT 1.0 (1999). XPath is used in several XML languages besides XSLT, e.g. XQuery. The XPath tutorial - basics article introduces additional features of XPath.
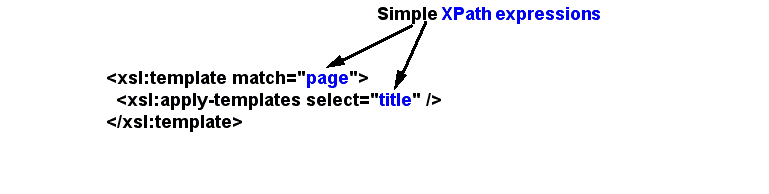
Within XSLT, for example, match and select attributes are XPath expressions. The picture show a simple use case.
XSLT beginners don't need to know a lot about XPath, so don't worry right now and simply stick to the idea of writing a XSLT template for each XML tag, as explained before. You should understand that XSLT templates, when applied using the xsl:apply instruction are always executed within a given context, i.e. within the XML element the XSLT processor is currently working with. This is why you can away using XSLT without understanding any XPath.
XPath expressions can be more complicated. Such expressions can be used for value extraction, for writing templates treating a same type of element in different way, for conditional expressions, and so forth.
<xsl:apply-templates select="course/module[position()=1]/section[position()=2]"/>
means: "find rule for 2nd section of the first module of course"
XPath expressions also may include arithmetic and tests
"//Participant[string-length(Nom)>=8]"
means: "return all participant nodes with content of name longer than 7 characters"
- Examples of a few simple XPath expressions
- These should remind you of CSS selectors
|
Syntax |
(Type of path) |
Example path |
Example matches |
|---|---|---|---|
|
tag |
element name |
project |
<project> ...... </project> |
|
/ |
separates children |
project/title |
<project> <title> ... </title> |
|
/ |
(root element) | ||
|
// |
descendant |
project//title |
<project><problem> <title>....</title> |
|
//title |
<racine>... <title>..</title> (any place) | ||
|
* |
"wildcard" |
*/title |
<bla> <title>..</title> and <bli> <title>...</title> |
|
| |
"or operator |
title|head |
<title>...</title> or <head> ...</head> |
|
*|/|@* |
All elements: root, children and attributes | ||
|
. |
current element |
. |
|
|
../ |
parent element |
../problem |
<project> |
|
@ |
attribute name |
@id |
<xyz id="test">...</xyz> |
|
@* |
Any attribute | ||
|
element/@attr |
attribute of child |
project/@id |
<project id="test" ...> ... </project> |
|
@attr='type' |
type of attribute |
list[@type='ol'] |
<list type="ol"> ...... </list> |
Basic value extraction
Extracting contents of elements and attributes is important in three simple use cases:
- Creating HTML code for links and images
- Creating the HTML title element (if you got some kind of main heading in your XML document)
- Dealing with data-centric XML that represent data-base like structures
The xsl:value-of instruction
xsl:value-of allows to insert the value of an XPath expression, e.g. of some element data
- Example - Value-of
Let's assume
- that we have an author element somewhere in the XML code and that we would like to put this author information on top of the page
- that we have a revision attribute and that we would like to display.
XML fragment
<page>
<title>Hello</title>
<content revision="10 ">
Here is some content</content>
<comment>Written by <author>DKS</author> </comment>
</page>
XSLT rules
<xsl:template match="page">
<p><xsl:value-of select="comment/author" /></p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="content">
<P>Revision number: <xsl:value-of select="@revision" /></P>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
Inserting a value inside an HTML attribute string
If you want to insert information inside an HTML attribute value, things get a little bit tricky, since HTML value attributes are quoted and usually information within quotes is not interpreted. Read on ...
XSLT special syntax for inserting values into quoted attribute values
{....}
This {...} construct is the equivalent of < xsl:value-of select="..."/> which can not be used here !!
Example - Building an HTML href tag from an XML email attribute
- We will use both the {...} and the value-of select="" constructs.
- The XML fragment
<contact-info email="test@test">
- The XSLT rule
<xsl:template match="contact-info">
<a href="mailto:{@email}"><xsl:value-of select="@email"/></a>
</xsl:template>
- The result
<a href="mailto:test@test">test@test</a>
Producing HTML Links
Think !! XSLT does not understand HTML. All you have to do is to translate your XML to HTML and not try to do any dark magic ....
(1) Links defined as simple element contents
XML example:
<info>http://test.com/test/</info>
XSLT solution, take 1 - Display "Click here" as link text
<xsl:template match="info">
<a href="{.}">Click here</a>
</xsl:template>
XSLT solution, take 2 - displays the URL as link text
<xsl:template match="info">
<a href="{.}"><xsl:value-of select="."/> </a>
</xsl:template>
(2) Links defined with two tags
XML example:
<address>
<name>TECFA</name>
<url>http://tecfa.unige.ch</url>
</address>
XSLT solution:
<xsl:template match="address">
<a href="{url}"> <xsl:value-of select="name"/> </a>
</xsl:template>
(3) Links defined like an HTML link
XML Example:
<link url="http://tecfa.unige.ch">TECFA</link>
XSLT solution:
<xsl:template match="link">
<a href="{@url}"> <xsl:value-of select="."/> </a>
</xsl:template>
XML Example exactly like in HTML
<a href="http://tecfa.unige.ch">TECFA</a>
XSLT solution:
<xsl:template match="a">
<a href="{@href}"> <xsl:value-of select="."/> </a>
</xsl:template>
Example files, look at the source of each:
- Source code: html-links.xml - html-links.xsl
- More examples:links.xml - links.xsl
Dealing with pictures
There is no special "magic" for dealing with images, links, style sheets etc. Simply look at your XML and figure out how to translate into equivalent HTML (or whatever else)
The following example demonstrates the use of value extraction. Several other solutions than the one we demonstrate below exist ...
Example - Dealing with pictures
File images.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="images.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
<page>
<title>Hello Here are my images</title>
<list>
<!-- pictures are either contents or attribute values of elements -->
<image>dolores_001.jpg</image>
<image>dolores_002.jpg</image>
<image3 source="dolores_002.jpg">Recipe image</image3>
</list>
<comment>Written by DKS.</comment>
</page>
File images.xsl
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="page">
<html> <head> <title> <xsl:value-of select="title"/> </title> </head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="title">
<h1 align="center"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </h1>
</xsl:template>
<!-- pictures are either contents or attribute values of elements -->
<xsl:template match="list">
Images are element contents, apply a template to all image elements:
<xsl:apply-templates select="image"/>
Images are attribute values of an element, we do it differently:
<xsl:apply-templates select="image3"/>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="image">
<p> <img src="{.}"/> </p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="image3">
<p> <img src="{@source}"/><br/><xsl:value-of select="."/> </p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="comment">
<hr/> <i><xsl:apply-templates/></i>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Real life example (examine the source of both files):
Information filtering and dealing with position
Information filtering
Instead of letting the XSLT processor select and apply templates (that we also call rules here) in "natural order", you can define which templates should by applied within a given context.
Example - Displaying the hello text without content
In the template for the root element, we only apply templates for the "title" and the "comment" element.
<xsl:apply-templates select="title"/>
<xsl:apply-templates select="comment"/>
The XSLT processor executing the template for the ''page'' element, will first try to find and apply a template for the "''title''" element, and after that, for the "''comment''" element.
That implies that information within a ''content'' tag will not be displayed (since we don't let the processor find templates by itself)
- Hello2.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="hello2.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
<page>
<title>Hello</title>
<content>Here is some content</content>
<comment>Written by DKS.</comment>
</page>
- Hello2.xsl
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="page">
<html> <head> <title> <xsl:value-of select="title"/> </title> </head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<!-- Steering rule execution below -->
<xsl:apply-templates select="title"/>
<xsl:apply-templates select="comment"/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="title">
<h1 align="center"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </h1>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="comment">
<hr/> <i><xsl:apply-templates/></i>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
- Hello2.html, i.e. the resulting HTML file
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN""http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<h1 align="center">Hello</h1>
<p align="center"> Here is some content</p>
<hr><i>Written by DKS</i>
</body>
</html>
Working with positions
Imagine that you would like to apply different templates for the same type of element, according to its position. A typical use case are comma separated items. The last item should finish with a "."
Simple comma-separated list
- XML File: ingredient-list1.xml (live example)
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="ingredient-list1.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
.....
<ingredients>
<item>6 sliced caterpillars</item>
<item>1 shrivelfig</item>
<item>4 rat spleens</item>
<item>minced daisy roots</item>
<item>5 drops of leech juice</item>
</ingredients>
.....
- XSLT File ingredient-list1.xsl (full source code)
The following code fragment demonstrate that we define two rules for the item element. By default the first one is applied. Since the XSLT processor only will apply one rule per element and also the most complex one, the second rule is chosen for the last element.
<xsl:template match="ingredients">
<p>
<b>Ingredients:</b> <xsl:apply-templates />
</p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="item">
<xsl:apply-templates/>,
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="item[position()=last()]">
<xsl:apply-templates/>.
</xsl:template>
Numbering
The XPath position() function also can be used to number elements. However, in order to make this work, we must first strip out whitespace. Each Whitespace between elements is also counted.
- The XML source code is the same as above (file ingredient-list2.xml)
- ingredient-list2.xsl (full XSLT source code)
<!-- must remove white spaces within the list element,
otherwise numbering will not work -->
<xsl:strip-space elements="ingredients"/>
<xsl:template match="ingredients">
<p>
<b>Ingredients:</b> <xsl:apply-templates />
</p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="item">
(<xsl:value-of select="position()"/>)
<xsl:apply-templates />,
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="item[position()=last()]">
(<xsl:value-of select="position()"/>)
<xsl:apply-templates />.
</xsl:template>
numbering using a selection instruction
You also could obtain the same result by using the choose or if selection instructions. However, we believe that one should stick to simple data-driven rule-based programming for simple translation problems. Conditional programming constructs only should be used in complex functional programming code...
- ingredient-list3.xsl (full XSLT source code)
....
<xsl:template match="item">
(<xsl:value-of select="position()"/>)
<xsl:apply-templates/>
<xsl:choose>
<xsl:when test="position() != last()">
<xsl:text>, </xsl:text>
</xsl:when>
<xsl:otherwise>.</xsl:otherwise>
</xsl:choose>
</xsl:template>
....
Sorting
Sometimes you wish to sort elements. This should encourage you to study what I call XSLT level 2 (programming constructs).
- XML
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="participants.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
<participants>
<participant>
<FirstName>Daniel</FirstName>
<qualification>8</qualification>
<description>Daniel will be the tutor</description>
<FoodPref picture="dolores_001.jpg">Sea Food</FoodPref>
</participant>
<participant>
<FirstName>Jonathan</FirstName>
<qualification>5</qualification>
<FoodPref picture="dolores_002.jpg">Asian</FoodPref>
</participant>
<participant>
<FirstName>Bernadette</FirstName>
<qualification>8</qualification>
<description>Bernadette is an arts major</description>
</participant>
<participant>
<FirstName>Nathalie</FirstName>
<qualification>2</qualification>
</participant>
</participants>
- XSL
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output method="html"
encoding="ISO-8859-1"
doctype-public="-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<head>
<title>Participants List</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<h1>Participants list</h1>
Shows how to build a simple sorted table with XSLT.
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="participants">
<table border="2" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="6">
<tr><th>Qualification</th>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Food Picture</th>
</tr>
<xsl:for-each select="participant">
<xsl:sort select="qualification"/>
<tr>
<td><xsl:value-of select="qualification"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="FirstName"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="description"/></td>
<td><xsl:if test="FoodPref/@picture"><img src="{FoodPref/@picture}"/></xsl:if></td>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
</table>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
For some more XSLT filtering tricks, read XPath tutorial - basics. You could, for instance, learn how to write custom rules for the same element sitting in different positions...
Exercise
Here is a simple XML file and an unfinished XSLT Stylesheet. Try to complete it.
- XML (copy/paste)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="cooking.xsl" type="text/xsl"?>
<recipe>
<recipe_head>
<recipe_name>Cold Salmon in Creamy Spiced Sauce</recipe_name>
<recipe_author>Hilaire Walden</recipe_author>
<meal_type>Fish and Shellfish</meal_type>
</recipe_head>
<recipe_body>
<ingredients>
<ingredient>1/2 teaspoon finely crushed cumin seeds</ingredient>
<ingredient>1 teaspoon chilli powder</ingredient>
<ingredient>salt and freshly ground black pepper</ingredient>
<ingredient>2 tablespoons olive oil</ingredient>
<ingredient>2 cloves garlic, crushed</ingredient>
<ingredient>1.25 cm (1/2 in) fresh ginger root, finely chopped</ingredient>
<ingredient>4 pieces salmon fillet, skinned</ingredient>
<ingredient>125 ml (4 fl oz / 1/2 cup) double (heavy) cream</ingredient>
<ingredient>250 ml (8 fl oz / 1 cup) thick plain yogurt</ingredient>
<ingredient>large pinch of saffron threads, toasted and crushed</ingredient>
<ingredient>seeds from 6 cardamom pods, toasted and finely crushed</ingredient>
<ingredient>salt</ingredient>
<ingredient>coriander (cilantro) to garnish</ingredient>
</ingredients>
<directions>
<direction>Mix together the cumin seeds, chilli powder and pepper and rub into the fish.</direction>
<direction>Heat the oil in a frying pan, add the garlic and ginger and heat until they sizzle.</direction>
<direction>Add the salmon fillets and fry until they start to colour (about 15-20 seconds on each side).</direction>
<direction>Stir in the cream, yogurt, saffron, cardamom and salt.</direction>
<direction>Adjust the heat so that the sauce is just bubbling and cook,
turning the fish once, until the flesh just flakes when tested
with the point of a sharp knife (about 3-4 minutes each side).
</direction>
<direction>Transfer the fish to a shallow dish.
Boil the sauce until it has reduced and thickened, pour over the fish and leave to cool.</direction>
<direction>Cover the dish and chill until 15-20 minutes before serving.</direction>
<direction>Garnish with coriander (cilantro).</direction>
</directions>
</recipe_body>
<recipe_footer>
<serving>4</serving>
<preparation_time>15 minutes</preparation_time>
</recipe_footer>
<document_info>
<document_author>Hilaire Walden</document_author>
<date_updated>21/01/07</date_updated>
<origin>Easy to Cook, Hot & Spicy</origin>
</document_info>
</recipe>
- XSLT (not complete)
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output
method="xml"
doctype-system="http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"
doctype-public="-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
indent="yes"
encoding="iso-8859-1" />
<xsl:template match="recipe">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title> <xsl:value-of select="title"/> </title>
<link href="cooking-html.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#ffffff">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="recipe_head">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="recipe_body">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="recipe_name">
<h1 align="center"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </h1>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="recipe_author">
<p align="center"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="meal_type">
<p align="center"> Type: <xsl:apply-templates/> </p>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="ingredients">
<h2 align="center">Ingredients</h2>
<ol>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</ol>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="ingredient">
<li> <xsl:apply-templates/> </li>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="directions">
<h2 align="center">Directions</h2>
<ol>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</ol>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="direction">
<li> <xsl:apply-templates/> </li>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="recipe_footer">
<h2 align="center">More info</h2>
<p>This stylesheet is unfinished ... some rules are missing.
This is why you can't see properly formatted contents below ....
</p>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Last advice and links
Links
- See XSLT (more tutorials, software, online services, etc.)
Moving on
Advice
- Ignore textbooks that start by explaining how to use the for-each construct.
- You can do a lot just with templates (rules) !
- Try to complete the example problem above. In my experience, people absolutly don't get the mechanism of this kind of data-driven rule-based programming before they really tried understanding and completing an example. (This includes programmers that only have been trained in procedural languages. Btw, those programmers really freak out when they have to learn writing functional programming code with XSLT and cope with the fact that there no variables as they understand them in XSLT).
- Learn how to use an XSLT debugger / tracing program. E.g. use the Exchanger XML Editor, version 3.3 or better, which includes a debugger. This editor works fine on Windows 7, Ubuntu 10.x, but not as well on Mac OsX it seems.
- Look up other tutorials, some are listed in the XSLT article.
- An excellent reference guide can be found on ZVON: "http://zvon.org/comp/r/ref-XSLT_1.html" and "http://zvon.org/comp/r/ref-XSLT_2.html"