Adafruit Sensors: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
In [[MakeCode]], there are two means to read the code : through '''events''' or by reading '''live data''': | In [[MakeCode]], there are two means to read the code : through '''events''' or by reading '''live data''': | ||
* | * Events: code runs when an event is detected. For example, the <code>On shake</code> event runs code when a certain type of shaking is detected by the accelerometer. | ||
* Live data: live reading of the sensor data. | |||
= Adafruit Capacitive touch = | = Adafruit Capacitive touch = | ||
Revision as of 11:29, 24 September 2019
Introduction
In this article,we propose an overview of the Adafruit Circuit Playground Express (CPX) built-in sensors. This aim of this page is to show you how to leverage them in MakeCode. So, if you are not familiar with MakeCode, we advise to have a look on MakeCode page in this wiki.
In MakeCode, there are two means to read the code : through events or by reading live data:
- Events: code runs when an event is detected. For example, the
On shakeevent runs code when a certain type of shaking is detected by the accelerometer. - Live data: live reading of the sensor data.
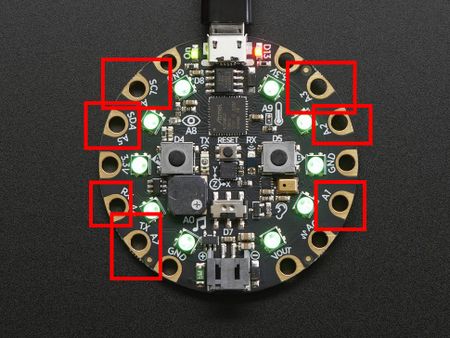
Adafruit Capacitive touch
On the CPX, there are 7 capacitive pins (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6 and A7). They can be used as buttons (like buttons A or B). There are two means to read the
Links
Aknowledgement
Pictures as well as some text was reproduced from the Adafruit circuit playground express documentation. Some pictures are available under a CC BY-NC-SA license. Others are copyright AdaFruit and "all rights reserved" and reproduced with permission. Before you reuse any picture from this website, make sure to look at the license information.
For more information about using Adafruit, see https://learn.adafruit.com.