RDF: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Turtle syntax) |
m (→RDF basics) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
xmlns:mon_schema="http://tecfa.unige.ch/lib/mon_schema" > | xmlns:mon_schema="http://tecfa.unige.ch/lib/mon_schema" > | ||
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://tecfa.unige.ch/perso/staf/lattion/"> | <rdf:Description rdf:about="http://tecfa.unige.ch/perso/staf/lattion/"> | ||
<mon_schema:Creator> | <mon_schema:Creator>Stéphane Lattion</mon_schema:Creator> | ||
</rdf:Description> | </rdf:Description> | ||
</rdf:RDF> | </rdf:RDF> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:03, 15 March 2013
Definition
- The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a language for representing information about resources in the World Wide Web.
- Originally RDF was primarily intended to represent metadata about Web resources, such as the title, author, and modification date of a Web page, copyright and licensing information about a Web document, or the availability schedule for some shared resource. However, by generalizing the concept of a "Web resource", RDF can also be used to represent information about things that can be identified on the Web, i.e. the semantic web.
Major RDF vocabularies
- Metadata
- Content syndication and social software
- RSS 1.0 which is not very popular, most RSS formats are not RDF since bloggers don't understand issues related to the semantic web :)
- FOAF Friends-of-a-friend vocabulary for person networks
- Semantic Web
RDF basics
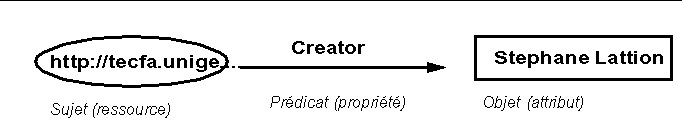
At its core, RDF has a simple relational data model: Subject - Verb - Object or expressed differently Predicate (Subject, Object)
- Subject = The resource
- Object = Value
- Verb = Predicate = propriety = relation of the subjet with the object
Here is a typical RDF fragment
<?xml version="1.0"?> <rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#" xmlns:mon_schema="http://tecfa.unige.ch/lib/mon_schema" > <rdf:Description rdf:about="http://tecfa.unige.ch/perso/staf/lattion/"> <mon_schema:Creator>Stéphane Lattion</mon_schema:Creator> </rdf:Description> </rdf:RDF>
It expresses a relation like this:
RDF and the semantic web
The RDF Software stack
The RDF bus
Turtle syntax
Since XML/RDF code is some verbose, writing it manually is fairly time consuming. The W3C team proposes a "textual syntax for RDF called Turtle that allows RDF graphs to be completely written in a compact and natural text form, with abbreviations for common usage patterns and datatypes" (Turtle - Terse RDF Triple Language, retrieved 15:31, 10 March 2008 (MET)).
Example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
xmlns:ex="http://example.org/stuff/1.0/">
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-syntax-grammar"
dc:title="RDF/XML Syntax Specification (Revised)">
<ex:editor>
<rdf:Description ex:fullName="Dave Beckett">
<ex:homePage rdf:resource="http://purl.org/net/dajobe/" />
</rdf:Description>
</ex:editor>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
becomes in turtle syntax:
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix dc: <http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/> .
@prefix ex: <http://example.org/stuff/1.0/> .
<http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-syntax-grammar>
dc:title "RDF/XML Syntax Specification (Revised)" ;
ex:editor [
ex:fullname "Dave Beckett";
ex:homePage <http://purl.org/net/dajobe/>
] .
Links
Standards
- Resource Description Framework (RDF) Overview
- Resource Description Framework (RDF): Concepts and Abstract Syntax, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004
- Resource Description Framework (RDF) Model and Syntax.
- RDF Semantics, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004 (rather difficult reading).
- RDF/XML Syntax Specification, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004.
- RDF Vocabulary Description Language 1.0: RDF Schema, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004
- Turtle - Terse RDF Triple Language
- RDF Namespaces
- RDF and XHTML
- See the RDFa article
- RDFa Primer 1.0 Embedding RDF in XHTML (Working Draft in March 2007)
- OWL
- OWL Web Ontology Language Overview, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004.
- OWL Web Ontology Language Guide, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004
- OWL Web Ontology Language Semantics and Abstract Syntax, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004
- Dean M., Schreiber G (Editors); van Harmelen F., Hendler J., Horrocks I., McGuinness D.L., Patel-Schneider P.F., Stein L.A. (Authors), OWL Web Ontology Language Reference, W3C Recommendation, 10 February 2004. HTML
- Other RDF Applications
- SPARQL Query Language for RDF (W3C Recommendation, 15 January 2008)
- PICS (Platform for Internet Content Selection)
- SKOS Simple Knowledge Organization System (W3C WD Jan 2008)
Overviews
- Mozilla's RDF pointers
- Oasis Resource Description Framework (RDF)
- W3C Data Formats A older (1997) note on the planned XML-centered framework
- Chris Waterson, RDF in Fifty Words or Less, Mozilla Magazine.
On-line validation
Various to sort out
- Supercharging WSDL with RDF Managing structured Web service metadata article by Uche Obbuji
- Rudolf: RDFViz Exploring tools for RDF Graph Visualisation by Dan Brickely, project page.
References
- Eric Miller An Introductionto the Resource Description Framework (1998), D-Lib Magazine May 1998, ISSN 1082-9873, HTML
- Manola Frank and Eric Miller (2004). RDF Primer, W3C Recommendation 10 February 2004, W3C.