BPMN and BPMS software: Difference between revisions
m (→The workflow) |
m (→The workflow) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
|+ Bonitasoft's vision of BPMN-related skills (slightly modified by DKS) | |+ Bonitasoft's vision of BPMN-related skills (slightly modified by DKS) | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Profile !! Subject area !! | ! Profile !! Subject area !! Tasks | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Business analyst || Process design || Model a process, define actors, check the model, and more, to create a process diagram ([[BPMN]]) for collaboration | | Business analyst || Process design || Model a process, define actors, check the model, and more, to create a process diagram ([[BPMN]]) for collaboration | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 20 December 2012
Introduction
This page will include a description of Business process management notation (BPMN) software and associated Business process management systems.
A Business process modeling lifecycle includes the ability to design, model, execute and monitor business processes. "Business" refers to any kind of environment where humans and machines have to coordinate in some kind of goal-oriented workflow.
See also:
- BPMN
- BPMN 1.2 tutorial (for a technical overview)
- BPMN 2 tutorial (not yet written ...)
- Workflow and Business process modeling (short overview articles)
- BPEL, the most popular process execution language for BPMN models.
- Intalio BPMS
The workflow
There is a lot of marketing waffle about how easy it is to implement BPMN models. Certainly, using a PBMN software combo can save a lot of time, but the processseems to be neither straight forward nor simple as of December 2012. There is no simple way from a BPMN model to an executable application.
The basic workflow (lifecycle) looks like this:
1) Modeling and simulation'
- Design / model a process
2) Data configuration, interface configuration and/or integration
This step is technically speaking the most difficult and implies configuring / implementing a lot of various types of parameters through various interfaces. E.g. specify the integration with other services, the interfaces, etc. This can be done in many different ways and is vendor specific. Often, it requires programming or at least scripting.
- Model data. Each type of data that participants can input/output has to be modeled in some way. Data can flow from one task to another or just be made available.
- User interface forms have to be defined for the execution engine
- A way to manage documents produced must be found (e.g. a WebDav document repository)
- Interaction with other services must be defined.
- Business rules can be defined (e.g. when a person has the right to obtain a higher salary for writing wiki contributions)
- Generate the server application(s)
3) Execute and manage
- Add processes
- Manage
4) Monitor
- Track activities and produce reports
Each of these steps require different competences and may be performed by people with very different profiles. E.g. Bonitasoft, in their introductory tutorials, presents a table that distinguishes between the business analyst, the process engineer, the application developer, and the (process) adminstrator and/or end user. In addition, a systems engineer may be needed.
| Profile | Subject area | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Business analyst | Process design | Model a process, define actors, check the model, and more, to create a process diagram (BPMN) for collaboration |
| Process engineer | Process definition | Add variables, define conditions on transitions, add connectors, and more, to make a process diagram executable |
| Application developer | Application development | Customize web forms, configure page flow, customize look 'n' feel, and more, to customize process web applications |
| Administrator | Process administration | Manage processes, cases, steps, users, etc. |
| End User | Use processes and process data | Use the system, use monitoring and reporting tools. Also can include process administration. |
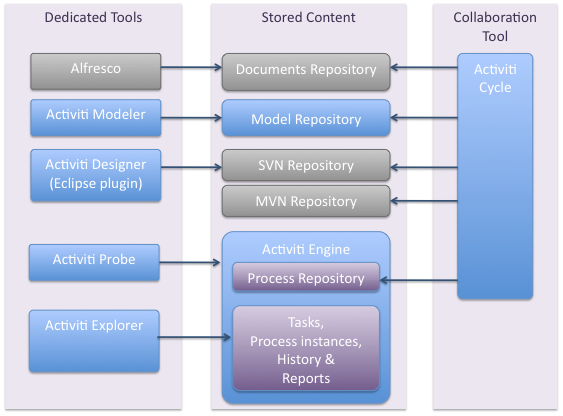
The following figure explains how different Activiti components (a popular BPMN suite) combine to form a complete solution for BPM in the full context of software development. The blue components are part of the Activiti scope. The gray components are out of scope. (Activiti Components, retrieved 14:30, 19 December 2012 (CET))
That kind of picture doesn't really tell what a designer has to do in order to have a working model. It involves a lot of XML parametrization and Java programming. In other words, going from a BPMN drawing to something that is executable is a long route. It may not require programming skills, but good understanding of data modeling, web services, UI design and so forth.
List of software
There exist several free tools. The commercial versions of the (commercial) free diagramming tools often include an execution engine. It is not always obvious to understand exactly what version of BPMN is supported. Some vendors already provide tools that implement draft versions of BPMN 2.0. See also diagramming software. Some general purpose diagramming tools allow to create BPMN models (although with all sorts of restrictions).
This list is by no means complete, see also the links sections below for better resources.
Free modelers
See rather the suites below. Most vendors provide both a modeller and an execution engine plus other middleware.
- Only drawing and simulation
- Oryx, (Signavio) a project to create BPMN 2.0 diagrams, EPCs or Petri nets online. Free for academics.
- OMII-BPEL, Modelling, monitoring, executing scientific workflows with BPEL. (We did not manage to install this, didn't find any installation instructions either ....)
- Yaoqiang BPMN Editor. Free BPMN 1.2 editor. See also their XPDL editor which does seem to use BPMN "syntax".
- Interfacing BPMN modeler. Free module for Viso. Registration required (not tested)
- BPMN 1.1 stencils for Visio and OmniGraffle by Frank Puhlmann and Alexander Großkopf.
- Additional functionality like simulation and BPM formats output
- FreeModeler.com. Free online modeling tool (design, validation, documentation and simulation).
- Sketchpad BPMN is a tool for drawing and editing BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation) diagrams. Sketchpad process models are serialized and stored as XPDL 2.1 files. Sketchpad was originally developed by Global 360 as Process Modeler Analyst Edition. (not tested)
- ADONIS:Community Edition (Windows only, needs SQL server).
- BPMN plugin for Eclipse. Made by Intalio. The tool can be download through the Eclipse IDE.
Totally or somewhat free suites
- Activiti
- Activiti BPM Suite, a workflow and Business Process Management (BPM) Platform (authoring tool and execution engine) targeted at business people, developers and system admins. This suite draws from prior experience with jBPMN (see below) and includes several tools, including a modeler and an execution engine.
- Activity designer (implemented as Eclipse plugin)
- Activity BPMN 2 process engine implemented in Java. It can run in a Java application
- See also the commercial alfresco product, the principal sponsor of Activiti.
- ARIS
- ARIS Express. Closed source freeware for BPMN 2/EPC from Software AG. (Java-based, tested under Ubuntu 10, works - Daniel K. Schneider 10:43, 23 June 2010 (UTC))
- Bonita
- Bonita includes “an innovative Studio for process modeling, a powerful BPM and workflow engine, and a breakthrough user interface.” (dec 2012). Basic functionality (modler and engine) is free and there are three subscription packs.
- Bonita Studio is a BPMN modeler, connector and forms creator
- The Bonita execution engine
- Documentation requires to register
- Jadex
- Jadex process. LGPL licence. “The Jadex Processes project provides modelling and execution facilities for workflows. Main focus is on graphical forms of process representation (e.g. the Business Process Modelling Notation - BPMN) and direct execution of modelled processes (i.e. without prior code generation).” ([1]). This is part of a larger project. Jadex is a Belief Desire Intention (BDI) reasoning engine that allows for programming intelligent software agents in XML and Java.
- Bizagi
- Bizagi Process Modeler. Closed source freeware for BPMN 1.x (?).
- Runs under Windows and requires .NET framework 2.0 (free) plus Visio 2003 or better for exporting features.
- Academics can get a free version of the BizAgi BPM Suite, i.e. a server that can run a model.
- Documentation is good, see e.g. My first process. (Tested, works - Daniel K. Schneider)
- Intalio
- Intalio|BPMS, claimed to be the world's most widely deployed Business Process Management System (BPMS). Designed around the open source Eclipse BPMN Modeler, Apache ODE BPEL engine, and Tempo. The free community edition runs under a TomCat server (Windows and Red Hat officially supported) and either Derby or MySQL enterprise server. The software includes a BPMN designer, a BPEL server and WS-Human Task Service.
- BPMN 1.x (as of dec 2012)
- Read Intalio BPMS
- jBPM
- jBPM is “a flexible Business Process Management (BPM) Suite. It makes the bridge between business analysts and developers”.
- BPMN 2.0 support
- Implemented under jBoss.
Online BPMN modeling tools
- Modelers
- Free online validation
- Signavio BPMN 2.0 validator (very first prototype, URL may change, 20:08, 4 October 2012 (CEST)
Commercial only
(not complete since edutechwiki is not about BPM ...)
- Intalio BPM, includes the interesting Social BPM that combines the BPM design tool with a social portal building framework. Very cool, has the potential for use in education to implement learning design/web 2.0 combos.
- BariumLive Authoring and runtime tools available as web applications (free 30 day trials).
Links
- Overviews
- The Great Unknown: BPM Open Source by Alberto del Rio @ Decide Soluciones | March 22, 2012
- Lists of software
- BPMN Implementors and Quotes (best link, at OMG, however no extra information)
- Comparison of Business Process Modeling Notation tools (Wikipedia)
- Tools (BPM forum, not very complete)
- BPM solutions at bpmnleader.com