Hype cycle: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Introduction) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
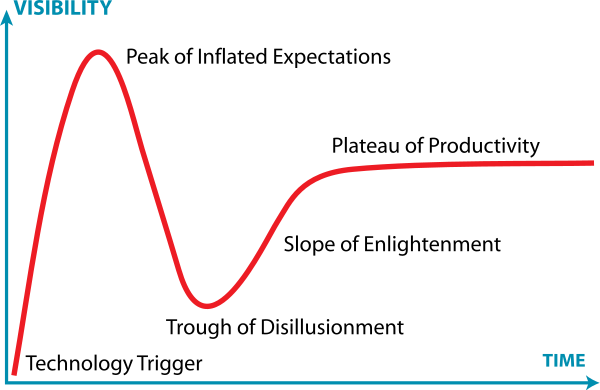
[[File:Gartner_Hype_Cycle-wikipedia|thumb]] | [[File:Gartner_Hype_Cycle-wikipedia.svg|thumb|600px|none|The Gartner Hype Cycle curve]] | ||
[[File:Hype-Cycle-General.png|thumb| | |||
[[File:Hype-Cycle-General.png|thumb|600px|none|A detailed explanation by Jeremy Kemp]] | |||
== The relation to other innovation curves == | == The relation to other innovation curves == | ||
The hype cycle curve does not display adoption. Altough there is a relationship, the curve looks very different, i.e. is cumulative until the items drops out of history. | The hype cycle curve does not display adoption. Altough there is a relationship, the curve looks very different, i.e. is cumulative until the items drops out of history. | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
Revision as of 18:02, 30 November 2016
Introduction
According to Wikipedia (11/2016), “the hype cycle is a branded graphical presentation developed and used by American information technology (IT) research and advisory firm Gartner for representing the maturity, adoption and social application of specific technologies. The hype cycle provides a graphical and conceptual presentation of the maturity emerging technologies through five phases.”
The relation to other innovation curves
The hype cycle curve does not display adoption. Altough there is a relationship, the curve looks very different, i.e. is cumulative until the items drops out of history.
Links
- General
- Hype cycle (Wikipedia)
- In education / educational technology
- Interactive Hype cycle for educational technology (University of Minnesota). This is the best address for hype trending. Various filters can be applied and each item has an attache explanation page.