Citizen science
Links and bibliography below was directly taken from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Citizen_science
I will start working on this piece on January 2012 and try to do some quick literature review, in particular with respect to topics like "how do participants learn", "in what respect are citizens creative", "what is their motivation", "how to communities work"
- Daniel K. Schneider 16:43, 23 December 2011 (CET)
Introduction
Citizen science does not have a uniquely accepted definition. It could mean:
- Participation of citizen for collection of data, for example observation of animals, pollution, or plant growth.
- Participation of citizen for analyzing data, in various forms. For example, some provide computing power (a typical example is the captcha mechanism in this wiki for curbing spam). Another would be helping to recognize patterns (e.g. forms of galaxies)
- Dissemination of scientific thought and result in schools in order to promote engagement with science or with the intent to help updating the curriculum.
- Amateur science, i.e. citizen create scientific thoughts and other products.
- Citizen assessment of science and scientific projects.
The variety of citizen science programs is important with respect to many criteria, e.g.: aims, target population, locations (schools, museums, media, Internet groups), forms, subject areas, etc.
Wiggins and Crowston (2011) identified “five mutually exclusive and exhaustive types of projects, which [they] labelled Action, Conservation, Investigation, Virtual and Education. Action projects employ volunteer-initiated participatory action research to encourage participant intervention in local concerns. Conservation projects address natural resource management goals, involving citizens in stewardship for outreach and increased scope. Investigation projects focus on scientific research goals in a physical setting, while Virtual projects have goals similar to Investigation projects, but are entirely ICT-mediated and differ in a number of other characteristics. Finally, Education projects make education and outreach primary goals”.
Wiggins and Crowston (2012) then created two typologies of citizen science projets, using data from 63 projects. A first typology is based on twelve participation tasks, i.e. Observation, Species identification, Classification or tagging, Data entry, Finding entities, Measurement, Specimen/sample collection, Sample analysis, Site selection &/or description, Geolocation, Photography, Data analysis, and Number of tasks. The other typology is based on ten project goals, i.e. Science, Management, Action, Education, Conservation, Monitoring, Restoration, Outreach, Stewardship, and Discovery.
Participation clusters:
- Involve observation and identification tasks, but never require analysis. (13)
- Involve observation, data entry, and analysis, but include no locational tasks such as site selection or geolocation (6)
- Engage participants in a variety of tasks, the only participation task not represented is sample analysis (17)
- Engage the public in every participation task considered (15)
- Involve reporting, using observations, species identification, and data entry, but with very few additional participation opportunities (12)
Goal clusters:
- Afforded nearly equal weights (midpoint of the scale or higher) to each of the goal areas
- Most strongly focused on science
- Science is the most important goal, but education, monitoring, and discovery are only slightly less important on average
- Science, conservation, monitoring and stewardship are most important, while discovery is less valued than in the preceding clusters
- Outlier
For other typologies, see Wiggins and Crowston (2012).
Topics in the study of citizen science projects
Motivation
Motivation and motivation in education are complex constructs. A typical general model includes several components. E.g. Herzberg's (1959) five component model of job satisfaction includes achievement, recognition, work itself, responsibility, and advancement.
Some recent research by Raddick et al. (2010) about motivations of participants in cyberscience projects analyzed free forum messages and structured interviews. The first mentioned categories include the subject (astronomy), contribution and vastness. Learning (3%) and Science (1%) were minor. Looking at all responses, the same motivations - subject (46%), contribution (22%), vastness (24%) - still dominate, but other motivations exceed 10%, e.g. beauty (16%), fun (11%) and learning (10%).
It might be interesting to also look at personality traits of participants. E.g. Furnham et al. (1999) in a study aboubt personality and work motivation found out that extraverts on the Eysenck Personality Profile correlate with a preference for Herzberg's motivators, whereas "neuroticism" correlates with so-called hygiene factors, i.e. the environment. In other words, extraverts are rather motivated by intrinsic factors whereas others by extrinsic ones.
Virtual organisations for citizen science
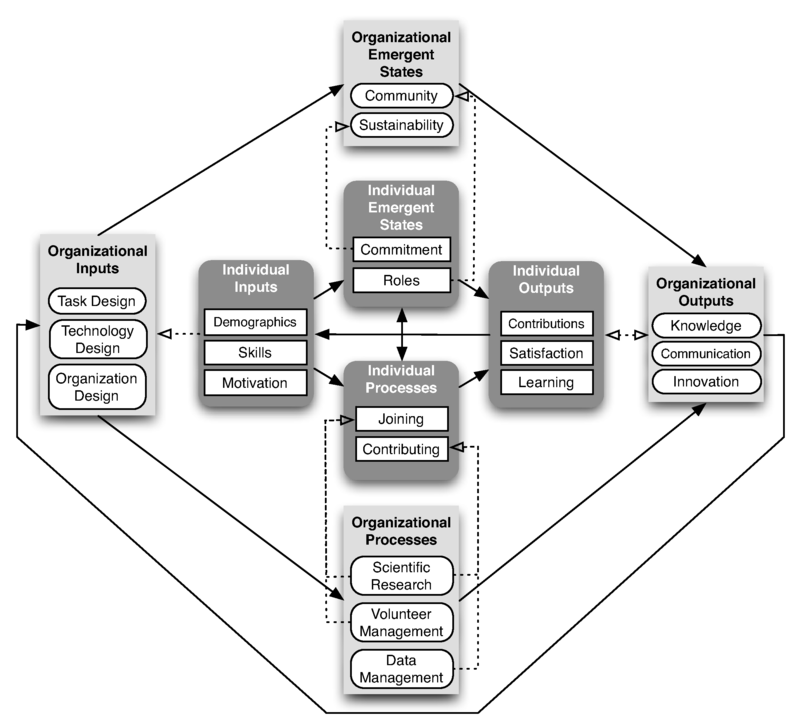
An important variant of citizen science uses citizens as helpers for research. “Citizen science is a form of organisation design for collaborative scientific research involving scientists and volunteers, for which internet-based modes of participation enable massive virtual collaboration by thousands of members of the public.” (Wiggins and Crowson, 2010:148). The authors argue that virtual organisations for citizen science are a bit different from other virtual organizations: “The project level of group interaction is distinct from those of small work groups and organisations (Grudin, 1994), which has implications for organisation design efforts. Project teams and communities of practice can be distinguished by their goal orientation among other features (Wenger, 1999), but empirical observation of citizen science VOs to date indicates a hybrid ‘community of purpose’ might better describe many projects, with characteristics of both a project team and a community of practice or interest.” (p 159).
Wiggins and Crowson then suggest a conceptual model of citizen science VOs:
Evaluation of informal science education
Informal science education refers mostly to larger or smaller top-down initiatives that aim to raise interest for STEM (Science, technology, engineering and mathematics) subjects. As an example, “The Informal Science Education (ISE) program at the National Science Foundation (NSF) invests in projects designed to increase interest in, engagement with, and understanding of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by individuals of all ages and backgrounds through self-directed learning experiences” (Ucko, 2008: 9)
Dierking (2008:19), a contributor to the US Framework for Evaluating Impacts of Informal Science Education Projectsin Friedman (2008), suggests that a project should be able to answer at least the following questions at the outset of initiating a project:
- What audience impacts will this project facilitate?
- What approach/type of project will best enable us to accomplish these goals and why do we feel that this is the best approach to take?
- How will we know whether the activities of the project accomplished these intended goals and objectives and with what evidence will we support the assertion that they did?
- How will we ensure that unanticipated outcomes are also documented?
This US "Informal education and outreach framework" (Uko 2008:11, Dierking 2008:21) identifies six impact categories with respect to both public audiences and professional audiences.
| Impact Category | Public Audiences | Professional Audiences | Generic Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Awareness, knowledge or understanding (of) | STEM concepts, processes, or careers | Informal STEM education/outreach research or practice. | Measurable demonstration of assessment of, change in, or exercise of awareness, knowledge, understanding of a particular scientific topic, concept, phenomena, theory, or careers central to the project. |
| Engagement or interest (in) | STEM concepts, processes, or careers | Advancing informal STEM education/outreach field | Measurable demonstration of assessment of, change in, or exercise of engagement/interest in a particular scientific topic, concept, phenomena, theory, or careers central to the project. |
| Attitude (towards) | STEM-related topic or capabilities | Informal STEM education/outreach research or practice | Measurable demonstration of assessment of, change in, or exercise of attitude toward a particular scientific topic, concept, phenomena, theory, or careers central to the project or one’s capabilities relative to these areas. Although similar to awareness/interest/engagement, attitudes refer to changes in relatively stable, more intractable constructs such as empathy for animals and their habitats, appreciation for the role of scientists in society or attitudes toward stem cell research. |
| Behavior (related to) | STEM concepts, processes, or careers | Informal STEM education/outreach research or practice | Measurable demonstration of assessment of, change in, or exercise of behavior related to a STEM topic. These types of impacts are particularly relevant to projects that are environmental in nature or have some kind of a health science focus since action is a desired outcome. |
| Skills (based on) | STEM concepts, processes, or careers | Informal STEM education/outreach research or practice | Measurable demonstration of the development and/or reinforcement of skills, either entirely new ones or the reinforcement, even practice, of developing skills. These tend to be procedural aspects of knowing, as opposed to the more declarative aspects of knowledge impacts. Although they can sometimes manifest as engagement, typically observed skills include a level of depth and skill such as engaging in scientific inquiry skills (observing, classifying, exploring, questioning, predicting, or experimenting), as well as developing/practicing very specific skills related to the use of scientific instruments and devices (e.g. using microscopes or telescopes successfully). |
| Other | Project specific | Project specific | Project specific |
From this table, Dierking (2008:23) then derives a simple worksheet for Developing Intended Impacts, Indicators & Evidence
| ISE Category of Impact | Potential indicators | Evidence that impact was attained |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness, knowledge or understanding of STEM concepts, processes or careers | ||
| Engagement or interest in STEM concepts, processes, or careers | ||
| Attitude towards STEM-related topics or capabilities | ||
| Behavior resulting from experience | ||
| Skills based on experience | ||
| Other (describe) |
Links
General
Organizations
- Citizen Science Alliance
- OpenScientist.org
- The Society of Amateur Scientists
- Citizen CyberScience Centre
- Expert and Citizen Assessment of Science and Technology
- Research2Practice, US web site for informal STEM education.
- InformalScience.org. A resource and online community for informal learning projects, research and evaluation. (USA)
Index pages
- scistarter (Science we ca do together)
On-line environments
- foldit is described as “a revolutionary new computer game enabling you to contribute to important scientific research.” I'd rather qualify it as en engaging cognitive tool.
- World Water Monitoring Day
- Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology projects
- Galaxy Zoo (Wikipedia)
- ParkScan
- Stardust@home (Wikipedia)
- Clickworkers (Wikipedia)
- Christmas Bird Count (Wikipedia)
- Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology projects (Wikipedia)
- CoCoRaHS (Wikipedia)
- Field Expedition: Mongolia
- ZooinVerse
Evaluation
- Informalscience.org/ is a resource and online community for informal learning projects, research and evaluation. It includes evaluations of several informal science learning projects
- Friedman, A. (Ed.). (March 12, 2008). Framework for Evaluating Impacts of Informal Science Education Projects [On-line]. http://informalscience.org/evaluations/eval_framework.pdf. Originally at: http://insci.org/resources/Eval_Framework.pdf (broken link)
- The 2002 User-Friendly Handbook for Project Evaluation, NSF (USA) by Joy Frechtling Westat
Bibliography
- Ballard, H., Pilz, D., Jones, E.T., and Getz, C. (2005). Training Curriculum for Scientists and Managers: Broadening Participation in Biological Monitoring. Corvalis, OR: Institute for Culture and Ecology.
- Baretto, C., Fastovsky, D. and Sheehan, P. (2003). A Model for Integrating the Public into Scientific Research. Journal of Geoscience Education. 50 (1). p. 71-75.
- Bauer, M., Petkova, K., and Boyadjieva, P. (2000). Public Knowledge of and Attitudes to Science: Alternative Measures That May End the "Science War". Science Technology and Human Values. 25 (1). p. 30-51.
- Bonney, R. and LaBranche, M. (2004). Citizen Science: Involving the Public in Research. ASTC Dimensions. May/June 2004, p. 13.
- Bonney, R., Cooper, C.B., Dickinson, J., Kelling, S., Phillips, T., Rosenberg, K.V. and Shirk, J. (2009). Citizen Science: A Developing Tool for Expanding Science Knowledge and Scientific Literacy. BioScience. 59 (11). P. 977-984.
- Bracey, G.L. 2009. “The developing field of citizen science: A review of the literature.” Submitted to Science Education. (not published yet as of 1/2011 ?)
- Bradford, B. M., and G. D. Israel. 2004. Evaluating volunteer motivation for sea turtle conservation in Florida. University of Florida: Agriculture Education and Communication Department, Institute of Agriculture and Food Sciences, AEC 372.
- Brossard, D., Lewenstein, B., and Bonney, R. (2005). Scientific Knowledge and Attitude Change: The Impact of a Citizen Science Project. International Journal of Science Education. 27 (9). p. 1099-1121.
- Cooper, C.B., Dickinson, J., Phillips, T., and Bonney, R. (2007). Citizen Science as a Tool for Conservation in Residential Ecosystems. Ecology and Society. 12 (2).
- Cooper, Seth, Firas Khatib, Adrien Treuille, Janos Barbero, Jeehyung Lee, Michael Beenen, Andrew Leaver-Fay, David Baker, Zoran Popović and Foldit players. Predicting protein structures with a multiplayer online games. Nature 466, 756-760 (2010).
- Firehock, K. and West, J. (2001). A brief history of volunteer biological water monitoring using macroinvertebrates. Journal of the North American Benthological Society. 14 (2) p. 197-202.
- Khatib, Firas; Seth Cooper, Michael D. Tyka, Kefan Xu, Ilya Makedon, Zoran Popović, David Baker, and Foldit Players. Algorithm discovery by protein folding game players. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2011).
- King, K., C.V. Lynch 1998. “The motivation of volunteers in the nature conservancy - Ohio chapter, a non-profit environmental organization.” Journal of Volunteer Administration 16, (2): 5.
- Herzberg, F., Mausner, B., and Snyderman, B. The Motivation to Work. (2nd rev. ed.) New York: Wiley, 1959.
- McCaffrey, R.E. (2005). Using Citizen Science in Urban Bird Studies. Urban Habitats. 3 (1). p. 70-86.
- Osborn, D., Pearse, J. and Roe, A. Monitoring Rocky Intertidal Shorelines: A Role for the Public in Resource Management. In California and the World Ocean: Revisiting and Revising California's Ocean Agenda. Magoon, O., Converse, H., Baird, B., Jines, B, and Miller-Henson, M., Eds. p. 624-636. Reston, VA: ASCE.
- Raddick, M. Jordan; Georgia Bracey, Pamela L. Gay, Chris J. Lintott, Phil Murray, Kevin Schawinski, Alexander S. Szalay, and Jan Vandenberg (2010). Galaxy Zoo: Exploring the Motivations of Citizen Science Volunteers, Astronomy Education Review 9, 010103 (2010), DOI:10.3847/AER2009036 - PDF Preprint
- Silvertown, J. (2009). A New Dawn for Citizen Science. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 24 (9). p. 467-471
- Spiro, M. (2004). What should the citizen know about science? Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 97 (1).
- Hand, Eric (2010). "Citizen science: People power". Nature 466, 685-687
- Ucko, David A. (2008), Introduction To Evaluating Impacts Of Nsf Informal Science Education Projects, in Friedman, A. (Ed.). Framework for Evaluating Impacts of Informal Science Education Projects [On-line]. http://informalscience.org/evaluations/eval_framework.pdf.
- Wiggins, A. and Crowston, K. (2010) ‘Developing a conceptual model of virtual organisations for citizen science’, Int. J. Organisational Design and Engineering, Vol. 1, Nos. 1/2, pp.148–162.
- Wiggins, A., & Crowston K. (2011). From Conservation to Crowdsourcing: A Typology of Citizen Science. Proceedings of the Forty-fourth Hawai'i International Conference on System Science (HICSS-44).
- Wiggins, A., & Crowston K. (2012). Goals and tasks: Two typologies of citizen science projects. Forty-fifth Hawai’i International Conference on System Science (HICSS-45)