Moodle
Introduction
Moodle is a popular LMS that is based on socio-constructivist concepts. The purpose of this page is to write down some tips and ideas about Moodle. It's neither an introduction nor a tutorial !
The reasons for its popularity relies in DSchneider's opinion on the facts that:
- The underlying teaching model comes very close to the way "it is done" in a typical anglo-saxon graduate presential course, i.e. students are active participants, have to do a variety of sometimes open ended assignments, group work, have to use teacher-prepared resources, do quizzes, etc.
- The system is quite stable and not too difficult to use.
- It has a nice user community that increasingly contributes to extensions.
See also: LAMS (Lams can be integrated with Moodle)
Discussion
- DSchneider doubts that a typical course found on a randomly chosen Moodle installation is truly socio-constructivist. They are most definitly not very constructionist, e.g. on-line student activity is often reduced to forum activities and uploads.
- The system is a bit slow, though version 1.9 is faster than 1.7. Version 2.2 didn't bring great performance gains. On a many user system one should install a PHP caching system - Daniel K. Schneider April 2008 / Dec 2011.
Useful extensions
- LAMS (to implement CSCL scripts and other guided learning designs)
Installation tips
Moodle should install without any problem on all kinds of LAMP installations. Make sure that your PhP meets all the requirements.
what version do you have
It is very difficult to find the version number and there may be several ways.
In Moodle 3.x it should be in both
- Site Administration -> Notifications
- Site Administration -> Server Tab -> Environment
Updating and installing
At TECFA, we frequently upgrade. To keep up with minor upgrades, it is best to work with their Revision control system. See Upgrading Moodle.
Using CVS (older Moodle installations)
(outdated, see GIT below)
To update a same version, type:
cvs update -dP
or to get a new specific version
cvs -Q update -dP -r The_Moodle_Version_you_need
E.g.
cvs -Q update -DP -r MOODLE_22_STABLE
Using GIT
Newer installations are encouraged to use Git
In short, for a first time upgrade with GIT, save the old files
$ mv moodle moodle_old
Then clone into a directory called moodle
$ git clone git://git.moodle.org/moodle.git $ cd moodle $ mv ../moodle_old/config.php . $ git branch -a $ git branch --track MOODLE_23_STABLE origin/MOODLE_23_STABLE $ git checkout MOODLE_23_STABLE
To update within a stable branch (minor revisions):
$ cd /path/to/your/moodle/ $ git pull
To update to a new stable branch without backing up:
// check branches git branch -a // example for tracking new version and then updating git branch --track MOODLE_26_STABLE origin/MOODLE_26_STABLE git checkout MOODLE_26_STABLE git pull
To update to a new stable branch with backing up:
// copy all the files (ajust to your installation directory) cd moodle_install_partent_dir sudo cp -rp moodle moodle_old // (Optional) copy the data files (ajust to your installation directory) cp -rp datadir datadir_old // dump the database mysqldump -u root -p moodle > moodle.sql
After that, do as above.
Reversing an update
(using git)
// E.g. revert from Moodle 3.0
git checkout MOODLE_29_STABLE
// repair the database (adjust db name and file name)
mysql -u root -p moodle < moodle.sql
PHP parameters
- Memory and execution time
Make sure to allocate enough memory and execution time in php.ini, i.e. at least 128MB.
Type in a console:
php --info | grep php.ini
Then edit the configuration file shown. E.g. high values would be:
max_execution_time = 600 ; Maximum execution time of each script, in seconds max_input_time = 600 ; Maximum amount of time each script may spend parsing request data memory_limit = 256M ; Maximum memory
The make sure that there is no other php.ini override (e.g. in httpd.conf), type
php --info | grep mem
- File upload
Also in php.ini
upload_max_filesize = 30M ; or whatever you find reasonable.
- cron_php5
You also may have to hand edit file moodle/search/cron_php5.php and manually change the "ini_get" lines (for what strange reason I don't know)
- If your Moodle is hosted with a provider
If you don't have console access, then deposit a file called test.php with contents:
phpinfo();
and look at the page. It does the same as php --info. DELETE after usage or protect it.
Cron jobs
Moodle should regularly be triggered to do things, i.e. you should install a cron jog, e.g. under Ubuntu:
- Create a file /etc/cron.d/moodle
# https://docs.moodle.org/24/en/Cron */15 * * * * www-data cd /__your_path_to_moodle/admin/cli/; /usr/bin/php cron.php >/dev/null
Else, use sudo crontab -u www-data -e
Themes
Default themes, are incredibly bad. E.g. "Formal white" can't display the width of a serious grading rubric, links are difficult to see. One option is to redesign and that can take time that is better spent on something else (IMHO).
To make small fixes, create a user style sheet (Menu: Site Administration -> Appearance -> Themes -> [Selected Theme])
- Scroll down and add something, e.g.
div.title {background-color:#E3DFD4;}
a:link {color:#00008B ;}
a:visited {color:#191970;}
.gradingform_rubric{max-width:1200px};
Make sure to turn the CSS caching off while you test:
- Menu: Site Administration -> Appearance -> Themes -> Theme Settings
LTI support in MOODLE
Starting Moodle 2.2 there is IMS LTI support in two ways.
- The core activity plugin called either
LTI>orExternal toolin older versions, allows to integrate LTI services. In other words, Moodle can connect to another system and let the user access services and contents transparently. This will require some setup. - The LTI provider plugin can turn Moodle into a LTI provide, e.g. you could provide access to full courses or activities from a remote system that has LTI support. Read Review: LTI Provider for Moodle 2.2 (needs to be installed)
LTI consumption with external tool
As explained in Moodle's external tool and external tools settings documentation, a teacher can add an external tool from their course page and an administrator can make an external tool available to all teachers on the site.
Adding a tool sitewide
Administrators can add an configure external tools.
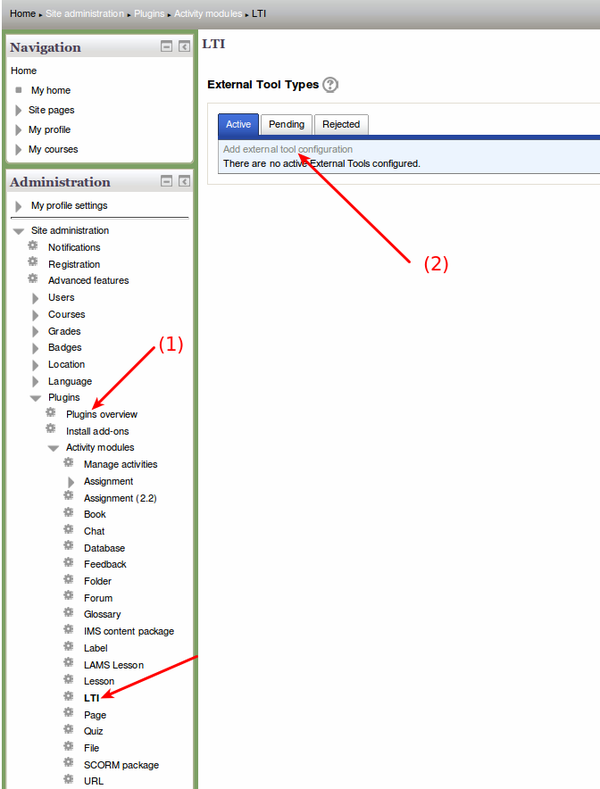
- (1) Find LTI Settings and add the external tool
- Settings > Site administration > Plugins Overview, then click on LTI Settings (In older versions, select "External tool" instead of LTI)
- Click on
Add external tool configuration
- (2) Configure the tools
You then configure new external tools. In order to do so, you should read the documentation of the external tool provider. You need to define a least
- A local name for the tool
- The URL of the tool
In addition you may have to define
- A consumer key, i.e. a kind of username used to authenticate access to the tool.
- A shared secret, i.e. password.
Under privacy, you can define if the launcher (i.e. Moodle student's ID and email) are forwarded to the tool and whether the tool can send grades back.
Added (active, pending or rejected) LTI modules then also can be seen here:
- Settings > Site administration > Plugins > Activity modules > LTI
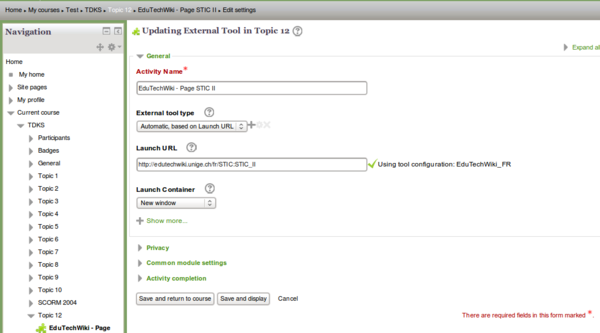
Adding a tool as teacher
- Turn editing on
- Add an activity or resource
- Select External Tool
The following screenshot shows a minimalistic setup, i.e. the equivalent of a simple web link. Such an LTI is of course pointless. In order to make this work, the wiki should at least accept a user login and password, i.e. be an LTI provider.
One could try out LTI4Mediawiki developed by Learning Apps.
- Sourceforge files: MediaWiki
The same group also developed plugins for a dozen other applications, such as Joomal, Mahara, Elgg, and Wordpress (see below) This MediaWiki plugin allows Moodle users to connect to a MediaWiki and create/edit files within a Category that has the name of the Moodle course. Members of the same Moodle class will use the same Mediawiki login/pw if we understood right.
An other alternative: Tools integration (Moodle and MediaWiki via OKI, probably outdated).
Wordpress integration
To do/try out, see:
- LTI4Wordpress (This is a IMS certified plugin for a Wordpress multisite).
List of external tools
- LTI Tools to try out yourself (Moodle News, Feb. 2013)
- LTI Store: share your demo connections (Moodle News).
- Edu Apps. Generic list of "educational apps" that are based on LTI.
Badges
Educational badges can be used in two contexts:
- Class badges: Each teacher can create badges for a class.
- System badges: Badges can be defined at the system level. These then also can be used by individual teachers, however this is quite cumbersome (read the FAQ). There are no prototype badges that a teacher could reuse. I.e. an enabled teacher can just award badges using the Site administration menu.
Documentation:
- Badges (Moodle v. 2.6). This documentation is well done.
- Badges FAQ
Use of badges
Badges can be given out automatically for course or activity completion (make sure that Completion tracking is enabled) or manually using the course or the site administration menu.
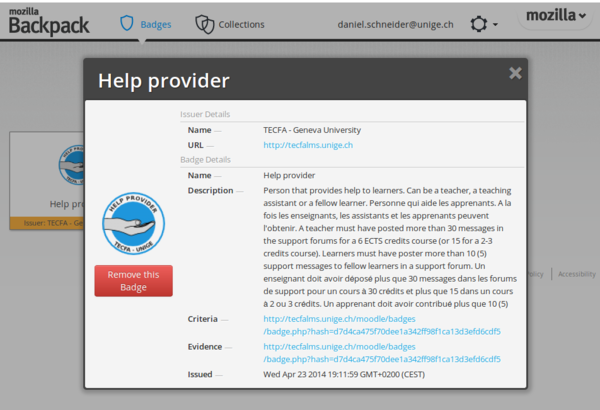
Badges can be uploaded by the receiver to the Mozilla Backpack by the users. You will have to create an account to do so.
Badge creation
Badge creation is pretty similar at the site and at the course level. You will have to define
- A name
- A description
- Criteria (manual by whom or automatic)
- An icon. SVG pictures don't seem to work well. Therefore it may be better to create a PNG image. A height of 80 to 100 pixels should be enough, but keep the original in case you plan to make changes.
E.g. the following was created from two SVG drawings in (roughly) the following way with Inkscape:
- Download Help, ungroup (several times), for the outer circle do stroke to path
- Download hand, import, move behind the outer circle
- Add the text. Use text path to align it to the circle.
Plugins
Installing a plugin is always a risk, since they go away after upgrading.
Plugins can be installed in different ways. The safest method is probably downloading a zip file or use git.
Plugins go to one of the following subdirectories:
- mod (for "normal" plugins)
- local (for "local" plugins)
- blocks
- themes
Google drive
URLS at Google
- Login to Google first (you need a Google account)
- https://console.developers.google.com/project
- Create a project, e.g. call it Google drive for Moodle
- Google: In API's: Drive API must be enabled (all the others can be off)
URLs in your Moodle
- admin/repository.php
... scroll down/search for Google Drive in the page
- admin/plugins.php
Bulk enrolment
Tested with Moodle 3.4 / Feb 2018.
Useful to enrol a whole bunch of students in a specific class with their email or Moodle ID. Can be used by teachers. Just use a text file with one column. Each line is either a Moodle login, id or email address. The first line will be skipped (!)
It must be installed in the ./local subdirectory !
The tool can be found in the Participants page, pulldown menu top right -> Bulk enrolments.
Exemple using Moodle IDs:
First line will be skipped schneiderd millera moodlegiant1
Alternative
Admins: If you use a CVS to create users you can use the same file to add user to a class by adding a column I believe. However, it may affect users and is potentially dangerous.
Links
- Moodle
- Help with Moodle
- Other
- Sloodle, a Second Life skin :)
- A more recent word from it's creator
- Some reflections about where Moodle is at, Martin Dougiamas, Posted on 22 May, 2015
References
- Dougiamas, M. & Taylor, P.C., Interpretive analysis of an internet-based course constructed using a new courseware tool called Moodle, Curtin University of Technology, [1]
- Philosophy (retrieved 16:40, 20 April 2006 (MEST))
- Brendan Moloney,Timothy Gutierrez. (2006) An Enquiry into Moodle Usage and Knowledge in a Japanese ESP program. PacCALL Journal Volume 2 No. 1 Summer 2006, Pp. 48-60. pdf