Sandberg learning environment functions: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
m (→References) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* Sandberg, J. A. (1994). Educational paradigms: issues and trends. In Lewis, R. Mendelsohn, P., (ed.), Lessons from Learning, (IFIP TC3/WG3.3 Working Conference 1993), pages 13--22, Amsterdam. North-Holland. | * Sandberg, J. A. (1994). Educational paradigms: issues and trends. In Lewis, R. Mendelsohn, P., (ed.), Lessons from Learning, (IFIP TC3/WG3.3 Working Conference 1993), pages 13--22, Amsterdam. North-Holland. | ||
[[Category: Instructional design | [[Category: Instructional design models]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:59, 28 May 2006
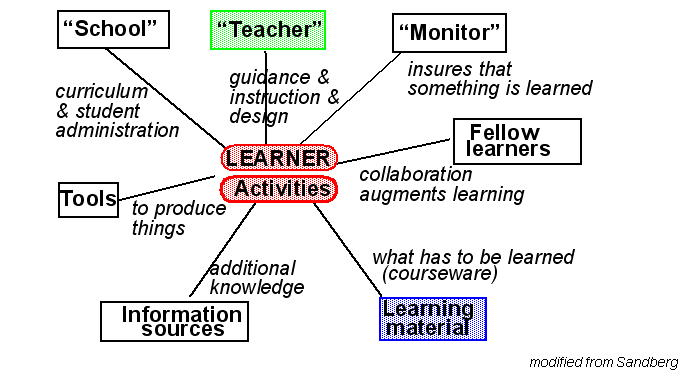
In discussing the role of technological support in education, [Sandberg, 1994, 225,] identifies the components of a (technologically rich) learning environment. These components must all be there in order to optimize learning. However, they can be ``implemented in many different ways. Each component has functionalities that we should insure:
- Teacher component: Its role is to provide something between loose guidance and direct instruction. It can be a human agent (present or distant), an intelligent agent, instructions like some text books provide, etc. This component provides information from the syllabus to the task level.
- Monitor component: Ensures that something is learned. A role taken by either the human teacher, the learner (self-control) or by some program.
- Fellow learners component: Improves the learning process by collaborative learning principle
- Learning material: Contains what has to be learned in a very broad sense (knowing what, knowing how). It can be computational in various ways (exploratory hypertext, lesson and task oriented hypertext, simulation software, task solving environments, etc.).
- External information sources: All kinds of information which is not directly stored in the learning material (e.g. the Internet as a whole, a web site, additional materials, handbooks, manuals, etc.).
- Tools: Everything which may help the learning process other then the learning material (e.g. calculators, communication software, etc.)
- School [a category we added]: Something that provides a curriculum.
References
- Sandberg, J. A. (1994). Educational paradigms: issues and trends. In Lewis, R. Mendelsohn, P., (ed.), Lessons from Learning, (IFIP TC3/WG3.3 Working Conference 1993), pages 13--22, Amsterdam. North-Holland.