Cybergogy: Difference between revisions
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
* Carrier, S. I., & Moulds, L. D. (2003). Pedagogy, andragogy, and cybergogy: exploring best-practice paradigm for online teaching and learning. Sloan-C 9th International Conference on Asynchronous Learning Networks (ALN), Orlando, USA [http://www.sloanc.org/conference/proceedings/2003/ppt/1471.ppt PPT] | * Carrier, S. I., & Moulds, L. D. (2003). Pedagogy, andragogy, and cybergogy: exploring best-practice paradigm for online teaching and learning. Sloan-C 9th International Conference on Asynchronous Learning Networks (ALN), Orlando, USA [http://www.sloanc.org/conference/proceedings/2003/ppt/1471.ppt PPT] | ||
* Wang, M. & Kang, M. (2006) Cybergogy for engaged learning: A framework for creating learner engagement through information and communication technology in Engaged Learning with Emerging Technologies Hung, D.; Khine, M.S. (Eds.), Springer. | * Wang, M. J. & Kang, M. (2006) Cybergogy for engaged learning: A framework for creating learner engagement through information and communication technology in Engaged Learning with Emerging Technologies Hung, D.; Khine, M.S. (Eds.), Springer. | ||
* Wang, M. (2007) Designing online courses that effectively engage learners from diverse cultural backgrounds British Journal of Educational Technology 38 (2), 294-311 | * Wang, M. J. (2007) Designing online courses that effectively engage learners from diverse cultural backgrounds British Journal of Educational Technology 38 (2), 294-311 | ||
* Wang, M. J. (2008). Cybergogy for engaged learning. Journal of Open and Distance Education in China, 14(2), 14-22, Retrieved June 12th, 2008 from http://openedu.shtvu.edu.cn/frontsite/series_details.asp?id=635 | |||
[[Category:Instructional design models]] | [[Category:Instructional design models]] | ||
[[Category:Pedagogic strategies]] | [[Category:Pedagogic strategies]] | ||
Revision as of 06:15, 1 December 2009
Cybergogy is an instructional design model created by Wang et al.
Summary
- Quotations in the text below should be more clearly identified - Daniel K. Schneider 13:21, 18 October 2008 (UTC).
The application of educational technology has created a new teaching and learning concept – Cybergogy. One of the central elements of cybergogy is the intent to combine fundamentals of both pedagogy and andragogy to arrive at a new approach to learning (Carrier & Moulds, 2003). Cybergogy focuses on helping adults and young people to learn by facilitating and technologically enabling learner-centered autonomous and collaborative learning in a virtual environment. At the core of cybergogy is awareness that strategies used for face-to-face learning may not be the same used in the virtual environment.
Facilitators need to be mindful of Cybergogy. As many studies reveal, learner’s active engagement in the learning process affects their learning outcomes. In any learning environment, truly engaged learners are behaviorally, intellectually, and emotionally involved in their learning tasks (Wang & Kang, 2006; Wang, 2007). Cybergogy for Engaged Learning Model is created by Dr. Minjuan Wang (Educational Technology, San Diego State University), and Dr. June Kang (Educational Technology, Ewha Womans University, South Korea). This model is a synthesis of current thinking, concepts, and theoretical frameworks on the extent and nature of the domains in learner online engagement. The Cybergogy model is published as a book chapter, a peer-reviewed journal article, and also recognized as an innovative model for instructional design.
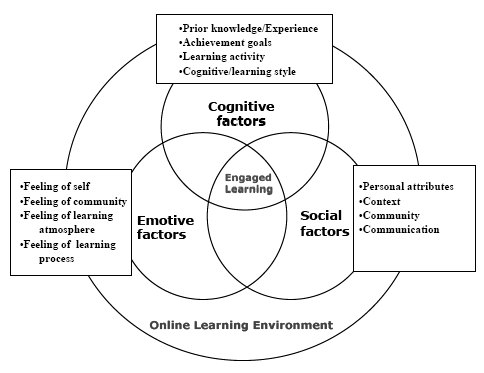
The Cybergogy for Engaged Learning model, as Wang and Kang (2006) present, has three overlapping/intersecting domains: cognitive, emotive, and social. For the online learning experience to be successful, students must be furnished with prior knowledge, motivated to learn, and positively engaged in the learning process. In addition, Wang and Kang suggest, students must also be comfortable with the learning environment and feel a strong sense of community and social commitment. The Cybergogy for Engaged Learning model could be used to conduct needs assessment and to lay out course design and facilitation techniques. Instructors could use this model to profile each student’s cognitive, emotive and social attributes and then effectively engage learners by addressing individual’s learning needs and attributes (Wang & Kang, 2006). The authors identify methods that instructors can use to detect learners’ emotional cues and cultivate their positive feelings; to increase learners’ self-confidence and arouse their curiosity through course design and e-facilitation; to conduct online communication and build a supportive learning environment.
The continued and growing need for new learning opportunities, linked with newer information systems and communication technologies, has pushed online learning into the center of the discussion of educational practice. There is a need to establish a framework for generating meaningful and engaging learning experiences for distance students with diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds. We coin the term “Cybergogy” as a descriptive label for the strategies for creating engaged learning online. Our model of Cybergogy for Engaged Learning (see the figure) has three overlapping/intersecting domains: cognitive, emotive, and social. This model is a synthesis of current thinking, concepts, and theoretical frameworks on the extent and nature of the three domains in learner engagement online. The instructors can use this model to profile each learner and then design tactics to engage individuals accordingly, a process we call “customized engagement.” As a consequence, learners will not only have the opportunity to accomplish their learning goals, but also will be actively involved in the learning process.
Literature
- Carrier, S. I., & Moulds, L. D. (2003). Pedagogy, andragogy, and cybergogy: exploring best-practice paradigm for online teaching and learning. Sloan-C 9th International Conference on Asynchronous Learning Networks (ALN), Orlando, USA PPT
- Wang, M. J. & Kang, M. (2006) Cybergogy for engaged learning: A framework for creating learner engagement through information and communication technology in Engaged Learning with Emerging Technologies Hung, D.; Khine, M.S. (Eds.), Springer.
- Wang, M. J. (2007) Designing online courses that effectively engage learners from diverse cultural backgrounds British Journal of Educational Technology 38 (2), 294-311
- Wang, M. J. (2008). Cybergogy for engaged learning. Journal of Open and Distance Education in China, 14(2), 14-22, Retrieved June 12th, 2008 from http://openedu.shtvu.edu.cn/frontsite/series_details.asp?id=635