Learner interaction scripting language: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The ''Learner interaction scripting language'' (LISL) is a design language model for creating, managing, maintaining, and learning about learning environment design. It is complemented by a proof of concept, the MUPPLE platform. | The ''Learner interaction scripting language'' (LISL) is a design language model for creating, managing, maintaining, and learning about learning environment design. It is complemented by a proof of concept, the MUPPLE platform. | ||
See also: [[Personal learning environment]], [[CSCL | See also: [[Personal learning environment]], [[CSCL script]] | ||
== The language == | |||
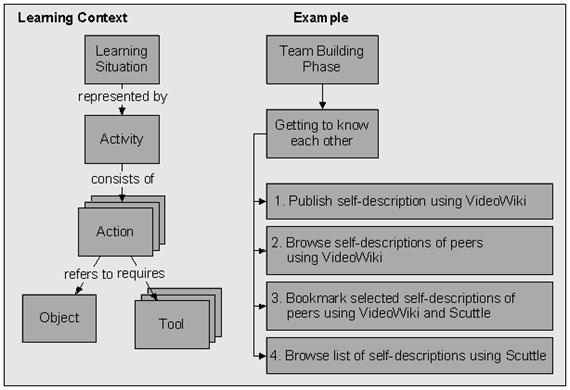
{{quotation|Basically, we break down the learning context into situations which describe the physical and social environment of learners. In such a situation, a learner is engaged in a so-called activity which consists of actions and includes tools, artefacts, and other actors (facilitators or peers). In contrast to instructional design, these actions represent more prominently commands for self-organising the learning process.}} (Wild et al. 2008: 6) | |||
== Example == | |||
The following example (including the figures) has been copied from [http://www.elearningeuropa.info/files/media/media15972.pd Wild et al. 2008]. | |||
[[image:mupple-example.jpg|frame|none|Semantic model behind MUPPLE, including | |||
the exemplary activity 'Getting to Know Each Other']] | |||
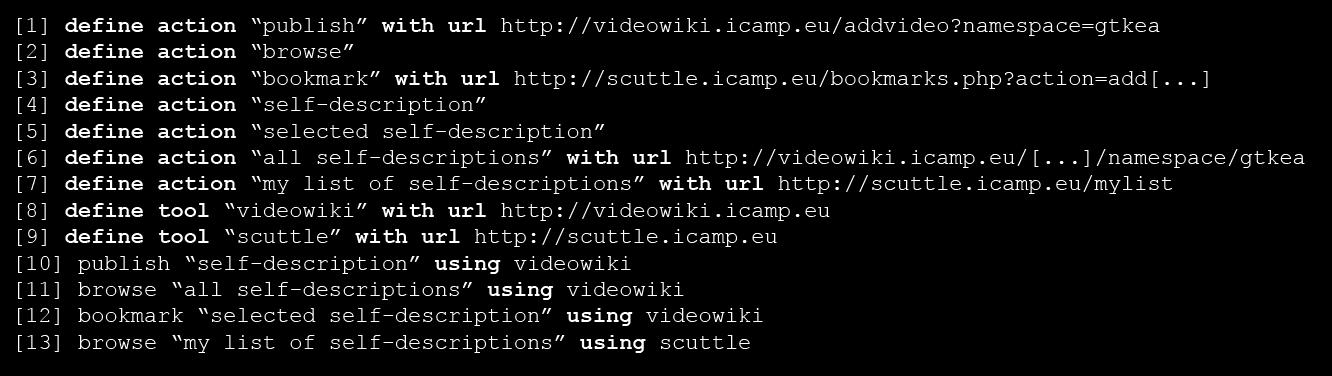
[[image:mupple-example-code.jpg|frame|none|LISL code for the exemplary learning | |||
activity 'Getting to know each other'.]] | |||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
* Wild Fridolin; Felix Mödritscher and Steinn Sigurdarson (2008). | * Wild Fridolin; Felix Mödritscher and Steinn Sigurdarson (2008). Designing for Change: Mash-Up Personal Learning Environments, ''eLearning Papers''. http://elearningpapers.eu, 9. ISSN 1887-1542. | ||
Designing for Change: Mash-Up Personal Learning Environments. | |||
[http://www.elearningeuropa.info/files/media/media15972.pdf PDF] | [http://www.elearningeuropa.info/files/media/media15972.pdf PDF] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category: Educational modeling languages]] | [[Category: Educational modeling languages]] | ||
[[Category: Educational technologies]] | [[Category: Educational technologies]] | ||
[[Category: Personal learning environments]] | |||
Revision as of 15:51, 20 August 2008
Definition
The Learner interaction scripting language (LISL) is a design language model for creating, managing, maintaining, and learning about learning environment design. It is complemented by a proof of concept, the MUPPLE platform.
See also: Personal learning environment, CSCL script
The language
“Basically, we break down the learning context into situations which describe the physical and social environment of learners. In such a situation, a learner is engaged in a so-called activity which consists of actions and includes tools, artefacts, and other actors (facilitators or peers). In contrast to instructional design, these actions represent more prominently commands for self-organising the learning process.” (Wild et al. 2008: 6)
Example
The following example (including the figures) has been copied from Wild et al. 2008.
Bibliography
- Wild Fridolin; Felix Mödritscher and Steinn Sigurdarson (2008). Designing for Change: Mash-Up Personal Learning Environments, eLearning Papers. http://elearningpapers.eu, 9. ISSN 1887-1542.
- Mödritscher, F., Neumann, G., García-Barrios, V.M., and Wild, F. (2008). A Web Application Mashup Approach for eLearning. Proceedings of the OpenACS and .LRN Conference, pp. 105-110.
- Wild, F., and Sigurdarson, S.E. (2008). Distributed Feed Networks for Learning. In: The European Journal for the Informatics Professional (UPGRADE),