HTML5 video and JavaScript: Difference between revisions
m (→Introduction) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{incomplete}} | |||
{{web technology tutorial|Intermediate}} | {{web technology tutorial|Intermediate}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
* Mp4 / H.264 with .mp4 extension | * Mp4 / H.264 with .mp4 extension | ||
* Ogg / Theora with .ogv extension | * Ogg / Theora with .ogv extension | ||
The advantage of having native elements for [[HTML5|HTML5]] media elements also implies the availability of an API to interact with <code>audio</code> and <code>video</code> elements with [[JavaScript|JavaScript]] . The Media Elements API provides: | The advantage of having native elements for [[HTML5|HTML5]] media elements also implies the availability of an API to interact with <code>audio</code> and <code>video</code> elements with [[JavaScript|JavaScript]] . The Media Elements API provides: | ||
| Line 38: | Line 37: | ||
In the rest of this section, we will illustrate some examples for each framework of use. The <code>audio</code> and <code>video</code> elements being very close, the examples will focus mainly on the video tag, but can be easily adapted to the audio tag. | In the rest of this section, we will illustrate some examples for each framework of use. The <code>audio</code> and <code>video</code> elements being very close, the examples will focus mainly on the video tag, but can be easily adapted to the audio tag. | ||
==Control audio / video with JavaScript== | |||
The JavaScript API for media elements provides 3 methods to control them: | The JavaScript API for media elements provides 3 methods to control them: | ||
| Line 137: | Line 50: | ||
myVideo.play () | myVideo.play () | ||
In addition, as objects, the audio / video elements also have several properties, among which are | In addition, as objects, the audio / video elements also have several properties, among which are: | ||
* <code>currentTime</code> : time at a given time in reading the media file in seconds | * <code>currentTime</code> : time at a given time in reading the media file in seconds | ||
| Line 143: | Line 56: | ||
* <code>volume</code> : <code>volume</code> level (between 0.0 and 1.0) | * <code>volume</code> : <code>volume</code> level (between 0.0 and 1.0) | ||
Like any property of an object, they | Like any property of an object, they are used in two ways: | ||
# Retrieve the value associated with a given property | # Retrieve the value associated with a given property | ||
# Associate a new value | # Associate a new value to a given property | ||
Here is an example with the <code>currentTime</code> property for a given instance of myVideo: | Here is an example with the <code>currentTime</code> property for a given instance of myVideo: | ||
| Line 154: | Line 67: | ||
myVideo.currentTime = 60; // Move the player of the video to 60 seconds | myVideo.currentTime = 60; // Move the player of the video to 60 seconds | ||
</ | </source> | ||
===Create controls for a video in HTML=== | |||
Thanks to the methods and properties associated with the <code>video</code> tag, one can easily create custom controls that replace the standard controls added by the browser if the <code>controls</code> attribute is declared. To do this, one must first have a video | Thanks to the methods and properties associated with the <code>video</code> tag, one can easily create custom controls that replace the standard controls added by the browser if the <code>controls</code> attribute is declared. To do this, one must first have a handle to a video for which the controls attribute is not declared, even if the presence or absence of standard controls does not influence the operation of external controls. An example is below: | ||
<source lang = "HTML5"> | <source lang = "HTML5"> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 78: | ||
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.mp4"> | <source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.mp4"> | ||
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.webm"> | <source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.webm"> | ||
</ | </video> | ||
</ | </source> | ||
Then we add three buttons with the <code>button</code> tag for the play, pause and stop controls. | Then we add three buttons with the <code>button</code> tag for the play, pause and stop controls. | ||
<source lang = "HTML5"> | <source lang = "HTML5"> | ||
<button id = "playBtn"> Play </ button> <button id = "pauseBtn"> Pause </ button> <button id = "stopBtn"> Stop </ button> | <button id = "playBtn"> Play </button> | ||
</ | <button id = "pauseBtn"> Pause </button> | ||
<button id = "stopBtn"> Stop </button> | |||
</source> | |||
Finally, we add the JavaScript code (in an external file or inside a <code>script</code> tag): | Finally, we add the JavaScript code (in an external file or inside a <code>script</code> tag): | ||
| Line 198: | Line 113: | ||
myVideo.currentTime = 0; | myVideo.currentTime = 0; | ||
} | } | ||
</ | </source> | ||
* [ | * [https://codepen.io/danielkschneider/pen/dmJYwY Test this example] | ||
* [http://codepen.io/mafritz/pen/zvWwGp See a more complex example, with volume control] | * [http://codepen.io/mafritz/pen/zvWwGp See a more complex example, with volume control] | ||
===Control an audio in background=== | |||
In some applications, such as video games, there is often background music that repeats itself in time, but that the user can decide | In some applications, such as video games, there is often a background music that repeats itself in time, but that the user can decide stop if he wishes. There are several ways to create a background audio element HTML5, but the easiest way is to '''insert an audio element without setting the <code>controls</code> attribute''' .In most web browsers that support the audio tag, this simply disguises the controls. | ||
Here is the HTML code that inserts audio with multiple sources as well as two ON and OFF buttons. | Here is the HTML code that inserts audio with multiple sources as well as two ON and OFF buttons. In order start audio in the background automatically it is necessary to declare the attribute <code>autoplay</code>. You also should add the attribute <code>loop</code>, in order to repeat the sound : | ||
<source lang = "JavaScript"> | <source lang = "JavaScript"> | ||
| Line 216: | Line 131: | ||
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-audio/audio/guitar.wav"> | <source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-audio/audio/guitar.wav"> | ||
Your browser does not support HTML5. Maybe you should upgrade. | Your browser does not support HTML5. Maybe you should upgrade. | ||
</ | </audio> | ||
</ | </source> | ||
To control the volume of the audio, instead of two buttons, you can use a range '''input''' (introduced with HTML5). For this type of input we can define: | To control the volume of the audio, instead of two buttons, you can use a range '''input''' (introduced with HTML5). For this type of input we can define: | ||
| Line 229: | Line 144: | ||
<source lang = "HTML5"> | <source lang = "HTML5"> | ||
Audio volume <input type = "range" min = "0" max = "1" step = "0.1" value = "1" id = "audioVolume"> | Audio volume <input type = "range" min = "0" max = "1" step = "0.1" value = "1" id = "audioVolume"> | ||
</ | </source> | ||
The basic volume of an audio / video source is the maximum value of 1, so that the range and the volume correspond we define a <code>value</code> of '''1''' which will then be modified with the cursor. Each move corresponds to a change of '''0.1''' (defined by the <code>step</code> value). | The basic volume of an audio / video source is the maximum value of 1, so that the range and the volume correspond we define a <code>value</code> of '''1''' which will then be modified with the cursor. Each move corresponds to a change of '''0.1''' (defined by the <code>step</code> value). | ||
| Line 244: | Line 159: | ||
audio.volume = audioVolume.value; | audio.volume = audioVolume.value; | ||
} | } | ||
</ | </source> | ||
[http://codepen.io/mafritz/pen/RWMyBe Test this example] | [http://codepen.io/mafritz/pen/RWMyBe Test this example] | ||
| Line 250: | Line 165: | ||
It is also possible to create the audio element directly in JavaScript using the <code>document.createElement("audio")</code> and specifying the <code>autoplay</code> and <code>loop</code> attributes. | It is also possible to create the audio element directly in JavaScript using the <code>document.createElement("audio")</code> and specifying the <code>autoplay</code> and <code>loop</code> attributes. | ||
==Interactive audio / video with JavaScript== | |||
Earlier we have seen that audio / video elements can be controlled by other elements of the DOM and, consequently, also by DOM-related events. You can, for example, trigger a video based on | Earlier we have seen that audio / video elements can be controlled by other elements of the DOM and, consequently, also by DOM-related events. You can, for example, trigger a video based on page scrolling, or stop it if the user is writing something in a text field. On the other hand, it is also possible to modify other elements of the DOM according to events directly related to the audio / video element. Here is a non-exhaustive list of events related to audio / video: | ||
* <code>onplay()</code> : event triggered each time the media starts or restarts; | * <code>onplay()</code> : event triggered each time the media starts or restarts; | ||
| Line 258: | Line 173: | ||
* <code>ontimeupdate()</code> : event triggered each time the playback time changes. | * <code>ontimeupdate()</code> : event triggered each time the playback time changes. | ||
=== | ===Prompt the user with a question at a given point in a video=== | ||
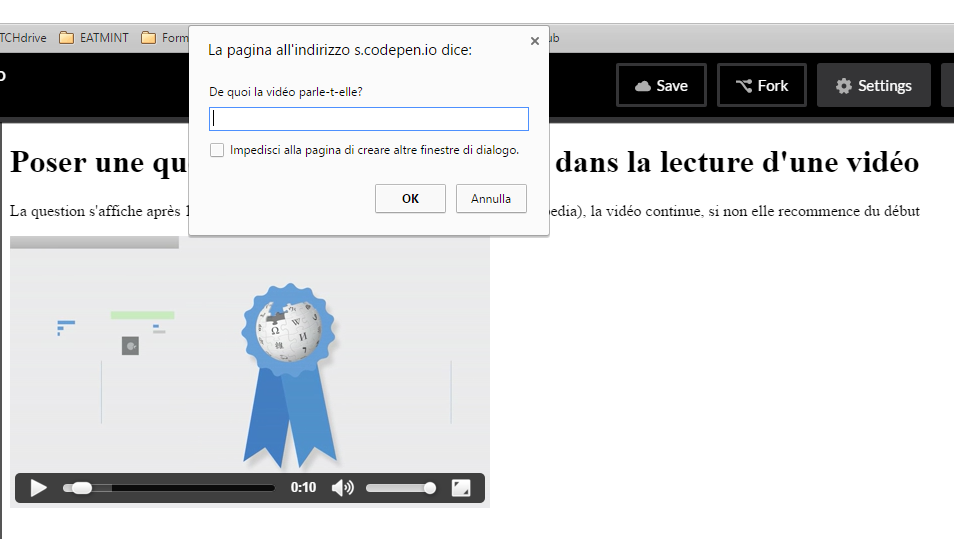
In this example, we will display a question (using the JavaScript <code>prompt()</code> ) after 10 seconds of playing the video. If the user answers the question correctly, the video will resume normally, otherwise it will resume from the beginning. Here is the result in image: | In this example, we will display a question (using the JavaScript <code>prompt()</code> ) after 10 seconds of playing the video. If the user answers the question correctly, the video will resume normally, otherwise it will resume from the beginning. Here is the result in an image: | ||
[[File:HTML5 audio et video audio prompt question.png|none|frame|A prompt box appears after 10 seconds, if the answer is correct the video continues, if not it starts again.]] | [[File:HTML5 audio et video audio prompt question.png|none|frame|A prompt box appears after 10 seconds, if the answer is correct the video continues, if not it starts again.]] | ||
| Line 268: | Line 183: | ||
<h1>Ask a question at a given point in a video</h1> | <h1>Ask a question at a given point in a video</h1> | ||
<p>The question is displayed after 10 seconds, if the answer given is correct ( | <p>The question is displayed after 10 seconds, if the answer given is correct (i.e. "Wikipedia"), the video continues, if not it starts again from the beginning</p> | ||
<video id = "myVideo" controls> | <video id = "myVideo" controls> | ||
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.mp4"> | <source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.mp4"> | ||
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.webm"> | <source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.webm"> | ||
</ | </video> | ||
</ | </source> | ||
And here the commented JavaScript code: | And here the commented JavaScript code: | ||
| Line 286: | Line 201: | ||
if (currentTime == 10) { | if (currentTime == 10) { | ||
myVideo.pause (); | myVideo.pause (); | ||
// Ask the question | // Ask the question with a promt | ||
var r = prompt ("What is the video about?" | var r = prompt ("What is the video about?"); | ||
// check the answer | // check the answer | ||
if (r.toLowerCase () == "wikipedia") { | if (r.toLowerCase () == "wikipedia") { | ||
| Line 297: | Line 212: | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
} </ | } | ||
</source> | |||
[http://codepen.io/mafritz/pen/GpdbEq Test this example] (Please note that using prompt is not ergonomic at all, it would be better to use an HTML form) | [http://codepen.io/mafritz/pen/GpdbEq Test this example] (Please note that using prompt is not ergonomic at all, it would be better to use an HTML form) | ||
[[ | ==Create audio / video elements with JavaScript == | ||
===Add a simple video=== | |||
The <code>video</code> tag can be treated like any other tag in the DOM, so you can easily create one with the <code>document.createElement("video")</code> and then set the video's attributes like source, controls, and so on. Here's an example that adds a video inside a <code>div</code> with '''id = "myVideo"''' . | |||
HTML code | |||
<source lang = "HTML5"> | |||
<h2>Video inserted with JavaScript</h2> | |||
<div id="myVideo"></div> | |||
</source> | |||
JavaScript code: | |||
<source lang = "JavaScript"> | |||
var c = document.getElementById ("myVideo"); | |||
// Create an element <video> | |||
var v = document.createElement ("video"); | |||
// Set the attributes of the video | |||
v.src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.ogv"; | |||
v.controls = true; | |||
// Add the video to <div> | |||
c.appendChild (v); | |||
</source> | |||
Which ultimately produces for the browser the following HTML code: | |||
<source lang = "HTML5"> | |||
<h2>Video inserted with JavaScript</h2> | |||
<div id="myVideo"> | |||
<video src = "video.mp4" controls = ""> </video> | |||
</div> | |||
</source> | |||
===Add a video with multiple sources and subtitles=== | |||
The same principle applies to insert a more complex video, with several source video formats and subtitles: always with the function <code>document.createElement()</code> we can create <code>source</code> and <code>track</code> elements and insert them into a <code>video</code> tag. Here is the JavaScript code: | |||
<source lang="JavaScript"> | |||
//Video avec plusieurs sources et sous-titres | |||
var cc = document.getElementById("myVideo"); | |||
var vc = document.createElement("video"); | |||
vc.controls = true; | |||
//Source 1 | |||
var source1 = document.createElement("source"); | |||
source1.src = "video.mp4"; | |||
//Source 2 | |||
var source2 = document.createElement("source"); | |||
source2.src = "video.webm"; | |||
//Track 1 | |||
var track1 = document.createElement("track"); | |||
track1.kind = "subtitles"; | |||
track1.src = "subtitles_en.vtt"; | |||
track1.label = "English"; | |||
track1.srclang = "en"; | |||
track1.type = "text/vtt"; | |||
//Track 2 | |||
var track2 = document.createElement("track"); | |||
track2.kind = "subtitles"; | |||
track2.src = "subtitles_fr.vtt"; | |||
track2.label = "Français"; | |||
track2.srclang = "fr"; | |||
track2.type = "text/vtt"; | |||
//Append everything | |||
vc.appendChild(source1); | |||
vc.appendChild(source2); | |||
vc.appendChild(track1); | |||
vc.appendChild(track2); | |||
cc.appendChild(vc); | |||
</source> | |||
Which corresponds to the following HTML code: | |||
<source lang = "HTML5"> | |||
<video controls = ""> | |||
<source src = "video.mp4"> | |||
<source src = "video.webm"> | |||
<track kind = "subtitles" src = "subtitles_en.vtt" label = "English" srclang = "en"> | |||
<track kind = "subtitles" src = "subtitles_en.vtt" label = "English" srclang = "en"> | |||
</video> | |||
</source> | |||
There are also two JavaScript functions to avoid having to create DOM elements for sources and tracks: | |||
* <code>canPlayType( ''type'' )</code> determines whether the browser supports a certain audio format, which allows you to create an <code>if... else</code> cycle to determine the <code>src</code> attribute instead of inserting multiple sources (see [http://www.w3schools.com/tags/av_met_canplaytype.asp canPlayType on W3Schools] ) | |||
*<code>addTextTrack( ''kind,label,language'' )</code> allows you to add textual content without creating <code>track</code> elements. It is used with the <code>addCue()</code> function and the <code>new TextTrackCue</code> object to directly add the contents without an external file. (see [http://www.w3schools.com/tags/av_met_addtexttrack.asp addTextTrack on W3Schools] ) | |||
== Acknowledgements == | |||
This material was initially preparred by [[User:Mattia A. Fritz|Mattia A. Fritz]] as part of the french [[:fr:HTML5 audio et video|HTML5 audio et video]] tutorial. | |||
[[ | [[Category: Javascript]] | ||
[[Category:HTML]] | |||
[[fr:HTML5 audio et video]] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:47, 28 March 2018
Introduction
This tutorial shows how to add interactivity to HTML5 multimedia audio and video elements. Let us first recall the essentials. The audio and video multimedia elements are fully integrated in the page, which allows:
- Using HTML5 attributes to define controls (play, pause, etc.)
- Setting CSS style properties to change the appearance of media items
- Using JavaScript to control elements and even add complex interactions
Before dealing with use of HTML5 tags, it is useful to understand what is a multimedia element. An audio or video file is actually a "container" (ie Multimedia container format) that contains different types of files with data (e.g. audio or video streams, subtitles, metadata, etc.). The "container" is then compressed with a codec, i.e. a compression algorithm that follows, for example, the same principle as the JPEG algorithm for images.
There are two aspects to browser compatibility:
- The browser is compatible with audio and video tags from HTML5 (most recent versions of browsers are in most cases now).
- The browser is compatible with the format (and codec) of the audio / video file
To resolve both compatibility issues, there are solutions that will be discussed later in the page, including the use of a JavaScript library for HTML5 tag compatibility and the use of multiple source files for audio / video format compatibility.
The most popular video formats on the web (with their default video codec) are:
- Webm / VP8 with .webm extension
- Mp4 / H.264 with .mp4 extension
- Ogg / Theora with .ogv extension
The advantage of having native elements for HTML5 media elements also implies the availability of an API to interact with audio and video elements with JavaScript . The Media Elements API provides:
- Methods (eg
play()) that mainly control the reading of the media - Properties (eg
currentTime) that allow to obtain or modify some media properties - Events (eg
timeupdate) that trigger certain behavior based on media events
See the full list on W3Schools
Thanks to this ability to interact with the audio / video elements, we can mainly imagine three frameworks of use:
- Use JavaScript to create audio / video elements
- Use JavaScript to control the broadcasting of audio / video elements
- Use JavaScript to add interactive elements triggered by audio / video elements or that modify audio / video elements
In the rest of this section, we will illustrate some examples for each framework of use. The audio and video elements being very close, the examples will focus mainly on the video tag, but can be easily adapted to the audio tag.
Control audio / video with JavaScript
The JavaScript API for media elements provides 3 methods to control them:
play(): starts (or restarts) playing the media filepause(): stops playback at the current locationload(): allows to substitute the active video in the player with another (for example, after changing the src attribute)
As a method (ie functions of an object), to execute them you must first identify the video (eg through the document.getElementById( id ) ) and then associate the method with the dot notation:
var myVideo = document.getElementById ("myVideo");
myVideo.play ()
In addition, as objects, the audio / video elements also have several properties, among which are:
currentTime: time at a given time in reading the media file in secondsduration: duration of the media file in secondsvolume:volumelevel (between 0.0 and 1.0)
Like any property of an object, they are used in two ways:
- Retrieve the value associated with a given property
- Associate a new value to a given property
Here is an example with the currentTime property for a given instance of myVideo:
console.log (myVideo.currentTime); // Displays in the console the playing time of a video
myVideo.currentTime = 60; // Move the player of the video to 60 seconds
Create controls for a video in HTML
Thanks to the methods and properties associated with the video tag, one can easily create custom controls that replace the standard controls added by the browser if the controls attribute is declared. To do this, one must first have a handle to a video for which the controls attribute is not declared, even if the presence or absence of standard controls does not influence the operation of external controls. An example is below:
<video id = "myVideo">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.ogv">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.mp4">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.webm">
</video>
Then we add three buttons with the button tag for the play, pause and stop controls.
<button id = "playBtn"> Play </button>
<button id = "pauseBtn"> Pause </button>
<button id = "stopBtn"> Stop </button>
Finally, we add the JavaScript code (in an external file or inside a script tag):
// Identify HTML elements
var myVideo = document.getElementById ("myVideo");
var playBtn = document.getElementById ("playBtn");
var pauseBtn = document.getElementById ("pauseBtn");
var stopBtn = document.getElementById ("stopBtn");
// start play with play ()
playBtn.onclick = function () {
myVideo.play ();
}
// pause playback
pauseBtn.onclick = function () {
myVideo.pause ();
}
// The stop () function does not exist, so we combine pause with currentTime = 0;
stopBtn.onclick = function () {
myVideo.pause ();
myVideo.currentTime = 0;
}
Control an audio in background
In some applications, such as video games, there is often a background music that repeats itself in time, but that the user can decide stop if he wishes. There are several ways to create a background audio element HTML5, but the easiest way is to insert an audio element without setting the controls attribute .In most web browsers that support the audio tag, this simply disguises the controls.
Here is the HTML code that inserts audio with multiple sources as well as two ON and OFF buttons. In order start audio in the background automatically it is necessary to declare the attribute autoplay. You also should add the attribute loop, in order to repeat the sound :
<audio id = "audioBg" autoplay loop>
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-audio/audio/guitar.mp3">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-audio/audio/guitar.ogg">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-audio/audio/guitar.m4a">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-audio/audio/guitar.wav">
Your browser does not support HTML5. Maybe you should upgrade.
</audio>
To control the volume of the audio, instead of two buttons, you can use a range input (introduced with HTML5). For this type of input we can define:
- The minimum value
- The maximum value
- The scale of each variation (ie the "step")
The volume of an audio / video source ranges from 0 (no sound) to 1 (maximum volume compared to the current audio of the computer). Here is the code to add a range input to control the volume:
Audio volume <input type = "range" min = "0" max = "1" step = "0.1" value = "1" id = "audioVolume">
The basic volume of an audio / video source is the maximum value of 1, so that the range and the volume correspond we define a value of 1 which will then be modified with the cursor. Each move corresponds to a change of 0.1 (defined by the step value).
To associate the range with the volume of the audio we can use the onchange event:
// Identify HTML elements
var audio = document.getElementById ("audioBg");
var audioVolume = document.getElementById ("audioVolume");
// associate volume with range type input
audioVolume.onchange = function () {
audio.volume = audioVolume.value;
}
It is also possible to create the audio element directly in JavaScript using the document.createElement("audio") and specifying the autoplay and loop attributes.
Interactive audio / video with JavaScript
Earlier we have seen that audio / video elements can be controlled by other elements of the DOM and, consequently, also by DOM-related events. You can, for example, trigger a video based on page scrolling, or stop it if the user is writing something in a text field. On the other hand, it is also possible to modify other elements of the DOM according to events directly related to the audio / video element. Here is a non-exhaustive list of events related to audio / video:
onplay(): event triggered each time the media starts or restarts;onpause(): event triggered each time the media is paused;ontimeupdate(): event triggered each time the playback time changes.
Prompt the user with a question at a given point in a video
In this example, we will display a question (using the JavaScript prompt() ) after 10 seconds of playing the video. If the user answers the question correctly, the video will resume normally, otherwise it will resume from the beginning. Here is the result in an image:
Here is the HTML code:
<h1>Ask a question at a given point in a video</h1>
<p>The question is displayed after 10 seconds, if the answer given is correct (i.e. "Wikipedia"), the video continues, if not it starts again from the beginning</p>
<video id = "myVideo" controls>
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.mp4">
<source src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.webm">
</video>
And here the commented JavaScript code:
// First identify the video in the DOM
var myVideo = document.getElementById ("myVideo");
myVideo.ontimeupdate = function () {
// Remove the decimal numbers from the time
var currentTime = Math.floor (myVideo.currentTime);
if (currentTime == 10) {
myVideo.pause ();
// Ask the question with a promt
var r = prompt ("What is the video about?");
// check the answer
if (r.toLowerCase () == "wikipedia") {
myVideo.currentTime = 11; // Add a second otherwise the question will be displayed again;
myVideo.play ();
} else {
myVideo.currentTime = 0; // Put the video back to 0;
myVideo.play ();
}
}
}
Test this example (Please note that using prompt is not ergonomic at all, it would be better to use an HTML form)
Create audio / video elements with JavaScript
Add a simple video
The video tag can be treated like any other tag in the DOM, so you can easily create one with the document.createElement("video") and then set the video's attributes like source, controls, and so on. Here's an example that adds a video inside a div with id = "myVideo" .
HTML code
<h2>Video inserted with JavaScript</h2>
<div id="myVideo"></div>
JavaScript code:
var c = document.getElementById ("myVideo");
// Create an element <video>
var v = document.createElement ("video");
// Set the attributes of the video
v.src = "http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/html/html5-video/videos/state-of-wikipedia-480x272.ogv";
v.controls = true;
// Add the video to <div>
c.appendChild (v);
Which ultimately produces for the browser the following HTML code:
<h2>Video inserted with JavaScript</h2>
<div id="myVideo">
<video src = "video.mp4" controls = ""> </video>
</div>
Add a video with multiple sources and subtitles
The same principle applies to insert a more complex video, with several source video formats and subtitles: always with the function document.createElement() we can create source and track elements and insert them into a video tag. Here is the JavaScript code:
//Video avec plusieurs sources et sous-titres
var cc = document.getElementById("myVideo");
var vc = document.createElement("video");
vc.controls = true;
//Source 1
var source1 = document.createElement("source");
source1.src = "video.mp4";
//Source 2
var source2 = document.createElement("source");
source2.src = "video.webm";
//Track 1
var track1 = document.createElement("track");
track1.kind = "subtitles";
track1.src = "subtitles_en.vtt";
track1.label = "English";
track1.srclang = "en";
track1.type = "text/vtt";
//Track 2
var track2 = document.createElement("track");
track2.kind = "subtitles";
track2.src = "subtitles_fr.vtt";
track2.label = "Français";
track2.srclang = "fr";
track2.type = "text/vtt";
//Append everything
vc.appendChild(source1);
vc.appendChild(source2);
vc.appendChild(track1);
vc.appendChild(track2);
cc.appendChild(vc);
Which corresponds to the following HTML code:
<video controls = "">
<source src = "video.mp4">
<source src = "video.webm">
<track kind = "subtitles" src = "subtitles_en.vtt" label = "English" srclang = "en">
<track kind = "subtitles" src = "subtitles_en.vtt" label = "English" srclang = "en">
</video>
There are also two JavaScript functions to avoid having to create DOM elements for sources and tracks:
canPlayType( type )determines whether the browser supports a certain audio format, which allows you to create anif... elsecycle to determine thesrcattribute instead of inserting multiple sources (see canPlayType on W3Schools )addTextTrack( kind,label,language )allows you to add textual content without creatingtrackelements. It is used with theaddCue()function and thenew TextTrackCueobject to directly add the contents without an external file. (see addTextTrack on W3Schools )
Acknowledgements
This material was initially preparred by Mattia A. Fritz as part of the french HTML5 audio et video tutorial.