Trotec Speedy 100R: Difference between revisions
| (45 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
=== Print === | === Print === | ||
* Calibrate the height | |||
* Make sure that the material to cut is flat (important for textiles). Otherwise either increase power or weigh down the material. You also can use "Seklema Haftmatten" (Trotec Shop) | |||
* <code>Establish Connection</code> in JobControl | * <code>Establish Connection</code> in JobControl | ||
| Line 113: | Line 117: | ||
* Press <code>START</code> button (green arrow) in Job Control. | * Press <code>START</code> button (green arrow) in Job Control. | ||
=== Wait === | === Wait === | ||
| Line 168: | Line 171: | ||
* In the '''Printing Preferences''' window, make sure that you are in expert mode (select the ''general'' tab) | * In the '''Printing Preferences''' window, make sure that you are in expert mode (select the ''general'' tab) | ||
'''(3) Steps 3 and 4: Define material settings and process options | '''(3) Steps 3 and 4: Define material settings and process options''' | ||
In the ''Print tab'' you then must define the print process: | In the ''Print tab'' you then must define the print process: | ||
| Line 190: | Line 193: | ||
<code>Relief</code> | <code>Relief</code> | ||
: {{quotation|This type of processing controls the laser power depending on the gray-scale value of the graphic.}} <ref name="operationmanual">Trotec (2015), ''Operation Manual Trotec JobControl. Basic, Advanced, Expert''. Retrieved from https://www.troteclaser.com/fileadmin/content/images/Contact_Support/Manuals/JobControl-Manual-EN.pdf, page 31</ | : {{quotation|This type of processing controls the laser power depending on the gray-scale value of the graphic.}} <ref name="operationmanual">Trotec (2015), ''Operation Manual Trotec JobControl. Basic, Advanced, Expert''. Retrieved from https://www.troteclaser.com/fileadmin/content/images/Contact_Support/Manuals/JobControl-Manual-EN.pdf, page 31</ref> | ||
This configuration requires 256 gray scale (8-bit). Lighter means less power and darker means more power. | This configuration requires 256 gray scale (8-bit). Lighter means less power and darker means more power. | ||
| Line 257: | Line 260: | ||
=== Material settings table === | === Material settings table === | ||
Since we just started with laser cutting, please consider the following very provisional ! In principle, the settings should work for a Trotec 50W CO laser... but they are by no means optimal (yet). | Since we just started with laser cutting, please consider the following very provisional ! In principle, the settings should work for a Trotec 50W CO laser... but they are by no means optimal (yet). Various materials that one could use with a CO2 Laser like the Speedy 100 are described in the [[laser cutting]] article. | ||
Often there are different solutions that lead to similar results. Remember that laser power received is a function of power and speed, and pulse (in case of cutting) | Often there are different solutions that lead to similar results. Remember that laser power received is a function of power and speed, and pulse (in case of cutting) | ||
| Line 272: | Line 275: | ||
! Engraving power | ! Engraving power | ||
! Engraving speed | ! Engraving speed | ||
!N engraving passes | |||
! Engraving resolution | ! Engraving resolution | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| Line 282: | Line 286: | ||
| 50 | | 50 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
|2 | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| 2 passes reduced burning | | 2 passes reduced burning | ||
| Line 292: | Line 297: | ||
| 50 | | 50 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| | |||
|- | |||
|Maple Wood 5mm | |||
|80 | |||
|1 | |||
|1000 | |||
|1 | |||
|100 | |||
|70 | |||
|2 (is prettier) | |||
|500 | |||
|To create darker engraving, reduce speed a bit. To go deeper, do 2 passages. | |||
|- | |||
|Plywood poplar 3mm | |||
|100 | |||
|1.1 | |||
|1000 | |||
|1 | |||
|100 | |||
|100 (70) | |||
|1 (2 at 70 is prettier) | |||
|600 | |||
|Very easy, since weak material. | |||
|- | |||
|Plywood poplar 5mm | |||
|100 | |||
|0.9 (0.8 if uneven) | |||
|1000 | |||
|1 | |||
|100 | |||
|100 (70) | |||
|1 (2 at 70 is prettier) | |||
|600 | |||
|Poplar plywood is not very strong, but easy to engrave and to cut. | |||
|- | |||
|Plywood linden Creality (tilleuil) 10mm | |||
|100 | |||
|0.32 | |||
|1000 | |||
|2 | |||
|100 | |||
|80 | |||
|2 | |||
|500 | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Plywood birch 4mm | | Plywood birch 4mm | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| 1. | | 1.2 (for large objects maybe a bit less) | ||
| 1000 | | 1000 | ||
| 1 | | 1 | ||
| 80 ( | | 80 (or better 2 at 60) | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | |||
| Birch plywood is strong quality but difficult to laser, in particular larger than 4mm sizes. | |||
Watch out for flames | |||
|- | |||
| Plywood birch 6.5mm (difficult) | |||
| 80 | |||
| 0.5 | |||
| 1000 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 60 (2x) | |||
| 70 | |||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| | | Set correction to 15. These are minimal settings to test and some larger cuts with lots of details could fail. Result is very black and requires washing. You could put some painters tape on the cut lines to avoid blackening of the surface. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Plywood birch 6.5mm ( | | Plywood birch 6.5mm (variants) | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| 0. | | 0.5 - 0.6 | ||
| | | 2500 - 5000 | ||
| | | 2 | ||
| 80 | | 80 | ||
| 70 | | 70 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| Result is very black and needs washing. | | Result is always very black and needs washing. More pulse and more power doesn't change that much. Result looks similar and flames are a bit bigger and will destroy thin elements. Also try '''three passes with a bit less power or higher speed'''. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Plexi 10mm | ||
| | | 100 | ||
| 0.5 | | 0.5 | ||
| | | 10000 | ||
| 2 | | 2 | ||
| | | 80 | ||
| | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | |||
| Better, position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | |||
|- | |||
| Plexi 5mm | |||
| 100 | |||
|0.8 | |||
| 4000 | |||
|2 | |||
| 80 | |||
| 100 | |||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| | | Better, position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Plexi 4mm | | Plexi 4mm | ||
| Line 332: | Line 408: | ||
| 80 | | 80 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| Position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | | Position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | ||
| Line 342: | Line 419: | ||
| 80 | | 80 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 352: | Line 430: | ||
| 80 | | 80 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |||
| Trolase Textures 1.6 mm matte | |||
| 50 | |||
| 0.8 | |||
| 4000 | |||
| 1 | |||
| 100 | |||
| 50-60 | |||
| | |||
| 600 | |||
| This is a bi-color acrylic plastic from TroTec, much cheaper than Plexiglass, i.e. a 60.5 x 30.5cm costs 12.20 CHF. '''Extra settings''': Z-offset is 2 (as opposed 0) in order to make the laser a bit thicker. (2) Start position at bottom (right-click, select properties) | |||
|- | |||
|Trolase 0.8 mm smooth | |||
|50 | |||
|1.5 | |||
|1000 | |||
| | |||
|100 | |||
|50-60 | |||
| | |||
|600 | |||
|Z-offset = 2. Verify. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Ondulated Cardboard | | Ondulated Cardboard | ||
| Line 362: | Line 463: | ||
| 60 | | 60 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 1000 | | 1000 | ||
| Rough settings, thickness and density is widely different. If the first layer is thicker you can go with engraving P = 80 | | Rough settings, thickness and density is widely different. If the first layer is thicker you can go with engraving P = 80 | ||
|- | |||
| Ondulated Cardboard (cuts) | |||
| 20 | |||
| 1 | |||
| 1000 | |||
| 1 | |||
| 7 | |||
| 3 | |||
| | |||
| 5000 | |||
| Rough settings. Engraving parameters are meant for engraving lines, i.e. cuts defined with another color ! Both speeds could be higher. Please test first with a small design. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Thick paper 0.25mm ? | | Thick paper 0.25mm ? | ||
| Line 372: | Line 485: | ||
| 80 | | 80 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 1000 | | 1000 | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |||
| Gunold Step | |||
| 22 | |||
| 1.9 | |||
| 1000 | |||
| 1 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| 1000 | |||
| Special embroidery textile for creating patches. Set Power to 30 (instead of 22) for larger pieces. The tissue can warp and the laser will be less focused and therefore less strong | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Cotton (pants) | | Cotton (pants) | ||
| 30 | | 30 | ||
| 3 | | 3 | ||
| 1000 | | 1000-3000 | ||
| 1 | | 1 | ||
| | | 20 | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | | | ||
| Test this, engraving effects differ for each type of cotton. I made a Halloween mask from a cut off pant leg) | | 200-300 | ||
| Test this, engraving effects differ for each type of cotton. I made a Halloween mask from a cut off pant leg). Make sure to work with a low DPI (else you can create cuts that will appear later). In addition use an offset of 2 to 20mm (defocalize) and turn off the ventilator. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Wood Wine box 7mm | | Wood Wine box 7mm | ||
| Line 392: | Line 518: | ||
| 60 | | 60 | ||
| 70 | | 70 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| | | Nice and easy, if the wood is light. Testing required | ||
|- | |||
|Heavy Wood Wine box 9.5mm | |||
|100 | |||
|0.35 | |||
|2000 | |||
|3 | |||
|40 | |||
|100 | |||
|2 | |||
|500 | |||
|Some use tougher wood, so it won't be nice and easy. Testing required. Maybe 0.23 for cutting speed. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Anodized aluminum, e.g. Laptops (this needs to be tested !) | | Anodized aluminum, e.g. Laptops (this needs to be tested !) | ||
| Line 402: | Line 540: | ||
| 100 ? | | 100 ? | ||
| 100 | | 100 | ||
| | |||
| 500 | | 500 | ||
| Not tested, probably also depends a lot on the coating. Use weaker settings for plastic cases !! | | Not tested, probably also depends a lot on the coating. Use weaker settings for plastic cases !! | ||
| Line 407: | Line 546: | ||
| Material | | Material | ||
| | | | ||
| | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 416: | Line 556: | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | == Cutting to engrave == | ||
== | |||
Let's assume that you only want to draw some lines, e.g. for a large board. This can take up to an hour of raster engraving. | |||
Alternative: | |||
* Define another color for cutting, e.g. blue | |||
* Then set to something like power = 100 and speed = 20 '''and defocus by z=1'''. This will lower the platform and make the lines fatter. | |||
* | |||
= | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| Line 542: | Line 572: | ||
=== Various tutorials and other useful texts === | === Various tutorials and other useful texts === | ||
* [http://wiki.happylab.at/w/Trotec Trotec]. Happylab "how to". | |||
* [http://wiki.epfl.ch/lapa-studio/documents/DTS/laser%20tutorial.pdf Laser tutorial] (EPFL, for a trotec speedy 500) | * [http://wiki.epfl.ch/lapa-studio/documents/DTS/laser%20tutorial.pdf Laser tutorial] (EPFL, for a trotec speedy 500) | ||
* [https://www.sculpteo.com/en/lasercutting/prepare-your-file-laser-cutting/ Sculpteo tutorials] (focused on designing with various tools) | |||
=== Local (Geneva area) shops for materials to cut === | === Local (Geneva area) shops for materials to cut === | ||
* Migros Materials (local do-it-yourself shop) | * Migros Materials (local do-it-yourself shop) | ||
** Wood | ** Wood, Plywood, MDF,etc. | ||
** e.g. [http://www.doitgarden.ch/fr/bauen---handwerk/baubedarf/kunststoff/acrylglas-flach-extrudiert/ verre acrylique] (500 x 250 x 5 = CHF 12.90) | ** Plexi XT, e.g. [http://www.doitgarden.ch/fr/bauen---handwerk/baubedarf/kunststoff/acrylglas-flach-extrudiert/ verre acrylique] (500 x 250 x 5 = CHF 12.90) | ||
* Polyplast | * Polyplast | ||
| Line 563: | Line 595: | ||
* Serex | * Serex | ||
** E.g. [http://www.serex-plastiques.ch/verre-acrylique-pmma-plexiglas-prix | ** E.g. [http://www.serex-plastiques.ch/verre-acrylique-pmma-plexiglas-prix PLEXIGLAS XT], CHF 50 / m2 3mm and CHF 83 / m2 for 5mm | ||
=== Trotec online Shop === | |||
Only companies and organizations seem to be able to buy. Materials on average cost less than in local shops and are tested with Trotec machines. | |||
* [https://www.gravurmaterialien.ch/ Gravurmaterialien.ch] | |||
== Références == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category: Fab lab]] [[Category:3D]] [[Category: hardware]] [[Category: laser cutting]] | [[Category: Fab lab]] | ||
[[Category:3D]] | |||
[[Category: hardware]] | |||
[[Category: laser cutting]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:35, 9 September 2024
Introduction
This page will document the Trotec Speedy 100R that TECFA (me) that we just acquired - Daniel K. Schneider (talk) oct 2016
As far as I can tell for now, we will use this machine to create three types of objects:
- 2D objects, e.g. badges, games and toys (created from simple SVG drawings)
- 3D structures to assemble from 2D elements (created from simple SVG drawings), e.g. animals
- 3D structures glued together (made from sliced 3D objects). The slicing can be done with various tools, e.g. Netfabb, Slice3R, 123D Make.
All cut parts also can be engraved, either vector engraving or raster engraving (typically from pictures).
Specifications of the 100R at TECFA
This system easily fits into an office and it just needs two electrical standard plugs.
Speedy 100R
- 50 W CO2 laser (Iradion tube)
- 2 inch lens (standard)
- 61cm x 30.5cm working surface
- 180 cm/sec speed
- Box size: 982 x 780 x 457 mm
- 80 kg
- Air cooling
ATMOS Compact exhaust fan
- 815 x 675 x 555 mm
- 88kg
Official home page:
Laser cutting parameters
There are several parameters that must be set (you can create profiles for that)
Basic
- Cutting power, typically 100
- Cutting speed, typically 1
- Cutting pulse (faster = stronger, but more inflammable), typically 1000
- Engraving power, typically 50
- Engraving speed, typically 100
- Engraving resolution, typically 500PPI
- Material thickness, typically 2-5mm
Advanced
- "Print file creation" parameters can define whether using the standard color scheme (e.g. hairline red for cutting and black for engraving) and how to render pictures, etc.
- Repetition for both cutting and engraving. Some materials need 2-3 passes.
Outline of the workflow
Preparation steps
(0) Clean the lens (with a microfiber cloth or equivalent)
(1) Switch the machine on
(2) Place work piece
- open cover
- Place piece into upper left-hand corner, against horizontal and vertical rules
(3a) Focus laser beam (manually)
- By default (for the mid-resolving lens) the beam is located 5.08 cm (2.0 in) below the lens.
- Position the processing head over the work piece
- Hang the focus tool on the external ring of the working head
- Then, move up (by little steps) the working table
(3b) Alternatively, focus laser beam with software
- Click the icon “focus laser” in the Trotec JobControl (make sure that material thickness, table height and lens type are OK !)
Create a graphic
- Any vector graphic will do, since jobcontrol will work from the print file, i.e. the control software will analyse the postscript and let you configure the print from there.
- However, we noticed that something doesn't work properly with Inkscape drawings (old 0.4x version), i.e. TroTec Job control cannot identify some vectors. Try producing a PDF first ("print to PDF file" in Inkscape), then print the file from PDF. Anyhow, make sure to install the latest version of Inkscape and read Using Inkscape for laser cutting
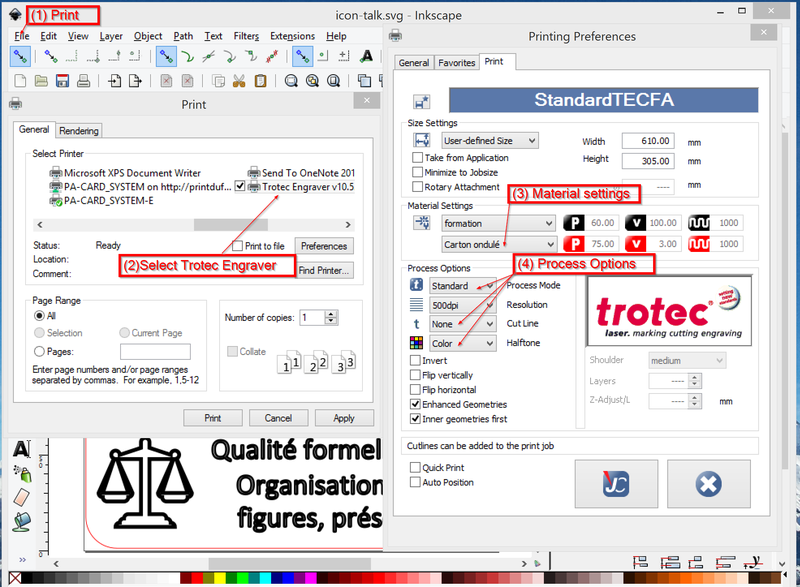
Preparing the print file
From your drawing or rendering software, File->Print the drawing
- Select as printer
Trotec Engraver - Click on
Preferences - Define (at least):
- Material parameters, e.g. a setting you defined for a given type and thickness of Material (these parameters, however can be changed later)
- Algorithm (e.g. for simple vector-based cutting and engraving use color, if there are pictures, you could try Optimization, Stucki, etc.)
Then click bottom "print" icon and "print" again from the Windows software. Trotec JobControl now will open and the print file should appear in the jobs queue to the right.
Job Control software
In the Job Control software, verify or specify all the parameters
Establish Connectionin JobControl- On the laser move the cutting head to the position where you plan to start
- Position the job on the plate with a double click
- Verify engraving material
- Associated Power, velocity and Pulse parameters
- Thickness (important in case you do more than one passage)
- Color codes for engraving and cutting (check the panel to the left). Click update. If you see a warning about unidentified vectors, go back to you drawing tool and make sure that each object does have a good color (e.g. black for engraving). Inherited colors, in Inkscape for example, do not seem to work. Ungroup everything, select stuff to engrave and make sure that it has either stroke, fill or both.
- <Double click> on the workspace to bring up the Material library where you can change all parameters.
You also can change
- orientation of the work piece (
right-clickon the object) - orientation of the plate
Once the situation feels allright, click the Print button (lower right)
- Calibrate the height
- Make sure that the material to cut is flat (important for textiles). Otherwise either increase power or weigh down the material. You also can use "Seklema Haftmatten" (Trotec Shop)
Establish Connectionin JobControl
- Verify
Exhaust Readyin Engraver Control (green arrow) in the Control of the JobControl
- Press
STARTbutton (green arrow) in Job Control.
Wait
- After printing slightly toxic materials, e.g. MDS (glues) or foam (styrene), wait at least a minute (until the aspiration ventilator stops). This will help keeping the lens clean and also help your breathing...
Preparation of drawing
Principles:
Input
- Any 2D CAD or drawing file.
- For cutting, the stroke of the vectors should be less than than 0.01mm (or 0.25pt), i.e. hairline of a same color. At TECFA, we use red for cutting.
- Other elements will be engraved, depending on the settings
- If you use the standard "Color mode" to identify objects, pick the colors from the limited set of the basic RGB colors.
Colorcode at TECFA:
- red = cutting
- black = engraving (simple or double, depending on the profile)
- blue = simple engraving
Software
We suggest creating all models in SVG. That way they can be displayed directly on the web. Most drawing programs can import/export SVG
(section to be moved some day)
Online tools
Process Options and parameters - Tables for cutting and engraving
Let's recall the basic principles. Engraving depth is varied through the laser power or the speed (energy per area unit principle) For cutting, Hz settings (pulses per second) should be set to low, in particular if materials are flammable. Vector lines are color coded and for each color one can assign a cutting/engraving parameter. I.e. one could use "red" for cutting" and "greys" for engraving. A print job can include cutting, or engraving, or both.
In addition to these basic parameters, one can define so-called "process options", i.e. instructions on how to create a print file.
- Process Mode will identify major algorithms used to transform a drawing into a "cuttable/engraveable" drawing
- There are various options that depend on selection of "Process Mode".
To learn more about parametrization, one could look at published examples, for example:
- Do it yourself samples (Trotec)
- laser_cutter (tags on thingiverse, but most include little instructions
Process options are defined before printing. Here are the steps
(1) Step 1:
- From your application, e.g. Inkscape, Illustrator or PDF you will print your design.
(2) Step 2:
- From the Windows print menu select
Trotec Engraver Vxand then click onPreferences - In the Printing Preferences window, make sure that you are in expert mode (select the general tab)
(3) Steps 3 and 4: Define material settings and process options
In the Print tab you then must define the print process:
- Select <user defined size> in size settings and tick
minimize to job sizeand take from application. This way you can print several designs at the same time. If you leave the full dimensions (i.e. 600x300 you cannot). - Select
material settings(you can change these later again) - Define the
process options(these cannot be changed later, since the print driver must create the printable design)
More details are given below.
Process Mode
Process mode identifies the type of processing, i.e. how a drawing is interpreted and "translated" for laser cutting and printing
Standard
- Several design colors (at least two) will identify how a given object will be cut or engraved.
Stamp
- Is used to create rubber stamps.
Relief
- “This type of processing controls the laser power depending on the gray-scale value of the graphic.” [1]
This configuration requires 256 gray scale (8-bit). Lighter means less power and darker means more power.
- white = no engraving
- black = full power
- levels of grey = depends.
Therefore one should use pictures or drawings with good contrast. Also, to see an effect, materials should be fairly soft so that the laser can remove enough materials in one pass.
Layer
- Layer is similar to relief but works with several passes. “Gray-scale graphics are engraved in several passes. The number of passes can be set in the range from 2 to 255” (page 31), i.e. each grey value is translated to a number of passes. This allow to create stronger reliefs.
Photo
- Allows to engrave high resolution pictures without prior vectorization.
Seal
- Allows creating seals.
Cut
- Same as standard mode, except that all non cutting objects are eliminated from the job before processing.
Other options
Engraving resolution
Resolution
- defines engraving resolution in dots/inch (DPI) e.g. in dots/2.54cm2.
- Recommended size is 500 in most cases. Going higher means much longer printing time and you won't see the difference with most materials. Higher also means increasing the engraving depth. As an alternative to high DPI, you also could engrave in two passes.
Cut line
None:Normal operation, i.e. cutting will only happend along your cut lines.Rectangular:Will create a cutting line that follows the job margins (is that the document size ?)Circular:Same as above, but will create a circleOptimize:Creates a cutting line that is ajusted to the contour of all engraving objects. Warning: Do not use "optimized" unless you need this. Cutting along the contour doesn't make sense, usually.
Automatically created cuttin lines (rectangular, circular and optimize) are always created in red. Therefore you also should make sur the "cutting color" is set to red.
Half tones
Halftone options will convert (or not) grey-scale or color images to black and white images. Various levels of grey or color "heat" is translated to different dot sizes and pitches that will still allow recognizing the original more complex picture. This process is called dithering (Wikipedia). Not available for relief and layer processing (since these require grey levels). There are three advanced dithering algorithms (Stucki, Jarivs and Floyd Steinberg). For more information about [ dithering], read Image Dithering: Eleven Algorithms and Source Code
ordered dithering
- Creates soft constrasts between brightness gradients
Stucki
- Probably the most advanced Dithering algorithm for photo engraving.
Jarvis
- Advanced Dithering algorithm for photo engraving
Floyd Steinberg
- The first well known advanced Dithering algorithm for photo engraving
Color
- Deactivites the halftoning, i.e. engravable objects will be engraved if they fit a engraving color defined in the Materials.
Black & White
- Will transform each pixel to either black or white according to a threshold level
Checkboxes
- We suggest ticking
enhanced geometriesandinnner geometriesfirst.
Material settings table
Since we just started with laser cutting, please consider the following very provisional ! In principle, the settings should work for a Trotec 50W CO laser... but they are by no means optimal (yet). Various materials that one could use with a CO2 Laser like the Speedy 100 are described in the laser cutting article.
Often there are different solutions that lead to similar results. Remember that laser power received is a function of power and speed, and pulse (in case of cutting)
(Maybe outdated) profiles are in this web directory (selected groups)
| Material | Cutting power | Cutting speed | Cutting Hz | N cutting passes | Engraving power | Engraving speed | N engraving passes | Engraving resolution | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDF 5mm | 55 | 1.1 | 1000 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 2 | 500 | 2 passes reduced burning |
| MDF 3mm | 80 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 50 | 100 | 500 | ||
| Maple Wood 5mm | 80 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 100 | 70 | 2 (is prettier) | 500 | To create darker engraving, reduce speed a bit. To go deeper, do 2 passages. |
| Plywood poplar 3mm | 100 | 1.1 | 1000 | 1 | 100 | 100 (70) | 1 (2 at 70 is prettier) | 600 | Very easy, since weak material. |
| Plywood poplar 5mm | 100 | 0.9 (0.8 if uneven) | 1000 | 1 | 100 | 100 (70) | 1 (2 at 70 is prettier) | 600 | Poplar plywood is not very strong, but easy to engrave and to cut. |
| Plywood linden Creality (tilleuil) 10mm | 100 | 0.32 | 1000 | 2 | 100 | 80 | 2 | 500 | |
| Plywood birch 4mm | 100 | 1.2 (for large objects maybe a bit less) | 1000 | 1 | 80 (or better 2 at 60) | 100 | 500 | Birch plywood is strong quality but difficult to laser, in particular larger than 4mm sizes.
Watch out for flames | |
| Plywood birch 6.5mm (difficult) | 80 | 0.5 | 1000 | 2 | 60 (2x) | 70 | 500 | Set correction to 15. These are minimal settings to test and some larger cuts with lots of details could fail. Result is very black and requires washing. You could put some painters tape on the cut lines to avoid blackening of the surface. | |
| Plywood birch 6.5mm (variants) | 100 | 0.5 - 0.6 | 2500 - 5000 | 2 | 80 | 70 | 500 | Result is always very black and needs washing. More pulse and more power doesn't change that much. Result looks similar and flames are a bit bigger and will destroy thin elements. Also try three passes with a bit less power or higher speed. | |
| Plexi 10mm | 100 | 0.5 | 10000 | 2 | 80 | 100 | 500 | Better, position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | |
| Plexi 5mm | 100 | 0.8 | 4000 | 2 | 80 | 100 | 500 | Better, position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | |
| Plexi 4mm | 100 | 0.8 | 4000 | 1 | 80 | 100 | 500 | Position the plate on top of some wooden blocks, not directly on the grid. | |
| Plexi 3mm | 100 | 1 | 4000 | 1 | 80 | 100 | 500 | ||
| Plexi 2mm | 100 | 1.2 | 4000 | 1 | 80 | 100 | 500 | ||
| Trolase Textures 1.6 mm matte | 50 | 0.8 | 4000 | 1 | 100 | 50-60 | 600 | This is a bi-color acrylic plastic from TroTec, much cheaper than Plexiglass, i.e. a 60.5 x 30.5cm costs 12.20 CHF. Extra settings: Z-offset is 2 (as opposed 0) in order to make the laser a bit thicker. (2) Start position at bottom (right-click, select properties) | |
| Trolase 0.8 mm smooth | 50 | 1.5 | 1000 | 100 | 50-60 | 600 | Z-offset = 2. Verify. | ||
| Ondulated Cardboard | 75 | 3 | 1000 | 1 | 60 | 100 | 1000 | Rough settings, thickness and density is widely different. If the first layer is thicker you can go with engraving P = 80 | |
| Ondulated Cardboard (cuts) | 20 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 5000 | Rough settings. Engraving parameters are meant for engraving lines, i.e. cuts defined with another color ! Both speeds could be higher. Please test first with a small design. | |
| Thick paper 0.25mm ? | 30 | 3 | 1000 | 1 | 80 | 100 | 1000 | ||
| Gunold Step | 22 | 1.9 | 1000 | 1 | 1000 | Special embroidery textile for creating patches. Set Power to 30 (instead of 22) for larger pieces. The tissue can warp and the laser will be less focused and therefore less strong | |||
| Cotton (pants) | 30 | 3 | 1000-3000 | 1 | 20 | 100 | 200-300 | Test this, engraving effects differ for each type of cotton. I made a Halloween mask from a cut off pant leg). Make sure to work with a low DPI (else you can create cuts that will appear later). In addition use an offset of 2 to 20mm (defocalize) and turn off the ventilator. | |
| Wood Wine box 7mm | 100 | 1.5 | 1000 | 2 | 60 | 70 | 500 | Nice and easy, if the wood is light. Testing required | |
| Heavy Wood Wine box 9.5mm | 100 | 0.35 | 2000 | 3 | 40 | 100 | 2 | 500 | Some use tougher wood, so it won't be nice and easy. Testing required. Maybe 0.23 for cutting speed. |
| Anodized aluminum, e.g. Laptops (this needs to be tested !) | - | - | - | - | 100 ? | 100 | 500 | Not tested, probably also depends a lot on the coating. Use weaker settings for plastic cases !! | |
| Material |
Cutting to engrave
Let's assume that you only want to draw some lines, e.g. for a large board. This can take up to an hour of raster engraving.
Alternative:
- Define another color for cutting, e.g. blue
- Then set to something like power = 100 and speed = 20 and defocus by z=1. This will lower the platform and make the lines fatter.
Links
Models
Various tutorials and other useful texts
- Trotec. Happylab "how to".
- Laser tutorial (EPFL, for a trotec speedy 500)
- Sculpteo tutorials (focused on designing with various tools)
Local (Geneva area) shops for materials to cut
- Migros Materials (local do-it-yourself shop)
- Wood, Plywood, MDF,etc.
- Plexi XT, e.g. verre acrylique (500 x 250 x 5 = CHF 12.90)
- Polyplast
- Route des Acacias 11
- Plexi
- E.g. Plexiglass
- Elega
- E.g. Plexiglass
- Antalis
- https://www.antalis.ch
- E.g. Visacry (Plexi coulé CHF 71 / m2 5mm
- Serex
- E.g. PLEXIGLAS XT, CHF 50 / m2 3mm and CHF 83 / m2 for 5mm
Trotec online Shop
Only companies and organizations seem to be able to buy. Materials on average cost less than in local shops and are tested with Trotec machines.
Références
- ↑ Trotec (2015), Operation Manual Trotec JobControl. Basic, Advanced, Expert. Retrieved from https://www.troteclaser.com/fileadmin/content/images/Contact_Support/Manuals/JobControl-Manual-EN.pdf, page 31