Drupal: Difference between revisions
| Line 187: | Line 187: | ||
[[File:Drupal4.png]] | [[File:Drupal4.png]] | ||
===A glance to the administrators front-page=== | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
Revision as of 21:27, 6 May 2014
Definition
Drupal is a popular portalware of the C3MS or CMS variety. It is used to build all sorts of educational websites, including teaching platforms. Similar systems discussed in this Wiki are Joomla and PostNuke.
Purpose and features
According to the About Drupal page (retrieved 18:36, 11 May 2007 (MEST)) “Drupal is a free software package that allows an individual or a community of users to easily publish, manage and organize a wide variety of content on a website. Tens of thousands of people and organizations have used Drupal to power scores of different web sites, including Community web portals, Discussion sites, Corporate web sites, Intranet applications, Personal web sites or blogs, Aficionado sites, E-commerce applications, Resource directories, Social Networking sites.”
Features
The built-in functionality, combined with dozens of freely available add-on modules, will enable features such as:
- Content management systems
- Blogs
- Collaborative authoring environments (i.e. it is a collaborative writing tool.
- Forums
- Peer-to-peer networking
- Newsletters
- Podcasting
- Picture galleries
- File uploads and downloads
... and much more.
Software architecture
- Content in Drupal is created in individual "nodes". For nodes of type "story", users can add comments to the node (comments themselves are not considered nodes). Depending on site settings, adding new nodes and/or posting comments might or might not be allowed. Also, nodes or comments might require approval from the moderators before the node or comment is displayed. (Drupal terminology, retrieved 18:36, 11 May 2007 (MEST))
Drupal's basic set of note types include ([1]):
- Blog Entry
- Drupal blogs have typical functionality of blogware
- Book Page
- Book pages are designed to be part of a collaborative book. An example of a collaborative book is the Drupal developer documentation. All node types can be part of a book.
- Comment
- Comments actually aren't nodes, they are their own special content type. Comments are what allow people to add comments to any other node that has been created.
- Forum
- Forums are sets of nodes and their comments. These are grouped together as belonging in one forum by assigning them the forum name, which is a taxonomy term. These forum names can be grouped in forum containers, which are other terms, of which they are children in a hierarchical vocabulary which is called "forums", and configured as only applicable to nodes of the "forum" type.
- Page
- Pages are simple nodes, typically used for static content that can (but are not required to) be linked into the main navigation bar
- Poll
- A poll is where a multiple choice question is asked and users can answer and see other peoples answers to questions.
- Story
- Story pages are news engine entries. Stories are generally used for information which is only relevant for a period of time (eg. news stories) and is expected to expire off of the page.
Many other node types are included by [ contributed modules].
In education
Websites for educators and researchers
Drupal is very popular in education (all levels) to build community web sites within which members can post news, share resources or collaborate in other ways. Examples:
- Learning Networks (R&D in Learning Design)
- Council of Writing Program Administrators
- Kairosnews (Community of members interested in the intersections of rhetoric and pedagogy with technology)
- EdTech tools and Opinion for Educators (Blog)
- Fab Central at MIT, an online community for inventors, artists and digital fabricators.
- FreeTeach.com Community of teachers for lesson plans, worksheets, and teaching ideas.
There are dozens more ...
Teaching platforms
While Drupal as platform for education-related websites doesn't come as a surprise, using Drupal instead of a learning management system is a more interesting topic. We believe that drupal is good platform to implement project-oriented learning designs. Typically, a teacher (and not the institution) will run the platform. It's something that Daniel K. Schneider advocated in his C3MS project-based learning model (implemented a few years ago with PostNuke).
Examples:
- Archive of Welcome to English 420S (Distance Learning), Purdue University
- Maxetom Integrates educational on-line multimedia applications. “Maxetom propose aux enfants des coloriages en ligne qui leur feront découvrir les couleurs en espagnol ou en anglais.”
Typically, a teacher (or an organization) will design a custom environment to support various kinds of learning activities. One way to think about this, was presented in 2004 in the TECFA SEED Catalog. There is also a TECFA SEED Catalog version in this wiki and that will be updated a bit in some nearer future - Daniel K. Schneider 11:10, 1 June 2007 (MEST).
Links and resource management
Example:
Installation
Prerequisites
- Drupal should install without problems on a LAMP or WAMP system. So install Apache/MySQL/Php first. In case you just want to play, I recommend WOS, a free WAMP distribution that runs on a memory stick and that includes a Drupal (optional module) !
Drupal is open-source software distributed under the GPL ("General Public License") and is maintained and developed by a community of thousands of users and developers.
Standard Drupal
Drupal is ready to go from the moment you download it. It even has an easy-to-use web installer. However, a typical educator probably would like to download and install third-party modules.
- Download page. (includes core system and modules).
DrupalEd
A group of people (including Bill Fitzgerald) released an educational package (not tested yet).
“DrupalEd is a powerful open source content management system with the power to support the e-learning needs of large educational institutions. It is also easy enough to install and use for individual teachers/professors to implement in their own classes (for teachers who would like to abandon BlackBoard, sans IT Department backing)” ([2]).
- DrupalEd Is Ready For Download (Announcement of 04/17/2007)
- DrupalEd page
Other extensions of interest to education
Getting started with drupal 7.27
Before the instalation
Moving Drupal to its intended location
If you are working locally using a Wamp systeme extract the zip file and copy-past it into the “www.directory”. If you are using a web server (e.g Tecfa server) follow the same procedure and copy-paste the extracted file in the directory that will host your future site.
Create a database and user using phpMyAdmin
Local machine:
If you don’t know how to create a user and a database using phpMyAdmin see the example wordpress/create a database
Web server:
According to the drupals’ community documentation “Most web hosting accounts provide a Web-based control panel to help you administer your site. These tools include easy-to-use features for creating a new database, and for creating a "user" with rights to the database. To create a database using a browser-based control panel consult the documentation or ask your web host service provider.” Either you use a local machine or a web server it is important to take note of the username, password, database name and hostname while you are creating the database as you will enter these items into fields in your browser when running the install script. [3]
Run the installation script:
Local machine:
Insert the URL (the directory where you placed your Drupal files).If you are using a system like WAMP the URL is http://localhost/drupal. If for example you renamed the extracted folder to drupalTest the URL is http://localhost/drupalTest.
Web server:
If you have installed drupal in a web host insert the domain name. if you are using the TECFA server insert the URL http://www.tecfaetu.unige.ch/. If you have installed Drupal in a subfolder that is called projects point your browser to the folder, for example http://www.tecfaetu.unige.ch/projects.
Installation process
Note: Be very careful when clicking save and continue. There is no back button.
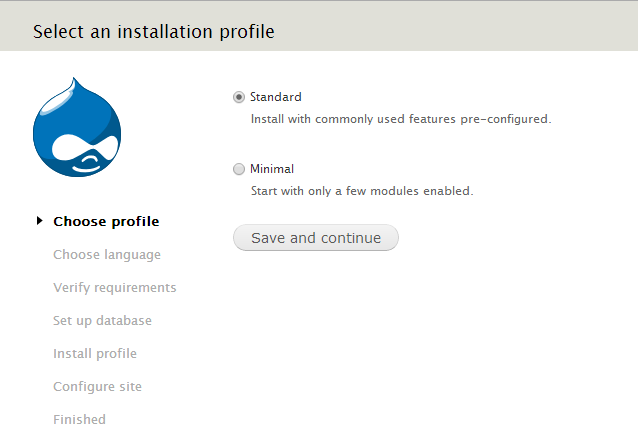
- Step 1
Select the Standard profile as shown in the picture.The Minimal profile is targeted toward more experienced Drupal site creators.
Click Save and continue
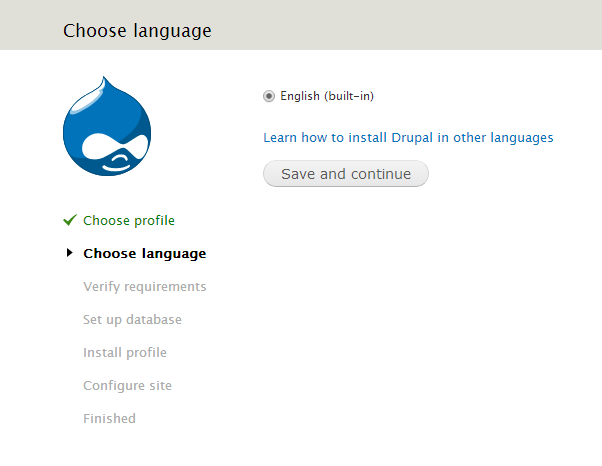
- Step 2
The default language is English, if you want to change the default language, click Learn how to install Drupal in other languages link.
Click Save and continue
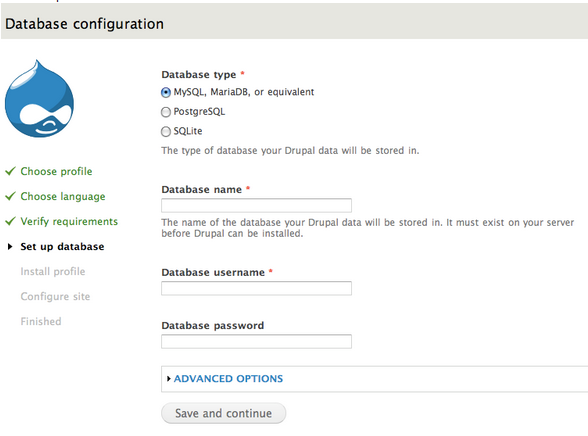
- Step 3
Select the database type, enter the database name and the database username that you created at the Create a database and user using phpMyAdmin step. According to Drupal community The Advanced options allow you to change the database host in case that you are using a web server, the port if you are using a non-standard port number and the table prefix if you are installing multiple instances of Drupal tables that share the same database. [4]
Click save and continue
- Step 4
The following progress bare will appear; wait for the installer to finish the installations.
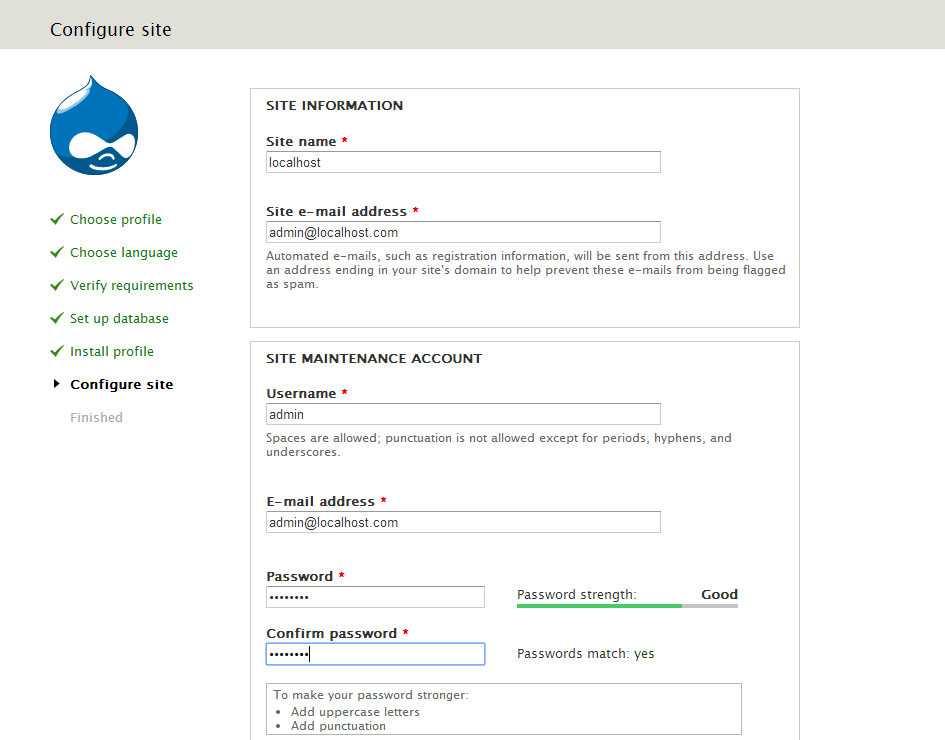
- Step 5
Provide the information for the first user accound. Note that all the following information can be changed later through the configuration panel.
- Site information: Enter the name of your site and the site e-mail address
- Site maintenance account: Enter the username and the password of the first user.
- Server settings: We can change the Default country and the Default time zone. Also you can uncheck the boxes in the Update notifications field if you don’t want to receive notifications for required updates.
Click Save and continue
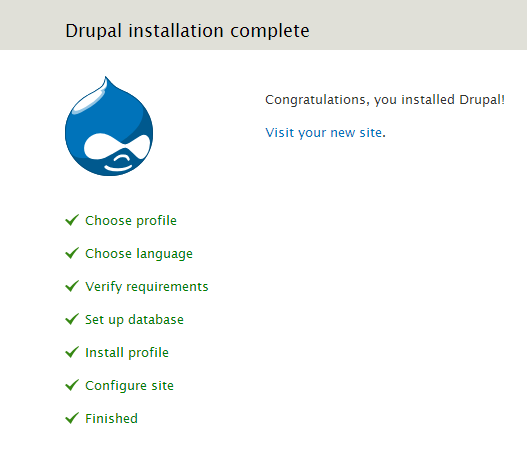
- Step 6
Your new site is ready. Click visit your new site
A glance to the administrators front-page
Links
Drupal
- Official
- Tutorial on the installation of Drupal avec Lamp/Wamp/Mamp (en anglais)
- Drupal Home
- Drupal sites.net
- Reviews and analysis on the Drupal website
- Choosing a platform for the telecentre.org distributed net
- Drupal and the New Paradigm for Content Management
- Drupal Themes
- drupal.org/project/Themes - Drupal Themes at drupal.org
- Drupal Theme Garden - Drupal Themes Showcase (live preview of Drupal Themes)
- Other
- A comparison of Drupal and Joomla Which is the best for You?
- Drupal Performance Tuning and Optimization for large web sites. A series of articles a 2BITS.
References
- There are many books about Drupal. See Books about Drupal.
- Albion, Peter (2005) 'Designing for an online doctoral studies community using an open source platform.' In: Crawford, C. and Carlsen, R. and Gibson, I. and McFerrin, K. and Price, J. and Weber, R. and Willis, D. A., (ed.). Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of the Society for Information Technology in Teacher Education, Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education, pp. 2138-2143. Abstract/HTML/PDF
- Norma, David Kent Distance Education Development And Delivery Tools (found with google scholar, no refs ..)
- Schneider Daniel; Mourad Chakroun, Pierre Dillenbourg, Catherine Frété, Fabien Girardin, Stéphane Morand, Olivier Morel and Paraskevi Synteta, (2004) TECFA Seed Catalog, unpublished, PDF