BPEL: Difference between revisions
m (→Links) |
m (→Tools) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{{quotation|Web service interactions can be described in two ways. Executable business processes model actual behavior of a participant in a business interaction. Abstract business processes are partially specified processes that are not intended to be executed. An Abstract Process may hide some of the required concrete operational details. Abstract Processes serve a descriptive role, with more than one possible use case, including observable behavior and process template. WS-BPEL is meant to be used to model the behavior of both Executable and Abstract Processes.([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_Process_Execution_Language Business Process Execution Language], retrieved jan 5 2009).}} | {{quotation|Web service interactions can be described in two ways. Executable business processes model actual behavior of a participant in a business interaction. Abstract business processes are partially specified processes that are not intended to be executed. An Abstract Process may hide some of the required concrete operational details. Abstract Processes serve a descriptive role, with more than one possible use case, including observable behavior and process template. WS-BPEL is meant to be used to model the behavior of both Executable and Abstract Processes.([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_Process_Execution_Language Business Process Execution Language], retrieved jan 5 2009).}} | ||
== The language == | |||
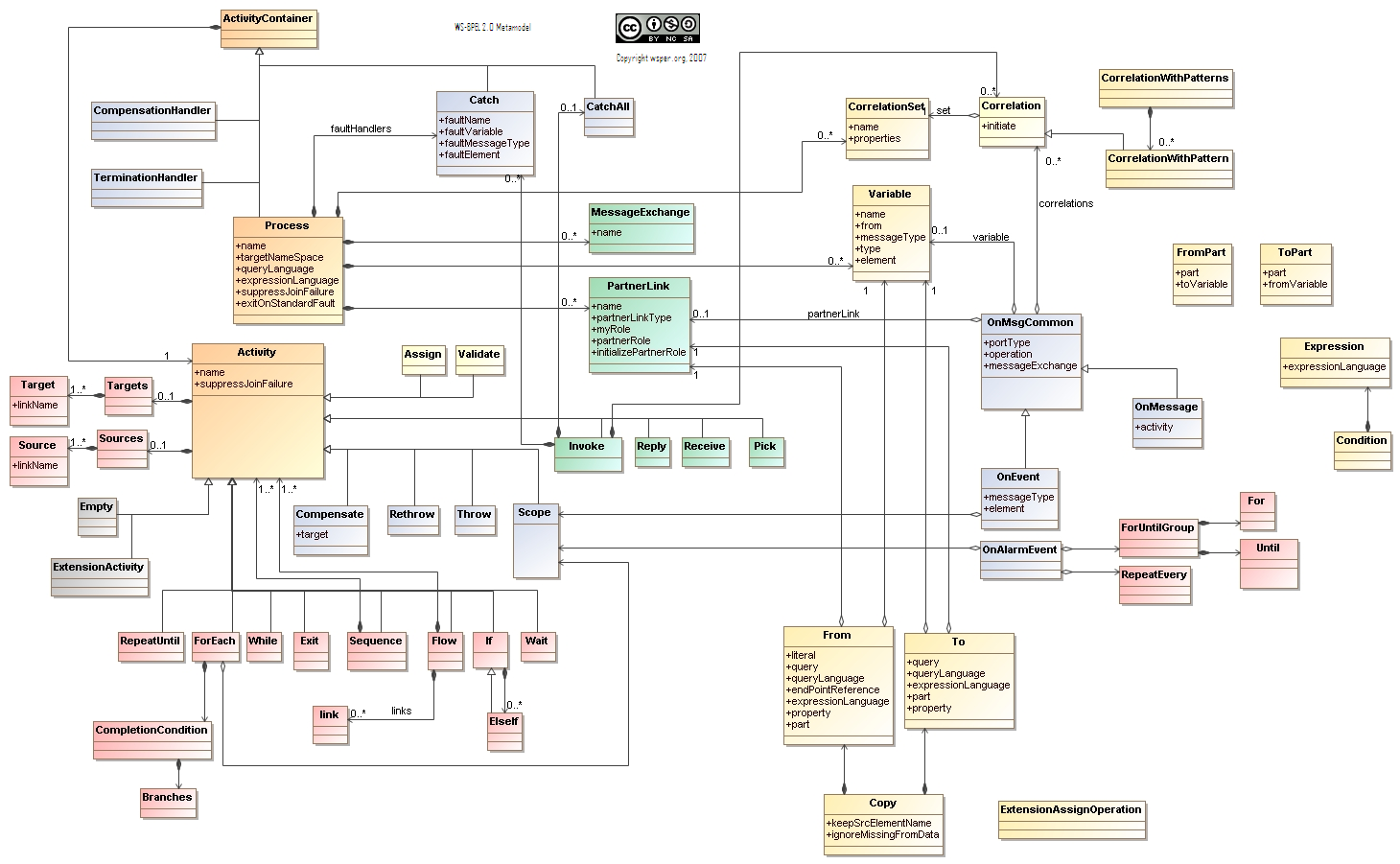
[[image:ws-bpel20b.png|frame|none|Simplified WS-BPEL 2.0 Meta model. Source: [http://www.ebpml.org/wsper/wsper/ws-bpel20.html WS-BPEL 2.0] ]] | |||
== Tools == | == Tools == | ||
; Visual design tools | ; Visual design tools | ||
* [[BPMN]] (not tested) is an example | * [[BPMN]] (not tested) is an example of a visual design language that compile into PBEL | ||
; BPEL applied to [[e-science]] | ; BPEL applied to [[e-science]] | ||
Revision as of 14:26, 22 June 2010
Definition
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL), short for Web Services Business Process Execution Language (WS-BPEL) is an executable language for specifying interactions with Web Services. (Wikipedia)
“Web service interactions can be described in two ways. Executable business processes model actual behavior of a participant in a business interaction. Abstract business processes are partially specified processes that are not intended to be executed. An Abstract Process may hide some of the required concrete operational details. Abstract Processes serve a descriptive role, with more than one possible use case, including observable behavior and process template. WS-BPEL is meant to be used to model the behavior of both Executable and Abstract Processes.(Business Process Execution Language, retrieved jan 5 2009).”
The language
Tools
- Visual design tools
- BPMN (not tested) is an example of a visual design language that compile into PBEL
- BPEL applied to e-science
- OMII-BPEL, OMII-BPEL brings an industrial standard, BPEL (Business Process Execution Language) to scientific workflow modeling and Grid services orchestration.
In education
Karampiperis and Sampson argued that BPEL (or rather a graphical representation language) could be used to design learning designs/ pedagogical scenarios that then can be compiled into IMS Learning Design Level A Representations.
Links
- Introductions
- Business Process Execution Language (Wikipedia)
- Standards
- * BPEL 2.0
Bibliography
- P. Karampiperis and D.Sampson: "Towards a Common Graphical Language for Learning Flows: Transforming BPEL to IMS Learning Design Level A Representations", in Proc. of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT 2007), ISBN: 9780769529165, pp. 798-800, Niigata, Japan, IEEE Computer Society, July 2007.