BioLogica: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Step 1: | Step 1: | ||
[[image:pedagogica-dragon0.jpg| | [[image:pedagogica-dragon0.jpg|thumb|600px|none|Dragon Baby - step 1]] | ||
Step 2: | Step 2: | ||
[[image:pedagogica-dragon1.jpg| | [[image:pedagogica-dragon1.jpg|thumb|600px|none|Dragon Baby - step 2]] | ||
Step 3: | Step 3: | ||
[[image:pedagogica-dragon2.jpg| | [[image:pedagogica-dragon2.jpg|thumb|600px|none|Dragon Baby - step 3]] | ||
Of course, I didn't learn much. This is a typical simulation without teacher and teaching scenario effect ;) | Of course, I didn't learn much. This is a typical simulation without teacher and teaching scenario effect ;) | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 18 August 2007
Definition
- BioLogica is a hypermodel, i.e. a kind of microworld for teaching fundamental concepts in biology. It runs within the Pedagogica system (that also runs other microworlds).
(About BioLogica, retrieved 17:00, 18 August 2007 (MEST)).
History
- Biologica is a sucessor system of GenScope. “Superficially, BioLogica looks a lot like GenScope. It has the same dragon species, though we plan to add more, and many of the same levels and tools. But whereas GenScope is a general purpose tool that students can use to investigate genetic phenomena, BioLogica is a tool with which researchers and teachers can develop genetics curriculum in the form of web-labs”. (retrieved 18:44, 21 July 2006 (MEST)).
Where GenScope's interface can be described as tool-driven, BioLogica's is activity-driven.
Conceptual Framework
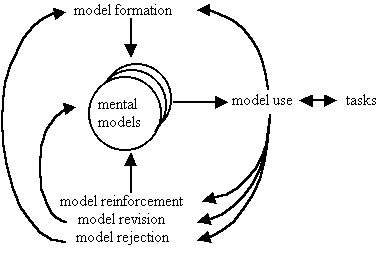
According to the BioLogica Research page (retrieved 17:00, 18 August 2007 (MEST)), the team's basic hypothesis is that understanding biological phenomena requires learners to construct, elaborate and revise mental models of the phenomena under study. Accordingly the state that “The importance of models and modeling in scientific research has been widely documented . Models are used both to describe scientific phenomena and to generate testable hypotheses . Today, models and modeling are considered essential components of scientific literacy . With the importance of models and modeling to science education comes the need for a coherent theory of model-based teaching and learning (MBTL).”
MBTL can be summarized with this picture:
(BioLogica Research Page, retrieved 17:00, 18 August 2007 (MEST). The author is maybe B. C. Buckley.)
Features and architecture
- Biologica runs as a model within a hypermodel, i.e. a designer must write a script to define a pedagogical scenario with educational activities.
Architecture
The BioLogica system is built with three separate layers, also called engines:
- At the lowest level is the domain engine, a database plus views to display information.
- Pedagogica, as the name suggests, handles all things pedagogical. It controls the flow of activity and is in charge of all interface details like placing text boxes, buttons, tools, domain engine views on the screen.
- The scripting engine allows the curriculum developper to create a "web-lab", i.e. a usable learning environment.
Note: The global system that runs GenScope is also called Pedagogica, a bit confusing, but maybe that was decided after the above information was written ...
My Dragon Baby
I made a dragon baby in 10 minutes (most of which was spent with downloading the software).
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Of course, I didn't learn much. This is a typical simulation without teacher and teaching scenario effect ;)
Requirements
- The system ran once over the Internet (now disabled 18:44, 21 July 2006 (MEST))
- An offline version is available from the Concord Consortium as of August 2007. Simply download Pedagogica. I will include Biologica plus other microworlds.
Links
BioLogica Home page.
References
- Boulter, C. J., & Buckley, B. C. (2000). Constructing a typology of models for science education. In J. K. Gilbert & C. J. Boulter (Eds.), Developing models in science education (pp. 25-42). Dordrecht, Holland: Kluwer.
- Buckley, B. C. (1992). Multimedia, misconceptions and working models of biological phenomena: Learning about the circulatory system. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, Stanford University.