SQL
Definition
According to Wikipedia, “SQL, commonly expanded as Structured Query Language, is a computer language designed for the retrieval and management of data in relational database management systems, database schema creation and modification, and database object access control management. SQL has been standardized by both ANSI and ISO.”, retrieved 11:47, 4 September 2007 (MEST).
See also: MySQL and the SQL and MySQL tutorial (this article just provides a short summary of SQL and points to further reading on Wikipedia)
Overview of language elements
This overview chapter is copied from Wikipedia SQL article. (retrieved 11:47, 4 September 2007 (MEST)) with minor markup modificiations. Its contents are available under the GNU Free Documentation License. Links lead to specialized Wikipedia articles.
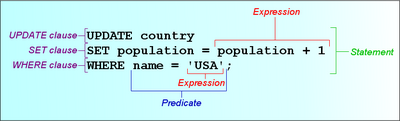
The SQL language is sub-divided into several language elements, including:
- Statements which may have a persistent effect on schemas and data, or which may control transactions, program flow, connections, sessions, or diagnostics.
- Queries which retrieve data based on specific criteria.
- Expressions which can produce either (computing) scalar values or tables consisting of columns and (database) rows of data.
- Predicates which specify conditions that can be evaluated to SQL three-valued logic (3VL) Boolean truth values and which are used to limit the effects of statements and queries, or to change program flow.
- Clauses which are (in some cases optional) constituent components of statements and queries.[1]
- Whitespace is generally ignored in SQL statements and queries, making it easier to format SQL code for readability.
- SQL statements also include the ";" statement terminator. Though not required on every platform, it is defined as a standard part of the SQL grammar.
Queries
The most common operation in SQL databases is the query, which is performed with the declarative SELECT keyword. SELECT retrieves data from a specified table, or multiple related tables, in a database. While often grouped with Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements, the standard SELECT query is considered separate from SQL DML, as it has no persistent effects on the data stored in a database. Note that there are some platform-specific variations of SELECT that can persist their effects in a database, such as Microsoft SQL Server's proprietary SELECT INTO syntax.
(SQL Server 2005 Books Online)
SQL queries allow the user to specify a description of the desired result set, but it is left to the devices of the management system database management system (DBMS) to plan, optimize, and perform the physical operations necessary to produce that result set in as efficient a manner as possible. A SQL query includes a list of columns to be included in the final result immediately following the SELECT keyword. An asterisk ("*") can also be used as a "wildcard" indicator to specify that all available columns of a table (or multiple tables) are to be returned. SELECT is the most complex statement in SQL, with several optional keywords and clauses, including:
- The
FROMclause which indicates the source table or tables from which the data is to be retrieved. TheFROMclause can include optionalJOINclauses to join related tables to one another based on user-specified criteria. - The
WHEREclause includes a comparison predicate, which is used to restrict the number of rows returned by the query. TheWHEREclause is applied before theGROUP BYclause. TheWHEREclause eliminates all rows from the result set where the comparison predicate does not evaluate to True. - The
GROUP BYclause is used to combine, or group, rows with related values into elements of a smaller set of rows.GROUP BYis often used in conjunction with SQL aggregate functions or to eliminate duplicate rows from a result set. - The
HAVINGclause includes a comparison predicate used to eliminate rows after theGROUP BYclause is applied to the result set. Because it acts on the results of theGROUP BYclause, aggregate functions can be used in theHAVINGclause predicate. - The
ORDER BYclause is used to identify which columns are used to sort the resulting data, and in which order they should be sorted (options are ascending or descending). The order of rows returned by a SQL query is never guaranteed unless anORDER BYclause is specified.
The following is an example of a SELECT query that returns a list of expensive books. The query retrieves all rows from the books table in which the price column contains a value greater than 100.00. The result is sorted in ascending order by title. The asterisk (*) in the select list indicates that all columns of the books table should be included in the result set.
SELECT * FROM books WHERE price > 100.00 ORDER BY title;
The example below demonstrates the use of multiple tables in a join, grouping, and aggregation in a SQL query, by returning a list of books and the number of authors associated with each book.
SELECT books.title, count(*) AS Authors FROM books JOIN book_authors ON books.isbn = book_authors.isbn GROUP BY books.title;
Example output might resemble the following:
Title Authors ---------------------- ------- SQL Examples and Guide 3 The Joy of SQL 1 How to use Wikipedia 2 Pitfalls of SQL 1 How SQL Saved my Dog 1
(The underscore character "_" is often used as part of table and column names to separate descriptive words because other punctuation tends to conflict with SQL syntax. For example, a dash "-" would be interpreted as a minus sign.)
Under the precondition that isbn is the only common column name of the two tables and that a column named title only exists in the books table, the above query could be rewritten in the following form:
SELECT title, count(*) AS Authors FROM books NATURAL JOIN book_authors GROUP BY title;
However, many vendors either don't support this approach, or it requires certain column naming conventions. Thus, it is less common in practice.
Data retrieval is very often combined with data projection when the user is looking for calculated values and not just the verbatim data stored in primitive data types, or when the data needs to be expressed in a form that is different from how it's stored. SQL allows the use of expressions in the select list to project data, as in the following example which returns a list of books that cost more than 100.00 with an additional sales_tax column containing a sales tax figure calculated at 6% of the price.
SELECT isbn, title, price, price * 0.06 AS sales_tax FROM books WHERE price > 100.00 ORDER BY title;
Data manipulation
First, there are the standard Data Manipulation Language (DML) elements. DML is the subset of the language used to add, update and delete data:
INSERT INTO my_table (field1, field2, field3) VALUES ('test', 'N', NULL);
UPDATEis used to modify the values of a set of existing table rows, eg:
UPDATE my_table SET field1 = 'updated value' WHERE field2 = 'N';
DELETEremoves zero or more existing rows from a table, eg:
DELETE FROM my_table WHERE field2 = 'N';
MERGEis used to combine the data of multiple tables. It is something of a combination of theINSERTandUPDATEelements. It is defined in the SQL:2003 standard; prior to that, some databases provided similar functionality via different syntax, sometimes called an "upsert".
Transaction controls
Transactions, if available, can be used to wrap around the DML operations:
BEGIN WORK(orSTART TRANSACTION, depending on SQL dialect) can be used to mark the start of a database transaction, which either completes completely or not at all.COMMITcauses all data changes in a transaction to be made permanent.ROLLBACKcauses all data changes since the lastCOMMITorROLLBACKto be discarded, so that the state of the data is "rolled back" to the way it was prior to those changes being requested.
COMMIT and ROLLBACK interact with areas such as transaction control and locking. Strictly, both terminate any open transaction and release any locks held on data. In the absence of a BEGIN WORK or similar statement, the semantics of SQL are implementation-dependent.
Example:
BEGIN WORK; UPDATE inventory SET quantity = quantity - 3 WHERE item = 'pants'; COMMIT;
Data definition
The second group of keywords is the Definition Language (DDL). DDL allows the user to define new tables and associated elements. Most commercial SQL databases have proprietary extensions in their DDL, which allow control over nonstandard features of the database system.
The most basic items of DDL are the CREATE, ALTER, RENAME, TRUNCATE and DROP statements:
CREATEcauses an object (a table, for example) to be created within the database.DROPcauses an existing object within the database to be deleted, usually irretrievably.TRUNCATEdeletes all data from a table (non-standard, but common SQL statement).ALTERstatement permits the user to modify an existing object in various ways -- for example, adding a column to an existing table.
Example:
CREATE TABLE my_table ( my_field1 INT, my_field2 VARCHAR (50), my_field3 DATE NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (my_field1, my_field2) );
Data control
The third group of SQL keywords is the Data Control Language (DCL). DCL handles the authorization aspects of data and permits the user to control who has access to see or manipulate data within the database. Its two main keywords are:
GRANTauthorizes one or more users to perform an operation or a set of operations on an object.REVOKEremoves or restricts the capability of a user to perform an operation or a set of operations.
Example:
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON my_table TO some_user, another_user.
Other
- ANSI-standard SQL supports double dash,
--, as a single line comment identifier (some extensions also support curly brackets or C style/* comments */for multi-line comments).
Example:
SELECT * FROM inventory -- Retrieve everything from inventory table
- Some SQL servers allow Function User Defined Functions.
References
- ↑ ANSI/ISO/IEC International Standard (IS). Database Language SQL, Part 2: Foundation (SQL/Foundation). 1999
Links
- Overviews
- SQL (Wikipedia)
- Introductory Tutorials
- What is SQL ? (SQL Course.com). Includes an online SQL interpreter where you can test expressions.
- Brockwood, Ted (2000). Getting Started With SQL, Web Developer.com
- Ted Brockwood (2000). Simple SQL: Pt. 1, SQL Etc, DataBase Journal.
- Gilfillan, Ian (2002), SQL joins - multi-table queries, SQL Etc., Database Journal.
- Greenspun, Philip (2003). Chapter 12: Database Management Systems HTML, part of Philip and Alex's Guide to Web Publishing.
- Greespun. Philip (2003). SQL for Web Nerds, HTML
- Hoffman, James (1998). Introduction to Structured Query Language: Version 4.11, Intermedia.net
- Sol, Selena (1998). Introduction to Databases for the Web: Pt. 1 - What is a database ?, Database Journal
- Sol, Selena (1998). Introduction to Databases for the Web: Pt. 2 - Retrieving Data, Database Journal
- Sol, Selena (1998). Introduction to Databases for the Web: Pt. 3, Server Side Database Communication with CGI, Database Journal
- PHP
- See also MySQL (since many tutorials focus on PHP-MYSQL)
- Gilfillan Ian (2003). An introduction to the ADOdb class library for PHP, Database Journal.
- Tools
- SchemaSpy analyzes schema metadata, letting you click through the hierarchy of tables' parent/child relationships. Works with just about any RDBMS that supports JDBC (Oracle/MySQL/DB2/SQL Server/PostgreSQL/Sybase/etc).