Stitch Era - vector graphics: Difference between revisions
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
=== Adding and deleting nodes === | === Adding and deleting nodes === | ||
'''Deleting a node''' | '''1) Deleting a node''' | ||
* Select | * Select a node. Make sure to select a white or cyan vector shape control node and not just one of the grey envelope controls (see above). Most shape control nodes then will also show curve control handlers ... one or two little pink circles. | ||
* Right click (context menu) and select ''delete'' or '''hit the delete key''' | * Right click (context menu) and select ''delete'' or '''hit the delete key''' | ||
'''Warning''', before you decide to use the quicker ''delete key'' method, you should be aware that sometimes you will fail to select a node | '''Warning''', before you decide to use the quicker ''delete key'' method, you should be aware that sometimes you will fail to select a node, select the whole vector object instead and then kill the whole object. Hit CTRL-Z to get it back. | ||
After deleting a node, you probably will have to adjust the curves. | After deleting a node, you probably will have to adjust the curves. | ||
'''Mass deletion of nodes''' | '''2) Mass deletion of nodes''' | ||
* You can select nodes in different places by holding down the CTRL key | * You can select nodes in different places by holding down the CTRL key | ||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
Btw you also can do other operations to a sequence of selected nodes, e.g. turn all nodes into straight nodes. Explore the context menu ! | Btw you also can do other operations to a sequence of selected nodes, e.g. turn all nodes into straight nodes. Explore the context menu ! | ||
'''Inserting a node''' | '''3) Inserting a node''' | ||
In SEU, inserting a node means adding a node within a curve between the currently selected node and the prior node. | In SEU, inserting a node means adding a node within a curve between the currently selected node and the prior node. | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 11 June 2011
<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>
Introduction
This is a beginner's tutorial for the Stitch Era embroidery software. It explains how create and edit vector graphics that later could be translated to embroidery objects (stitch sections).
There are three reasons for learning how to use vector graphics
- Repair/adjust vectorized bitmap (raster) images
- Work with imported vector graphics (as opposed to use the original source program)
- Draw vector art with Stitch Era
Of course, these three use cases can be combined in a project.
The Interface
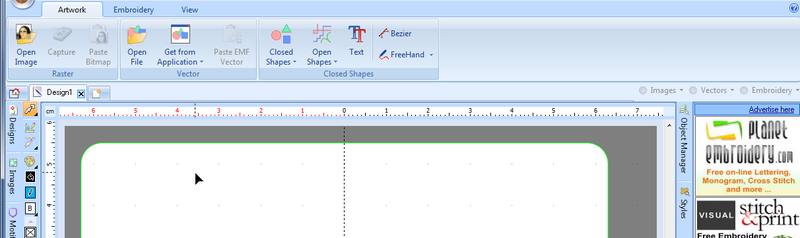
When you start a new empty project you will find yourself automatically in the Artwork tool, i.e. the vector graphics environment as shown in the following picture.
At this point you now either can import artwork, e.g. like discussed in Stitch Era - simple digitizing or start drawing. There are several kinds of drawings
- Insert pre-built closed shapes
- Insert pre-build open shapes
- Draw shapes with Bezier curves
- Draw shapes free-hand
- Draw letters with the text tool
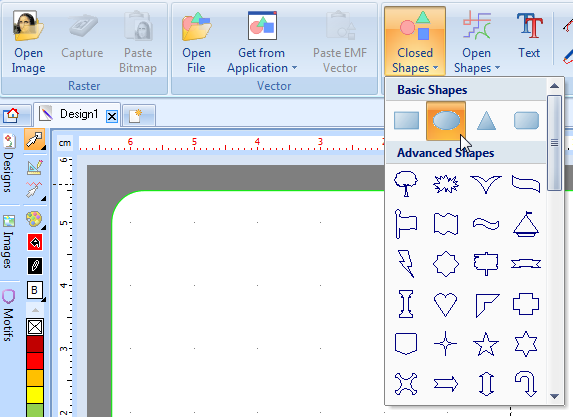
Let's insert an ellipse, i.e. a close shape, as shown below. Select the ellipse icon from the Closed shapes pull down menu, then move the mouse into the work area below and drag it.
If you aim to create a circle, you could watch the dimensions at the bottom of the Stitch Era screen. However, we suggest to draw an approximate object and then edit it's properties later.
After you inserted a first vector object or when you select one, the the interface will change and display the full tool set.
Firstly, you may want to change colors. Play with "fill color" and "border color". You also may notice the "Layout" tab in the top menu. It would allow you to change the size, position and rotation of the object and align/distribute several objects. More about this later.
Vector objects - fills and borders
Firstly, you must understand that vector objects like circles are made of two parts:
- The border (also called outline, stroke or line)
- The fill, i.e. the inside
In the format tab, by selecting one of the rectangles (see fig. below) you can select whether you want
- a fill-only object (Vectors-only body), i.e. the border is made invisible
- a stroke-only object (Vectors-only outline), i.e. the shape is made invisible
- an object that has both (Vectors outline + body).
For embroidery (as well as for other multi-media projects) you will work with all three.
Manipulation of vector shapes
Shape and shape adjustments of vector objects
The shape of a vector object is defined by its border, or more precisely by so-called control points or nodes that will define the exact path of the border. Control points are either white or cyan and can be moved and curves connecting to the next nodes can be changed through handles represented as small little pink points.
Tip: Pre-built shapes must be converted to vector objects first (right click).
Since borders are not defined by pixels but by control points, vector objects are scalable upwards or downwards. A drawing will remain the same whether it has the size of a bed linen or a shirt pocket or a football field.
In stitch era, there are different kinds of vector nodes. The way they connect to neighboring nodes are defined by three properties (parameters) that one can change in the Nodes ribbon:
- Straight / curved sides. A straight node (point) will have a straight line to the nodes before and after the path defining the outline or simple stroke. Curved nodes have curved lines to the nodes before and after (unless one of these nodes is a straight node). Straight nodes show as rectangles.
- Normal nodes / corner node. Normal nodes are white. Corner nodes are shown as filled cyan nodes.
- Symmetric / uniform nodes. Symmetric and uniformed nodes are not visually distinguishable. However handles of uniform nodes may be handled independently.
The following screen capture shows a mushroom being designed. It's hat is modelled with normal nodes, the stem with corner nodes and the bottom with straight nodes.
In order to change the curves connecting to a node, click on the node then move the pink curve controls in and out (for amplitude) and turn around the point for direction.
Adding and deleting nodes
1) Deleting a node
- Select a node. Make sure to select a white or cyan vector shape control node and not just one of the grey envelope controls (see above). Most shape control nodes then will also show curve control handlers ... one or two little pink circles.
- Right click (context menu) and select delete or hit the delete key
Warning, before you decide to use the quicker delete key method, you should be aware that sometimes you will fail to select a node, select the whole vector object instead and then kill the whole object. Hit CTRL-Z to get it back.
After deleting a node, you probably will have to adjust the curves.
2) Mass deletion of nodes
- You can select nodes in different places by holding down the CTRL key
- You can select a sequence of nodes by selecting the first, then selecting the second (end of the sequence) holding down the SHIFT key.
If you want to delete a sequence of nodes you also can just hit delete several times in a row. Deletion will happen in the direction of the more recent added node.
Btw you also can do other operations to a sequence of selected nodes, e.g. turn all nodes into straight nodes. Explore the context menu !
3) Inserting a node
In SEU, inserting a node means adding a node within a curve between the currently selected node and the prior node.
Adding a node is different operation (see below)
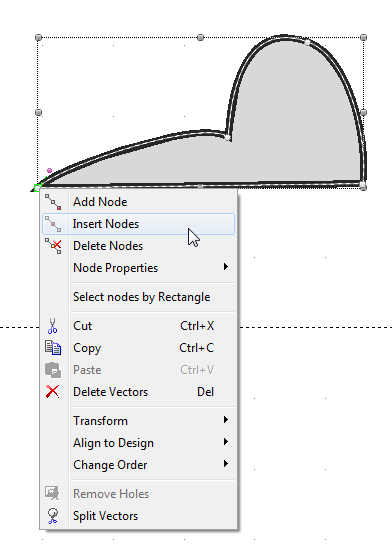
To insert a node:
- Select a node. In the picture below we selected the lowest left one.
- Right-click to access the context menu: You now can delete, insert and add
In a corner, it may be difficult to select a shape control node as opposed to an envelope node, or the other way round. The latter only can be used to change overall size and rotation. You may have to click twice. If you still can't select, then just drag the node inwards/upwards so that it won't fit into the corner. Drag it back later.
Size and rotation
In addition, a vector object is defined by its width, height, rotation and position. All of these can be manipulated through the eight grey rectangular controls that sit on the bounding box rectangle.
- Resizing an object uniformly: Drag one of the four corner points
- Resizing an object's height or width: Drag one of the four grey points in the middle
- Rotation: Hold down the CTRL key and drag clockwise or counter-clock wise a grey point in one of the corners
- Changing the rotation point: Hold down the CTRL key and move the light grey little circle that originally may be in the center.
Tip:
- Size (both direction) or height and width also can be changed using the Layout tool, i.e. change values to the left.
Free hand drawing
The FreeHand tool allows to create all four vector object types:
- shapes only
- outlines only (closed pathes)
- lines (pathes)
- shapes + outlines
To create a free hand object:
- Click on the FreeHand tool
- Then set the type of drawing, i.e. pick the right rectangle (Only Body, only outline, or outline+body) in the Format Tab.
Closed vs. open pathes (i.e. shapes vs. lines): A figure becomes closed when the end point (where you release the mouse) is very close to the starting point
The Create Perfect Figures option:
- TheFreeHand tool has a little pulldown menu that allows you to draw smoother figures, i.e. drawings that have less control points and simpler curves. Tick this option and try.
The following screen capture shows a perfect cloud (well, with respect to my drawing skills) made with the FreeHand tool and the following options:
- Create Perfect Figures = on,
- vectors outline + body = ticked
- Fill Color = light grey
- Border Color = dark grey
Of course, you now could make adjustments in several ways:
- Drag nodes
- Adjust curves with the curve control handlers (click on a node first). You may to transform a node into a different type (e.g. a normal node into a corner node using the Nodes panel)
- Add / Insert new nodes
- Add new drawings.
Drawing vector objects with Bezier curves
(.... more to come ...)