Design-based research: Difference between revisions
(using an external editor) |
(using an external editor) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Definition == | |||
According to Reeves (2000:8), Ann Brown (1992) and Alan Collins (1992) defined critical characteristics of design experiments as: | |||
* addressing complex problems in real contexts in collaboration with practitioners, | |||
* integrating known and hypothetical design principles with technological affordances to render plausible solutions to these complex problems, and | |||
* conducting rigorous and reflective inquiry to test and refine innovative learning | |||
environments as well as to define new design principles. | |||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
First, the central goals of designing learning environments and developing theories or “prototheories” of learning are intertwined. Second, development and research take place through continuous cycles of design, enactment, analysis, and redesign. Third, research on designs must lead to sharable theories that help communicate relevant implications to practitioners and other educational designers. Fourth, research must account for how designs function in authentic settings. It must not only document success or failure but also focus on interactions that refine our understanding of the learning issues involved. Fifth, the development of such accounts relies on methods that can document and connect processes of enactment to outcomes of interest. (Design-Based Research Collective, 2003). | First, the central goals of designing learning environments and developing theories or “prototheories” of learning are intertwined. Second, development and research take place through continuous cycles of design, enactment, analysis, and redesign. Third, research on designs must lead to sharable theories that help communicate relevant implications to practitioners and other educational designers. Fourth, research must account for how designs function in authentic settings. It must not only document success or failure but also focus on interactions that refine our understanding of the learning issues involved. Fifth, the development of such accounts relies on methods that can document and connect processes of enactment to outcomes of interest. (Design-Based Research Collective, 2003). | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
== DBR according to Reeves == | |||
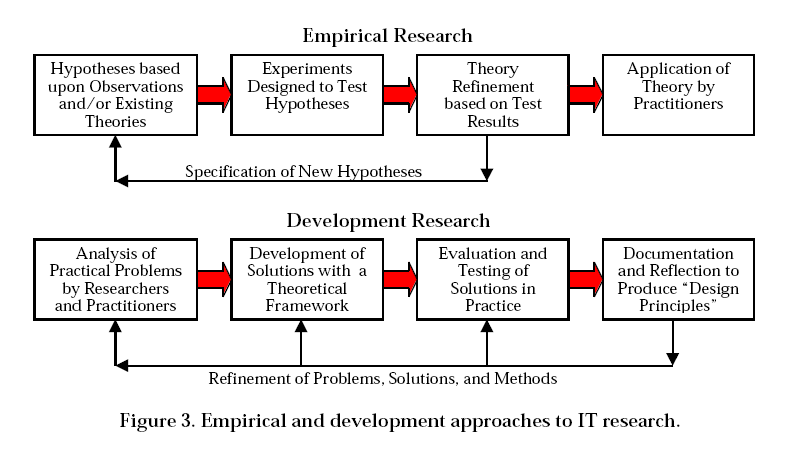
Reeves (2000:9) draws a clear line between research conducted with traditional empirical goals and that inspired by development goals leading to "Design Principles": | |||
[[image:design-research-reeves-2000.png]] | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 23: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* The Design-Based Research Collective (2003) Design-Based Research: An Emerging Paradigm for Educational Inquiry. Educational Researcher, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. | * The Design-Based Research Collective (2003) Design-Based Research: An Emerging Paradigm for Educational Inquiry. Educational Researcher, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 5 | ||
Thomas C. Reeves, Enhancing the Worth of Instructional Technology Research through Design Experiments and Other Development Research Strategies, Paper presented on April 27, 2000 at Session 41.29, International Perspectives on Instructional Technology Research for the 21st Century, a Symposium sponsored by SIG/Instructional Technology at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA, USA. [http://it.coe.uga.edu/~treeves/AERA2000Reeves.pdf] | |||
[[Category:Research Methodology]] | [[Category:Research Methodology]] | ||
Revision as of 15:12, 17 March 2006
Definition
According to Reeves (2000:8), Ann Brown (1992) and Alan Collins (1992) defined critical characteristics of design experiments as:
- addressing complex problems in real contexts in collaboration with practitioners,
- integrating known and hypothetical design principles with technological affordances to render plausible solutions to these complex problems, and
- conducting rigorous and reflective inquiry to test and refine innovative learning
environments as well as to define new design principles.
First, the central goals of designing learning environments and developing theories or “prototheories” of learning are intertwined. Second, development and research take place through continuous cycles of design, enactment, analysis, and redesign. Third, research on designs must lead to sharable theories that help communicate relevant implications to practitioners and other educational designers. Fourth, research must account for how designs function in authentic settings. It must not only document success or failure but also focus on interactions that refine our understanding of the learning issues involved. Fifth, the development of such accounts relies on methods that can document and connect processes of enactment to outcomes of interest. (Design-Based Research Collective, 2003).
DBR according to Reeves
Reeves (2000:9) draws a clear line between research conducted with traditional empirical goals and that inspired by development goals leading to "Design Principles":
Links
References
- The Design-Based Research Collective (2003) Design-Based Research: An Emerging Paradigm for Educational Inquiry. Educational Researcher, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 5
Thomas C. Reeves, Enhancing the Worth of Instructional Technology Research through Design Experiments and Other Development Research Strategies, Paper presented on April 27, 2000 at Session 41.29, International Perspectives on Instructional Technology Research for the 21st Century, a Symposium sponsored by SIG/Instructional Technology at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA, USA. [1]