XML
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- This page is juste a beginning. Several sub-topics will be factored out to other pages.
Definition
- XML means "Extended markup language". It allows to define all sorts of languages that describe information contents (e.g. web pages, vector graphics, programming languages). In technical terms, such languages are called XML applications or XML vocabularies.
- XML is designed as a machine readable self describing text editable persistent store for data. XML is a formalism or a meta-language (not to be confounded with HTML, a language to describe the structure of Web pages)
History
- XML is a subset of SGML (Standardized Generalized Markup Language). SGML has been used to define HTML whereas XHTML is defined with XML (This is why empty tags are not allowed anymore in XHTML).
- XML was formally defined in 1998 as W3C's XML Recommendation 1.0
- Since then, hundreds of XML languages have been defined and few dozens are popular and in production. Ken Sall's famous Big Picture only lists some, e.g. he misses out all the IMS e-learning standards.
The XML planet
One may look at XML from different angles.
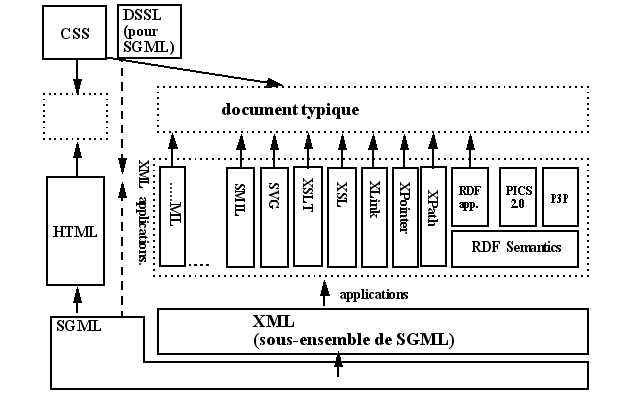
XML for better Web contents
Look at this nice picture drawn by DSchneider (needs translation and updating). It shows how future web documents will be composed:
XML as the foundation for the future semantic Web
- Essentially the RDF framework.
XML for machine to machine talk
- Web Services
XML as formalism to define other information structures
Some technical XML concepts
An XML document can refer to a physical file, a database entry, a datastream (any appropriate "text" that is delimited).
Wellformedness
An XML document is well formed if and only if
- There is an appropriate XML declaration at the beginning
- The document starts with an XML declaration that includes a version number (currently 1.0).
<?xml version="1.0"?>
- This declaration can also contain encoding information. By default encoding isUTF-8):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
- XML documents are hierarchical
- begin-tags and end-tags that match
- No tags crossing like
<i>...<b>...</i> .... </b>
- There must be single root
- It can only appear once and can not be used within other elements
- Other features
- XML is case sensitive, "LI" is not "li" for example
- "Empty" tags must be self closing, e.g.
- Attribute values are quoted
<a href= " http://tecfa.unige.ch:8080/xml.html " >)
- Special caracters: <,