Web accessibility
Definition
“Web accessibility refers to the inclusive practice of making websites usable by people of all abilities and disabilities. When sites are correctly designed, developed and edited, all users can have equal access to information and functionality.” (Wikipedia, retrieved no 18, 2010)
See also: web usability, usability, ergonomics and cognitive ergonomics
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
, Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0 retrieved 12:57, 4 June 2008 (UTC).
Users with accessibility problems
According to wikipedia
- Visual: Visual impairments including blindness, various common types of low vision and poor eyesight, various types of color blindness;
- Motor/Mobility: e.g. difficulty or inability to use the hands, including tremors, muscle slowness, loss of fine muscle control, etc., due to conditions such as Parkinson's Disease, muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, stroke;
- Auditory: Deafness or hearing impairments, including individuals who are hard of hearing;
- Seizures: Photoepileptic seizures caused by visual strobe or flashing effects.
- Cognitive/Intellectual: Developmental disabilities, learning disabilities (dyslexia, dyscalculia, etc.), and cognitive disabilities of various origins, affecting memory, attention, developmental "maturity," problem-solving and logic skills, etc.;
Some of you may think that you can ignore these populations since they are small. Besides ethical questions, also consider that you may be in situations where you are disabled:
- Visual: You drive a car, so you want an audio browser.
- Motor: You try to view web pages on your cell phone ;)
- Auditory: You are in a boring meeting or a class and want to "listen" to news
- Cognitive/Intellectual: You are drunk are really tired, but need to repair a server. So it's got to be both simple and effective.
Assistive technology
According to WAI's How to Make Presentations Accessible to All (retrieved nov 24 2010), “Assistive technologies are software or equipment that people with disabilities use to improve interaction with the web, such as screen readers that read aloud web pages for people who cannot read text, screen magnifiers for people with some types of low vision, and voice recognition software and selection switches for people who cannot use a keyboard or mouse.”
Software
NVDA NonVisual Desktop Access (NVDA) is a free and open source screen reader for the Microsoft Windows operating system. Providing feedback via synthetic speech and Braille, it enables blind or vision impaired people to access computers running Windows for no more cost than a sighted person. Major features include support for over 20 languages and the ability to run entirely from a USB drive with no installation.
Standards and Issues
Guidelines
See also Guidelines-based review (for checklists)
- Overviews at W3C
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines ( WCAG ) addresses web content, and is used by developers, authoring tools, and accessibility evaluation tools
- Evaluation and Report Language ( EARL ) addresses the expression of website evaluation test results in a platform independent format
- Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines ( ATAG ) addresses authoring tools
- User Agent Accessibility Guidelines ( UAAG ) addresses web browsers and media players, including some aspects of assistive technologies
- Accessible Rich Internet Applications ( WAI-ARIA ) addresses dynamic web content and web applications developed with Ajax, DHTML, and other web technologies.
- Other
- Introduction to Web Accessibility at WebAIM (Web Accessibility in mind). 'Excellent introduction. Also includes videos and links.
Formal recommendations
A first version of the web content guidelines (and that is still frequently cited) was published in 1999 as Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0 (WCAG), W3C Recommendation 5-May-1999
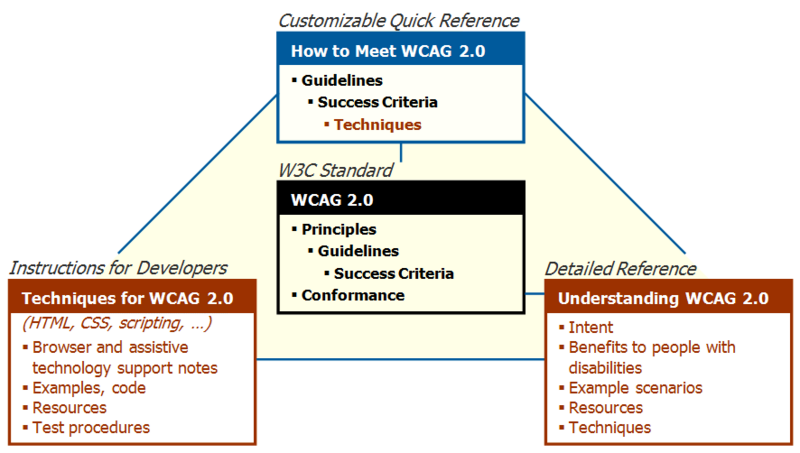
WCAG 2.0 became a formal recommentation (standard) in december 2008. According to the WCAG Overview (retrieved 16:37, 24 November 2010 (CET)), version 2 of the Web Content Accesssibility Guidelines “has 12 guidelines that are organized under 4 principles: perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. For each guideline, there are testable success criteria, which are at three levels: A, AA, and AAA.”. This standards document is completed by four supporting documents:
- How to Meet WCAG 2.0. This is a practical technical quick quide for web content developers.
- Understanding WCAG 2.0. This is very detailed text (many pages, some with further links).
- Techniques for WCAG 2.0
The relationship between these four texts is explained in The WCAG 2.0 Documents and its following figure:
Other
- Web Accessibility for Older Users: A Literature Review, W3C Working Draft 14 May 2008
Bodies
- Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI). Consult this pages for more W3C documents.
Links
- Web accessibility (Wikipedia)
- Issues in Digital Technology in Education/Accessibility and Usability (part of a wikibook)
- W3C Web Accessibility initiative's Presentation and Training material, in particular:
- Step-by-Step Guide for self-study, retrieved 16:37, 24 November 2010 (CET)
- Presentation format, retrieved 16:37, 24 November 2010 (CET)
- HTML/CSS for presentations, retrieved 16:37, 24 November 2010 (CET)