Developing design documents (3D) model
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The 3D model of design documentation is a framework to discuss various kinds of instructional design languages and documents.
Boot (2005:26) argues that “production-related information is typically embedded in three types of building blocks for the production process: (a) design documents as input, (b) programming structures as throughput, and (c) learning materials as output.”
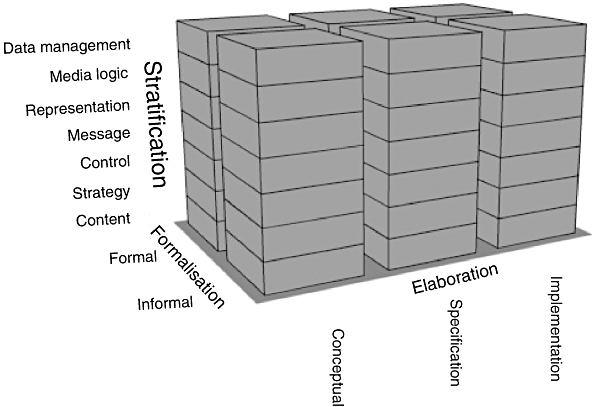
3D model includes three major dimensions:
- stratification: Functionally different instructional and technical structures
- degree of elaboration: conceptual, specification or implementation
- formality: formal vs. informal
The model
Stratification
Layers of instructional design
Gibbons (2000) argues that instructional designs are layered structures. Layering is a general design principle.
- Content layer
- Strategy layer
- Control layer
- Message layer
- Representation layer
- Media Logic layer
- Management layer
Each instructional design layer is the defined by:
- A specific set of design goals or problems
- Sets of layer-specific design structures, expressed in the terms of design languages
- Principles for the selection, arrangement, and mapping of structures within a layer
- Principles for the relation of structures across layers
Elaboration
Boot (2005:27) adopts Fowler's three perspectives for which different levels of detail can be specified:
- A conceptual perspective, with more or less superficial and descriptive information;
- a specification perspective, with more or less comprehensive and detailed information,
- an implementation perspective with more or less technical and meticulous information
Formalization
Designers can choose to use formal design languages or not.
- formal
- informal
References
- Boot, Eddy (2005), Building-block solutions for developing instructional software, PhD Dissertation, Open Universiteit Nederland. PDF and PDF
- Boot, Eddy W.; Jon Nelson, Jeroen J.G. van Merri��nboer, Andrew S. Gibbons (2007). Stratification, elaboration and formalisation of design documents: Effects on the production of instructional materials, British Journal of Educational Technology 38 (5), 917�%G�–�%@933. [doi:10.1111/j.1467-8535.2006.00679.x]
- Gibbons, A. S. (2003). What and how designers design? A theory of design structure. TechTrends, 47(5), 22-27. PDF (Access restricted)
- Gibbons, Andrew, S. and Erin K. Brewer, (2005) ���Elementary principles of design languages and design notation systems for instructional design���. In J.M. Spector, C. Ohrazda, A. Van Schaack, and D. Wiley (Eds.), Innovations to instructional technology: Essays in honor of M. David Merrill, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah NJ, pp. 111-129.
- Waters, Sandie, H. & Andrew, S. Gibbons (2004). Design languages, notation systems, and instructional technology: A case study: Educational Technology Research and Development, 52(2), 57-69. PDF (Access restricted)