MISA: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→References) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== Software == | == Software == | ||
MISA MOT Software is free for non-profit organizations we believe) that can be obtained from [http://www.cogigraph.com Cognigraph]. | |||
MOT is a | * MOT is a specialized concept map editor | ||
* [[MOTPlus]] includes support for [[IMS Learning Design]] | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
Revision as of 20:50, 8 December 2006
Definition
- MISA is an instructional engineering method describing graphically the instructional desing processes and their products which define completely a learning system. MISA supports 35 main tasks or processes and around 150 subtasks. The method has been totally represented within the MOT knowledge editor. [1]
- MISA = Méthode d'Ingéniérie cognitive de Systèmes de Téléapprentissage
MISA Components
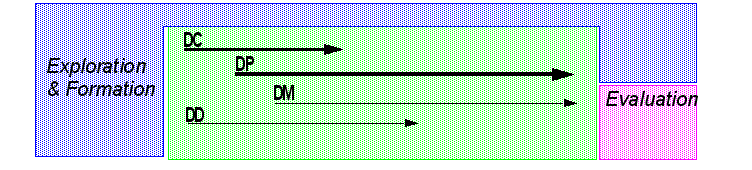
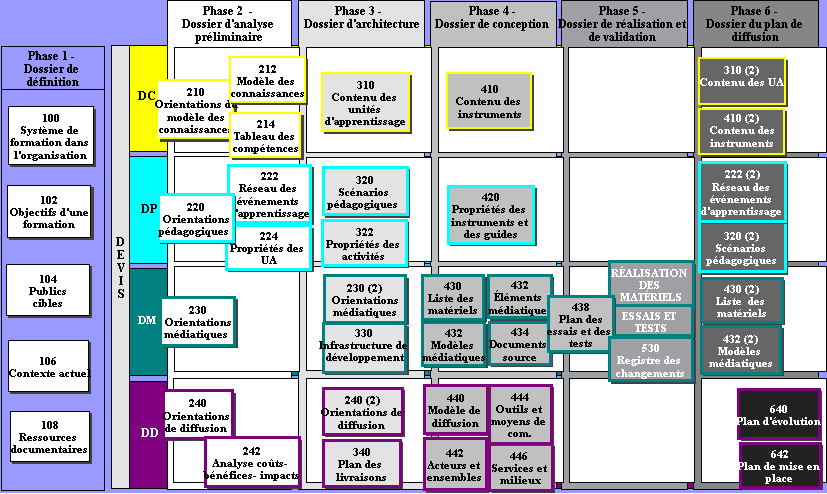
The MISA method identifies four axis
- DC: Design of Content (know-that and know-how)
- Knowledge and Skill Representation
- DP: Design of Pedagogical specifications
- Application of Teaching Methods and Approaches
- DM: Design of Materials
- Specification of Learning Materials
- DD: Design of Delivery
- Delivery Planning
There are 6 phases:
- Definition of the project (dossier)
- Preliminary analysis
- Definition of the course architecture
- Design of the various elements
- Implementation and validation
- Diffusion (field implementation)
Roughly, a timeline for development could look like this:
The 4 components split over the 6 phases lead to the 35 main tasks:
Software
MISA MOT Software is free for non-profit organizations we believe) that can be obtained from Cognigraph.
- MOT is a specialized concept map editor
- MOTPlus includes support for IMS Learning Design
Links
References
- Gilbert Paquette, Instructional Engineering in Networked Environments, Wiley, ISBN 0-7879-6466-2
- (Todo: Add the 2 french books)