Graphviz: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
* [http://www.graphviz.org/ Graphviz] is an open source graph visualization software. It has several main graph layout programs | * [http://www.graphviz.org/ Graphviz] is an open source graph visualization software. It has several main graph layout programs: | ||
; dot | |||
: ''hierarchical'' drawings of directed graphs. The layout algorithm aims edges in the same direction (top to bottom, or left to right) and then attempts to avoid edge crossings and reduce edge length. | |||
; neato | |||
: ''spring model'' - attempts to minimize a global energy function, which is equivalent to statistical multi-dimensional scaling. See also ''fdp''. | |||
; fdp | |||
: ''spring model'' layouts similar to those of neato, but does this by reducing forces rather than working with energy. | |||
; sfdp | |||
: multiscale version of fdp for the layout of large graphs. | |||
; twopi | |||
: ''radial layouts'', The nodes are placed on concentric circles depending their distance from a given root node. | |||
; circo | |||
: ''circular layout'' - suitable for certain diagrams of multiple cyclic structures such as certain telecommunications networks | |||
== The GraphViz language == | == The GraphViz language == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 27: | ||
See [http://www.graphviz.org/doc/info/command.html Command-line Invocation] (at graphviz.org). | See [http://www.graphviz.org/doc/info/command.html Command-line Invocation] (at graphviz.org). | ||
GraphViz includes several command line commands. The most imporant one is ''dot'' | |||
The syntax pattern is: | |||
cmd [ flags ] [ input files ] | |||
Example: | |||
dot -Tsvg GCF2.dot > GCF2.svg | |||
Important flags: | Important flags: | ||
; -T''format'' | ; -T''format'' | ||
| Line 19: | Line 42: | ||
; -T''format:renderer:formatter'' | ; -T''format:renderer:formatter'' | ||
: Defines the output format. You also can choose from a renderer and change the default formatter for the renderer. | : Defines the output format. You also can choose from a renderer and change the default formatter for the renderer. | ||
: See [http://www.graphviz.org/doc/info/output.html the list of output formats]. | |||
:: Most important ones for web pages: png, svg, cmapx (client-side html map), imap (server-side html map) and vrml (partially supported) | |||
:: Most important ones for printing: png, svg, ps, pdf | |||
:: Most important ones for specialized clients: '''dot''' (reproduces the input, along with layout information for the graph), '''xdot''' (same with lots of additional information) | |||
; -G''name[=value]'' | |||
: Defines attributes of the graph like overlaps, fonts, etc. | |||
; -o''outputfile'' | ; -o''outputfile'' | ||
: specify the output file. Otherwise it's written to default output. | : specify the output file. Otherwise it's written to default output. | ||
=== | === Format, rendering engines and formatters === | ||
; -Tcpmax | ; -Tcpmax | ||
: creates client-side image maps | : creates client-side image maps (of course you'll have to attache URLS to either nodes or edges or both) | ||
Example: | |||
dot -Tcmapx -oyour_graph.map -Tpng -oyour_graph.png your_graph.dot | |||
Then use something like: | |||
<IMG SRC="your_graph.png" USEMAP="#mainmap" /> | |||
... [content of your_graph.map] ... | |||
; -Tsvg | ; -Tsvg | ||
: creates SVG output | : creates SVG output | ||
; -Tsvg:twopi:cairo | |||
: Create SVG output using the twopi renderer. | |||
; -Tpng | ; -Tpng | ||
: creates PNG output | : creates PNG output | ||
; -Tpng:cairo:gd | |||
: specifies PNG output produced by Cairo formatted using the GD library | |||
=== Graphviz attributes === | === Graphviz attributes === | ||
Revision as of 11:19, 22 May 2010
Definition
- Graphviz is an open source graph visualization software. It has several main graph layout programs:
- dot
- hierarchical drawings of directed graphs. The layout algorithm aims edges in the same direction (top to bottom, or left to right) and then attempts to avoid edge crossings and reduce edge length.
- neato
- spring model - attempts to minimize a global energy function, which is equivalent to statistical multi-dimensional scaling. See also fdp.
- fdp
- spring model layouts similar to those of neato, but does this by reducing forces rather than working with energy.
- sfdp
- multiscale version of fdp for the layout of large graphs.
- twopi
- radial layouts, The nodes are placed on concentric circles depending their distance from a given root node.
- circo
- circular layout - suitable for certain diagrams of multiple cyclic structures such as certain telecommunications networks
The GraphViz language
Command line syntax
See Command-line Invocation (at graphviz.org).
GraphViz includes several command line commands. The most imporant one is dot
The syntax pattern is:
cmd [ flags ] [ input files ]
Example:
dot -Tsvg GCF2.dot > GCF2.svg
Important flags:
- -Tformat
- -Tformat:renderer
- -Tformat:renderer:formatter
- Defines the output format. You also can choose from a renderer and change the default formatter for the renderer.
- See the list of output formats.
- Most important ones for web pages: png, svg, cmapx (client-side html map), imap (server-side html map) and vrml (partially supported)
- Most important ones for printing: png, svg, ps, pdf
- Most important ones for specialized clients: dot (reproduces the input, along with layout information for the graph), xdot (same with lots of additional information)
- -Gname[=value]
- Defines attributes of the graph like overlaps, fonts, etc.
- -ooutputfile
- specify the output file. Otherwise it's written to default output.
Format, rendering engines and formatters
- -Tcpmax
- creates client-side image maps (of course you'll have to attache URLS to either nodes or edges or both)
Example:
dot -Tcmapx -oyour_graph.map -Tpng -oyour_graph.png your_graph.dot
Then use something like:
<IMG SRC="your_graph.png" USEMAP="#mainmap" /> ... [content of your_graph.map] ...
- -Tsvg
- creates SVG output
- -Tsvg
- twopi:cairo
- Create SVG output using the twopi renderer.
- -Tpng
- creates PNG output
- -Tpng
- cairo:gd
- specifies PNG output produced by Cairo formatted using the GD library
Graphviz attributes
See either (or both):
We we understood right (this is a disclaimer!)
- You may these (most?) as global settings in the command line
- As global settings in a file
- As "parameter" for each node
- size
- defines the size of the output in inches
- Consult Wikipedia's papersize or ISO 216 articles for pratical tables that translate ISO (European) A,B,C formats to inches.
Example of a portrait A2 page:
size="34.4,16.5";
- page
- Defines multiple page outputs (only works with PS)
Example of A3 output (biggest page a typical laser printer can handle)
page="16.5,11.7"
Some dot command line examples
Renders a (default) digraph in SVG with the default formatter
dot -Tsvg GCF2.dot > GCF2.svg
Some Neato command line examples
Lists configuration
neato -v
List all formats your installation can produce
neato -Tformat:
PNG output without overlap
neato -Tpng -Goverlap=false GCF.dot > GCF.png
SVG output
neato -Tsvg GCF.dot > GCF.svg neato -Tsvg -Goverlap=scale -Gfontsize=8.0 GCF.dot > GCF.sv
Simple graphviz for mediawiki examples
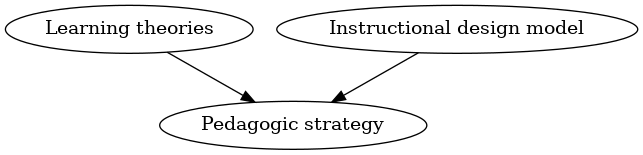
In this wiki, a directed graph that is represented like this (if you use the graphviz software, you should remove the XML tags).
<graphviz>
digraph G4 {
"Learning theories" [URL="Learning theory"];
"Pedagogic strategy" [URL="Pedagogic strategy"];
"Instructional design model" [URL="Instructional design model"];
"Learning theories" -> "Pedagogic strategy";
"Instructional design model" -> "Pedagogic strategy"
}
</graphviz>
could render like that (yes this wiki has a graphviz extension, but we may not keep it for sure since it is somewhat CPU intensive)
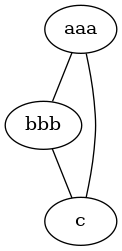
A simple non-directed graph (rendered with neato):
<graphviz renderer='neato' caption='Hello Neato'>
graph G1 {
aaa -- bbb;
bbb -- c;
aaa -- c;
}
</graphviz>
gives:
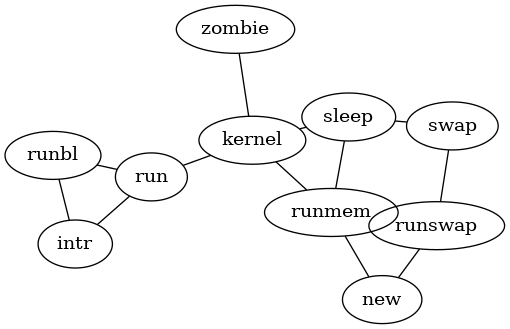
Or a more complex non-directed graph (rendered with neato):
<graphviz renderer='neato' caption='Hello Neato'>
graph G {
run -- intr;
intr -- runbl;
runbl -- run;
run -- kernel;
kernel -- zombie;
kernel -- sleep;
kernel -- runmem;
sleep -- swap;
swap -- runswap;
runswap -- new;
runswap -- runmem;
new -- runmem;
sleep -- runmem;
}
</graphviz>
like this
Tools
See Graphviz - Graph Visualization Software (a longer list of interfaces, bindings, generators, scripts, etc.). Usually also needs graphviz software and the other way round. I.e. after installing Graphviz, you likely want to install a viewer or generator.
Mediawiki extensions
- GraphViz Widget for Mediawikis (alpha status in Feb 2008).
- Extension:Graphical Category Browser for MediaWiki (>1.7x). This may be outdated.
- http://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Extension:GraphViz Extension:GraphViz] MediaWiki extension (Tested in this wiki. Worked with Mediawiki version 1.11, Graphviz 2.16.1 on Solaris 10 - DKS/2008)
GraphiViz Viewers
- ZGRViewer. GraphViz/DOT Viewer
- iDot - Incremental Dot Viewer
- "canviz" - HTML5 and Javascript
Installation
- Download of GraphViz software (source and Win/Linux binaries).
- Under Ubuntu I could install it through the package manager (there are quite a lot of dependencies).
sudo apt-get install graphviz
- For solaris, you can download a binary from sunfreeware.com plus these: cairo-1.4.10, freetype-2.3.1, glib-2.14.1, graphviz-2.16.1, pango-1.18.2, xrender-0.8.3,expat-2.0.1.
Tutorials and introductions
- Manual
- Graphviz - Graph Visualization Software Includes both introductions and manuals (the HTML versions on top are better currently - Daniel K. Schneider 14:40, 20 July 2009 (UTC)).
- dot guide
- Introductions
- Graphviz (Wikipedia)
- WikiSchool:Graphviz (Tutorial in German)
- An Introduction to GraphWiz, September 10th, 2004 by Mihalis Tsoukalos, Linux Journal
- Graphviz for UML
- UML Diagrams Using Graphviz Dot. Explains how to create UML class diagrams.