Flash Papervision3D tutorial: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
The only thing that really matters is that Flash can find the contents of the "src" directory | The only thing that really matters is that Flash can find the contents of the "src" directory | ||
== | == Some basic concepts == | ||
=== | === The coordinate system === | ||
An object's position in Papervision is defined by x, y, and z and pitch, yaw, roll. In addition it can | |||
be scaled or otherwise transformed. | |||
An object's position in Papervision is defined by x, y, and z and pitch, yaw, roll. In addition it can be scaled or otherwise transformed. | |||
Coordinates in 3D systems are defined as follows: | Coordinates in 3D systems are defined as follows: | ||
| Line 88: | Line 82: | ||
Therefore, in 3-D graphics there are six degrees of freedom: 3 positions (x,y,z) plus yaw (around the y axis ), pitch (around the x axis) and roll (around the z axis) | Therefore, in 3-D graphics there are six degrees of freedom: 3 positions (x,y,z) plus yaw (around the y axis ), pitch (around the x axis) and roll (around the z axis) | ||
=== The rendering mechanism === | |||
For objects to be seen, they need to have a visible material, be placed in the scene and rendered from a camera that looks at them. | For objects to be seen, they need to have a visible material, be placed in the scene and rendered from a camera that looks at them. | ||
== An introductory example == | |||
Some more explanation should be added sometimes. For now all the help is in the code :) | |||
=== A simple CS3 timeline script === | |||
If you look at pv3d examples on the web they all assume that you program with a class structure and external ActionScript files. Here we first show how to use pv3d in a simple timeline script. Of course, it doesn't do anything of interest. Look at this [http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/flash/ex/pv3d/simple-noclass-pv3d.html rotating cube] | |||
To make this example work you need a correctly configured classpath (as above). The just copy paste | |||
this code into a frame of your time line (e.g. frame 1 of layer 1). In the example we also added a layer with a background and a layer with a credits button. You won't need these. | |||
<source lang="actionscript"> | <source lang="actionscript"> | ||
// Probably some imports can be trimmed... | |||
import flash.display.*; | |||
import flash.filters.*; | |||
import flash.display.Stage; | |||
import flash.events.*; | |||
// Import Papervision3D | |||
import org.papervision3d.cameras.Camera3D; | |||
import org.papervision3d.scenes.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.objects.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.materials.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.materials.special.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.render.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.view.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.events.*; | |||
import org.papervision3d.core.utils.*; | |||
// Make sure we can see everything | |||
stage.scaleMode = "showAll"; | |||
// This will launch the loop function once a frame is loaded | |||
// It will turn the cube a bit. | |||
addEventListener( Event.ENTER_FRAME, loop ); | |||
// Create viewport | |||
var viewport = new Viewport3D(0, 0, true, true); | |||
addChild( viewport ); | |||
var renderer = new BasicRenderEngine(); | |||
// This will create the list of colors for each face of the cube | |||
var materials:MaterialsList = new MaterialsList( { | |||
front: new ColorMaterial(0xFF0000), | |||
back: new ColorMaterial(0x0000FF), | |||
right: new ColorMaterial(0x00FF00), | |||
left: new ColorMaterial(0x000000), | |||
top: new ColorMaterial(0xFF0000), | |||
bottom: new ColorMaterial(0xFF0000) } ); | |||
//Create my_cube and add it to the scene | |||
// We also define width, depth and height | |||
var my_cube = new Cube( materials, 500, 500, 1000 ); | |||
// Let's create a floor underneath the cube | |||
var wire_materials:MaterialsList = new MaterialsList({all: new WireframeMaterial(0xFF0000)}); | |||
var my_floor = new Cube(wire_materials, 800, 800, 50); | |||
my_floor.y = -600; | |||
// Create a 3D scene and add the cube to it | |||
var scene = new Scene3D(); | |||
scene.addChild(my_cube); | |||
scene.addChild(my_floor); | |||
// Create camera | |||
// By default the camera looks forward, we push it a bit backwards | |||
var camera = new Camera3D(); | |||
camera.z = -800 ; | |||
camera.zoom = 10; | |||
// ___________________________________________________________________ Loop | |||
function loop(event:Event):void { | |||
my_cube.yaw(.5); | |||
renderer.renderScene(scene, camera, viewport); | |||
} | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 100: | Line 174: | ||
* Directory: http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/flash/ex/pv3d/ | * Directory: http://tecfa.unige.ch/guides/flash/ex/pv3d/ | ||
=== | === Programming with a class structure === | ||
Most Papervision3D developers write code with a class structure in a *.as file. | |||
According to Anre Stubbe's [http://www.andrestubbe.com/downloads/papervision3d/ExampleBaseCode.as ExampleBaseCode article] in the Papervision3D wiki, it should look like this: | |||
<source lang="actionscript"> | |||
package | |||
{ | |||
import flash.display.Sprite; | |||
import flash.events.Event; | |||
import org.papervision3d.cameras.Camera3D; | |||
import org.papervision3d.scenes.MovieScene3D; | |||
[SWF(width='400',height='400',backgroundColor='0x000000',frameRate='30')] | |||
public class ExampleBaseCode extends Sprite | |||
{ | |||
private var container :Sprite; | |||
private var scene :MovieScene3D; | |||
private var camera :Camera3D; | |||
public function ExampleBaseCode() | |||
{ | |||
// create the container | |||
// the scene object will place all displayable objects into this container | |||
container = new Sprite; | |||
// center the containers screen coordinates to the middle of the flash stage | |||
// the scene world center (x=0,y=0,z=0) is now where the screen coordinates of the container are (x=200, y=200) | |||
container.x = 200; | |||
container.y = 200; | |||
// don't forget to add the container to the stage, otherwise you'll see nothing | |||
addChild( container ); | |||
// create a scene | |||
scene = new MovieScene3D( container ); | |||
//scene = new Scene3D( container ); more primitive alternative, compare scenes.Scene3D.as and scenes.MovieScene3D.as to discover why. | |||
// create a camera | |||
camera = new Camera3D(); | |||
camera.z = -500; // push the camera a bit backward | |||
camera.zoom = 5; | |||
// add something to your scene | |||
// scene.addChild( something ); | |||
// create an enterframe loop | |||
stage.addEventListener( Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame ); | |||
} | |||
private function onEnterFrame( event: Event ): void | |||
{ | |||
// render the scene | |||
scene.renderCamera( camera ); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
=== An AS version of the rotating cube === | |||
Revision as of 17:47, 25 November 2008
This article or section is currently under construction
In principle, someone is working on it and there should be a better version in a not so distant future.
If you want to modify this page, please discuss it with the person working on it (see the "history")
This is part of the Flash tutorials
Introduction
- Learning goals
- Create a simple 3D scene with Papervison3D (PV3D)
- The objective is to show the logic of such a library. Once you are done with this you will have to spend of few weeks going through real tutorials and the documentation...
- Flash and Papervision3D level
- Flash 9 / CS3
- Papervision 2.0
- Prerequisites
- Some ActionScript knowledge, e.g.
- Moving on
- Level and target population
- Absolute beginners
- Quality
Download and install
- Download
In nov 2008, Papervision 3D can be downloaded from the SVN repository (read the Revision control system tutorial)
The subversion URL can change, e.g.
- http://papervision3d.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/as3/trunk/ (nov 2008)
- http://papervision3d.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/ (before)
So create a new directory somewhere. On windows you can use a GUI client like like, under Linux go to the new directory and type:
subversion checkout http://papervision3d.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/as3/trunk/
You then should have a directory "trunk" with a sub-directory structure like this:
bin build docs examples src .svn
- CS3 setup
- CS3 must be able to find this library in a classpath. Read Flash using ActionScript libraries tutorial if you want to learn more about this. Otherwise, just follow precisely these instructions.
- Open the File->Publish Settings - Flash tab
- Then click on the Settings ... button next to the ActionScript version.
- Click on the "target"/"Browse to Path" icon and select the "src" directory of the Papervison library in your computer.
E.g. I keep the subversion tree on my Linux machine, but I copied the trunk directory to my laptop and renamed it. I added this classpath:
c:\lib\pv3d\src
On your PC you may have something like that:
s:\flash\pv3d\trunk\src
The only thing that really matters is that Flash can find the contents of the "src" directory
Some basic concepts
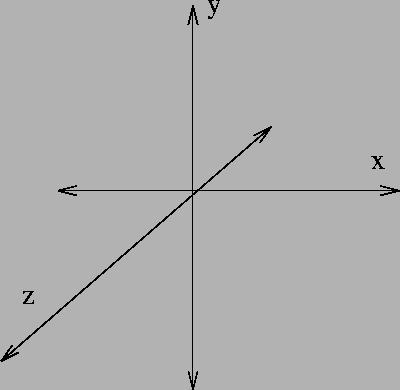
The coordinate system
An object's position in Papervision is defined by x, y, and z and pitch, yaw, roll. In addition it can be scaled or otherwise transformed.
Coordinates in 3D systems are defined as follows:
Papervision positions in space are defined with these x-y-z coordinates:
- x axis = Width, i.e. left(-) to right(+)
- y axis = Height, i.e. down(-) to up(+)
- z axis = Depth, i.e. close/forward (-) to far/backward (+)
- z axis = Depth, i.e. close/forward (+) to far/backward (-) (z-axis comes out of the screen)
In most other systems, e.g. X3D, the z-axis is inverted:
- z axis = Depth, i.e. close/forward (-) to far/backward (+) (z-axis goes into the screen)
You can picture the "normal" 3D coordinate system with the right hand rule: "x" is your thumb, "y" the index finger, and "z" the middle finger.
Orientation of an object is defined by "yaw", "pitch" and "roll". Imagine what a ship can do:
- Yaw is left-right orientation. Imagine turning your head or your body around to look at something. "The ship can't hold its track."
- Pitch is backwards-forwards up/down orientation. "The ship goes straight into big waves."
- Roll is left-right up/down orientation. "The ship is hit on the side by big waves."
Therefore, in 3-D graphics there are six degrees of freedom: 3 positions (x,y,z) plus yaw (around the y axis ), pitch (around the x axis) and roll (around the z axis)
The rendering mechanism
For objects to be seen, they need to have a visible material, be placed in the scene and rendered from a camera that looks at them.
An introductory example
Some more explanation should be added sometimes. For now all the help is in the code :)
A simple CS3 timeline script
If you look at pv3d examples on the web they all assume that you program with a class structure and external ActionScript files. Here we first show how to use pv3d in a simple timeline script. Of course, it doesn't do anything of interest. Look at this rotating cube
To make this example work you need a correctly configured classpath (as above). The just copy paste this code into a frame of your time line (e.g. frame 1 of layer 1). In the example we also added a layer with a background and a layer with a credits button. You won't need these.
// Probably some imports can be trimmed...
import flash.display.*;
import flash.filters.*;
import flash.display.Stage;
import flash.events.*;
// Import Papervision3D
import org.papervision3d.cameras.Camera3D;
import org.papervision3d.scenes.*;
import org.papervision3d.objects.*;
import org.papervision3d.objects.primitives.*;
import org.papervision3d.materials.*;
import org.papervision3d.materials.special.*;
import org.papervision3d.materials.utils.*;
import org.papervision3d.render.*;
import org.papervision3d.view.*;
import org.papervision3d.events.*;
import org.papervision3d.core.utils.*;
// Make sure we can see everything
stage.scaleMode = "showAll";
// This will launch the loop function once a frame is loaded
// It will turn the cube a bit.
addEventListener( Event.ENTER_FRAME, loop );
// Create viewport
var viewport = new Viewport3D(0, 0, true, true);
addChild( viewport );
var renderer = new BasicRenderEngine();
// This will create the list of colors for each face of the cube
var materials:MaterialsList = new MaterialsList( {
front: new ColorMaterial(0xFF0000),
back: new ColorMaterial(0x0000FF),
right: new ColorMaterial(0x00FF00),
left: new ColorMaterial(0x000000),
top: new ColorMaterial(0xFF0000),
bottom: new ColorMaterial(0xFF0000) } );
//Create my_cube and add it to the scene
// We also define width, depth and height
var my_cube = new Cube( materials, 500, 500, 1000 );
// Let's create a floor underneath the cube
var wire_materials:MaterialsList = new MaterialsList({all: new WireframeMaterial(0xFF0000)});
var my_floor = new Cube(wire_materials, 800, 800, 50);
my_floor.y = -600;
// Create a 3D scene and add the cube to it
var scene = new Scene3D();
scene.addChild(my_cube);
scene.addChild(my_floor);
// Create camera
// By default the camera looks forward, we push it a bit backwards
var camera = new Camera3D();
camera.z = -800 ;
camera.zoom = 10;
// ___________________________________________________________________ Loop
function loop(event:Event):void {
my_cube.yaw(.5);
renderer.renderScene(scene, camera, viewport);
}
- Source
Programming with a class structure
Most Papervision3D developers write code with a class structure in a *.as file. According to Anre Stubbe's ExampleBaseCode article in the Papervision3D wiki, it should look like this:
package
{
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import org.papervision3d.cameras.Camera3D;
import org.papervision3d.scenes.MovieScene3D;
[SWF(width='400',height='400',backgroundColor='0x000000',frameRate='30')]
public class ExampleBaseCode extends Sprite
{
private var container :Sprite;
private var scene :MovieScene3D;
private var camera :Camera3D;
public function ExampleBaseCode()
{
// create the container
// the scene object will place all displayable objects into this container
container = new Sprite;
// center the containers screen coordinates to the middle of the flash stage
// the scene world center (x=0,y=0,z=0) is now where the screen coordinates of the container are (x=200, y=200)
container.x = 200;
container.y = 200;
// don't forget to add the container to the stage, otherwise you'll see nothing
addChild( container );
// create a scene
scene = new MovieScene3D( container );
//scene = new Scene3D( container ); more primitive alternative, compare scenes.Scene3D.as and scenes.MovieScene3D.as to discover why.
// create a camera
camera = new Camera3D();
camera.z = -500; // push the camera a bit backward
camera.zoom = 5;
// add something to your scene
// scene.addChild( something );
// create an enterframe loop
stage.addEventListener( Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame );
}
private function onEnterFrame( event: Event ): void
{
// render the scene
scene.renderCamera( camera );
}
}
}
An AS version of the rotating cube
Links
- General
- PaperVision3D (PV3D) home page
- Papervision 3D blog. Includes all the information (downloads, tutorials, links, etc.)
- PV3World. Testing ground, tutorial and other resources.
- Papervision 3D downloads (at google code). There is also a CS3 component for version 1.5 made in 2007, Current (nov 2008) version is 3.0.
- Papervision3D documentation (Packages and classes)
- Examples
- Examples (Papervision3D Wiki)
- 'Papervision' Category, Meandering thoughts
- Tutorials