XML: Difference between revisions
m (using an external editor) |
m (using an external editor) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
* '''XML''' means "Extended markup language". XML is designed as a machine readable self describing text editable persistent store for data. XML is a formalism or a meta-language (not to be confounded with HTML, a language to describe the structure of Web pages) | * '''XML''' means "Extended markup language". It allows to define all sorts of languages that describe information contents (e.g. web pages, vector graphics, programming languages). In technical terms, such languages are called ''XML applications'' or ''XML vocabularies''. | ||
* XML is designed as a machine readable self describing text editable persistent store for data. XML is a formalism or a '''meta-language''' (not to be confounded with HTML, a language to describe the structure of Web pages) | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
=== XML as the foundation for the future semantic Web === | === XML as the foundation for the future semantic Web === | ||
* Essentially the [[RDF]] framework | |||
=== XML for machine to machine talk === | === XML for machine to machine talk === | ||
=== XML as formalism to define information structures === | * Web Services | ||
=== XML as formalism to define other information structures === | |||
| Line 65: | Line 71: | ||
=== Valid === | === Valid === | ||
An XML document is said valid if it conforms to some kind of grammar also called schema. | An XML document is said valid if it conforms to some kind of grammar also called schema. An XML grammar formally describes an XML application (or vocabulary or language). | ||
The most popular ones are in this order: | The most popular ones are in this order: | ||
| Line 71: | Line 77: | ||
* XML Schema | * XML Schema | ||
* Relax NG | * Relax NG | ||
XML applications in addition to DTDs may include other constraints. Some XML applications may include languages that are not XML-based (e.g. CSS or XPath). | |||
=== Text-centric vs. data-centric XML === | === Text-centric vs. data-centric XML === | ||
| Line 76: | Line 84: | ||
Data-centric XML as opposed to the text-centric XML refers to XML whose primary audience is not a human reader, but a computer program which will process the information, respond to it, store data items in a database, and so on. | Data-centric XML as opposed to the text-centric XML refers to XML whose primary audience is not a human reader, but a computer program which will process the information, respond to it, store data items in a database, and so on. | ||
== Software == | == XML Applications == | ||
{{coment | Again, this is just a stub, a lot is missing .... }} | |||
=== W3C applications === | |||
This is just a popular subset .... | |||
* XSL/FO (application XML): XML Style language | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/xsl/ | |||
* XSLT (application XML): XML Transformation language | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt | |||
* XLink: Hypertext links | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/xlink/ | |||
* XPointer (ressource pointers) | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/xptr/ | |||
* XPath (XML fragments identification) | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath | |||
** (used by XSLT, XInclude, XLink, XQuery, XPointer etc.) | |||
* RDF applications (a whole lot of languages for the semantic web) | |||
** See http://www.w3.org/RDF/ | |||
* PICS 2.0: Platform for Internet Content Selection | |||
** http://www.w3.org/PICS/ | |||
* SMIL: Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language | |||
** http://www.w3.org/AudioVideo/ | |||
* P3P: Platform for Privacy Preferences | |||
** http://www.w3.org/P3P/ | |||
* SVG: Scalable Vector Graphics | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG/ | |||
* MathML: Mathematical Markup Language | |||
** http://www.w3.org/Math/ | |||
* XHMTL (several variants for new generation HTML) | |||
** http://www.w3.org/TR/html/ | |||
=== Non W3C Document standards === | |||
* [http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/tc_home.php?wg_abbrev=docbook Docbook]. Most popular standard for writing large documents. | |||
* [http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/tc_home.php?wg_abbrev=dita DITA]. A more flexible module-based approach to documents, originally made by IBM. | |||
=== In education === | |||
* See the various [[Educational modelling languages]], in particular the ones produced by [[IMS]] | |||
* Content packaging and storage, e.g. | |||
** [[IMS Content Packaging]] | |||
** [[Learning Object Metadata Standard]] | |||
* In addition, there are languages, to sell them, for student data, curricula data etc. | |||
== General purpose XML Software == | |||
(longer entries have their own page) | (longer entries have their own page) | ||
Revision as of 20:39, 30 October 2006
{{Comment | This page is juste a beginning. Several sub-topics will be factored out to other pages.
Definition
- XML means "Extended markup language". It allows to define all sorts of languages that describe information contents (e.g. web pages, vector graphics, programming languages). In technical terms, such languages are called XML applications or XML vocabularies.
- XML is designed as a machine readable self describing text editable persistent store for data. XML is a formalism or a meta-language (not to be confounded with HTML, a language to describe the structure of Web pages)
History
- XML is a subset of SGML (Standardized Generalized Markup Language). SGML has been used to define HTML whereas XHTML is defined with XML (This is why empty tags are not allowed anymore in XHTML).
- XML was formally defined in 1998 as W3C's XML Recommendation 1.0
- Since then, hundreds of XML languages have been defined and few dozens are popular and in production. Ken Sall's famous Big Picture only lists some, e.g. he misses out all the IMS e-learning standards.
The XML planet
One may look at XML from different angles.
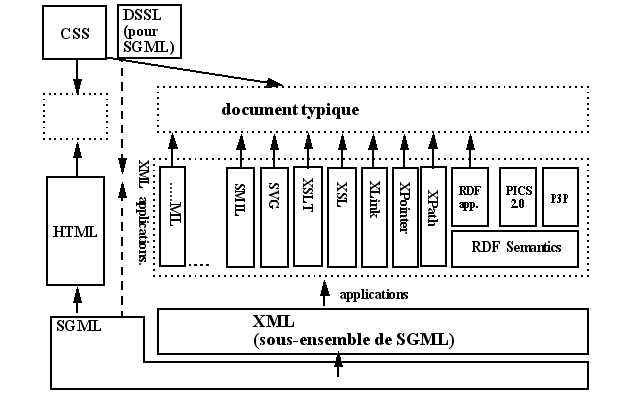
XML for better Web contents
Look at this nice picture drawn by DSchneider (needs translation and updating). It shows how future web documents will be composed:
XML as the foundation for the future semantic Web
- Essentially the RDF framework
XML for machine to machine talk
- Web Services
XML as formalism to define other information structures
Some technical XML concepts
An XML document can refer to a physical file, a database entry, a datastream (any appropriate "text" that is delimited).
Wellformedness
An XML document is well formed if and only if
- There is an appropriate XML declaration at the beginning
- The document starts with an XML declaration that includes a version number (currently 1.0).
<?xml version="1.0"?>
- This declaration can also contain encoding information. By default encoding isUTF-8):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
- XML documents are hierarchical
- begin-tags and end-tags that match
- No tags crossing like
<i>...<b>...</i> .... </b>
- There must be single root
- It can only appear once and can not be used within other elements
- Other features
- XML is case sensitive, "LI" is not "li" for example
- "Empty" tags must be self closing, e.g.
- Attribute values are quoted
<a href= " http://tecfa.unige.ch:8080/xml.html " >)
- Special caracters: <, &, >,", '
- Use < & > &aquot; ' instead of <, &, >,", '
- Including URLs !!
Valid
An XML document is said valid if it conforms to some kind of grammar also called schema. An XML grammar formally describes an XML application (or vocabulary or language).
The most popular ones are in this order:
- DTD
- XML Schema
- Relax NG
XML applications in addition to DTDs may include other constraints. Some XML applications may include languages that are not XML-based (e.g. CSS or XPath).
Text-centric vs. data-centric XML
Data-centric XML as opposed to the text-centric XML refers to XML whose primary audience is not a human reader, but a computer program which will process the information, respond to it, store data items in a database, and so on.
XML Applications
W3C applications
This is just a popular subset ....
- XSL/FO (application XML): XML Style language
- XSLT (application XML): XML Transformation language
- XLink: Hypertext links
- XPointer (ressource pointers)
- XPath (XML fragments identification)
- http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath
- (used by XSLT, XInclude, XLink, XQuery, XPointer etc.)
- RDF applications (a whole lot of languages for the semantic web)
- PICS 2.0: Platform for Internet Content Selection
- SMIL: Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language
- P3P: Platform for Privacy Preferences
- SVG: Scalable Vector Graphics
- MathML: Mathematical Markup Language
- XHMTL (several variants for new generation HTML)
Non W3C Document standards
- Docbook. Most popular standard for writing large documents.
- DITA. A more flexible module-based approach to documents, originally made by IBM.
In education
- See the various Educational modelling languages, in particular the ones produced by IMS
- Content packaging and storage, e.g.
- In addition, there are languages, to sell them, for student data, curricula data etc.
General purpose XML Software
(longer entries have their own page)
XML creation
- See XML editor
Validation
- Off-line validation
- Most decent XML editors do offer validation functionality. However, some free XML editors do not. Some (like Xemacs) only offer limited verification.
- xmllint, a command line tool which is distributed as part of the libxml2 C parser developed for the Gnome project. This means that it ships with most Linux installations, but there also distributions for Windows and other OSs.
- xmlTester.jar. This tools is based on the Xerxes parser.
- XML Nanny. XML Nanny is a Free Mac OS X developer tool that provides an Aqua interface for checking XHTML and XML documents for Well-Formedness and Validity either locally or across the network. (Tiger OS X 10.4) [sept 2005]
- On-line validation
Note: You may need to change DTD's local system identifier. These programs must be able to get the DTD. I rather suggest installing a local program on your machine (like xmllint or xmlTester).
- STG XML Validation Form, curtosy of Scholarly Technology Group, Brown University
- XML well-formedness checker and validator, Richard Tobin, University of Endinburgh (RXP parser)
- XML.com's (simple well-formedness)
- On-line validation for specific XML applications
- W3C HTML Validation Service This validator doesn't work with your own DTD's. Its primary function is to validate W3C vocabularies (HTML, XHTML, SVG, MathML, ... )
- FEED Validator. Validates various RSS Formats plus PIE
Links
Tutorials
- XML:Managing Data Exchange. Thi Wikibook project introduced XML from a Data exchange perspective.
News
- Cafe con Leche XML News and Resources (Best resource to keep in touch with XML-related news)
- TECFA's XML Page (DSchneider's "old" XML pointers page).
References
- Elliotte Rusty Harold, (2004). XML in a Nutshell, O'Reilly, Abstract/TOC ISBN 0-596-00764-7 (Best buy according to DSchneider).