Regular expression: Difference between revisions
m (Text replacement - "<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/>" to "<!-- <pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/> -->") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
Replace with: | Replace with: | ||
<!-- <pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/> --> | <!-- <!-- <pageby nominor="false" comments="false"/> --> --> | ||
== Mass editing HTML files with Perl == | == Mass editing HTML files with Perl == | ||
Latest revision as of 17:59, 22 August 2016
Definition
Regular expressions (regexps) provide a formalism to identify patterns in some text and any sort of other code. E.g. programmers when creating computer code use to find/replace text in some code, computer program scripts can use regexps to translate code from one form into another (e.g. HTML to Wiki), JavaScript programs may use regexps to check if user data entered in HTML form is correct, etc.
In computing, regular expressions provide a concise and flexible means for identifying strings of text of interest, such as particular characters, words, or patterns of characters. Regular expressions (abbreviated as regex or regexp, with plural forms regexes, regexps, or regexen) are written in a formal language that can be interpreted by a regular expression processor, a program that either serves as a parser generator or examines text and identifies parts that match the provided specification.
The following examples illustrate a few specifications that could be expressed in a regular expression:
- the sequence of characters "car" in any context, such as "car", "cartoon", or "bicarbonate"
- the word "car" when it appears as an isolated word
- the word "car" when preceded by the word "blue" or "red"
- a dollar sign immediately followed by one or more digits, and then optionally a period and exactly two more digits
Regular expressions can be much more complex than these examples.
(Wikipedia, retrieved 16:52, 29 August 2008 (UTC)).There exist several definitions / standards / implementations for regeps. They share a common core. The most popular ones are (see the Wikipedia article for details.
- POSIX Basic Regular expressions (BRE)
- POSIX Extended Regular expressions (ERE)
- Perl-derivative regular expressions
Note: Regular expressions (although useful) are difficult to learn and usually only computer programmers use these. However, HTML and XML coders may consider learning some. E.g. if plan to use JavaScript form validation code it's a good thing to know some.
Examples
Removing HTML code
Identifies both img and a begin tags ([http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3790681/regular-expression-to-remove-html-tags StackOverflow)
<(img|a)[^>]*>
Removes span (begin tag)
<span[^>]*>
Zip code
The following defines a somewhat legal Swiss Zip code:
CH-[0-9]{4,}
The following one defines a valid email address (example from http://www.regular-expressions.info/email.html)
\b[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z]{2,4}\b
Replacing Wiki text
Administrators of this wiki can use RegExps to make mass changes to pages.
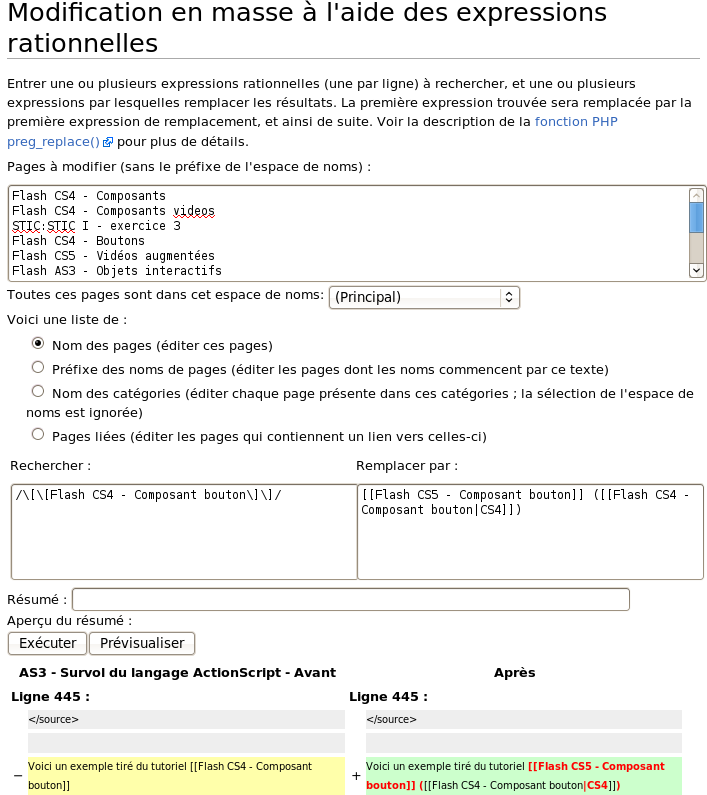
Example one
The example from the french version below shows how to replace
- [[Flash CS4 - Composant bouton]]/
by
- [[Flash CS5 - Composant bouton]] ([[Flash CS4 - Composant bouton|CS4]])
Note how we had to quote the [[ ]]
- /\[\[Flash CS4 - Composant bouton\]\]/
Example two
Removing pageby + args tag
Search for:
/<pageby nominor="false" comments="false"\/>/
Search for (a bit dangerous):
/<pageby.*\/>/
Replace with:
<!-- -->
Mass editing HTML files with Perl
Let's assume that you would like to add some line after each <body .....> tag.
Let's find all files that have body tags:
find . -type f -print | xargs grep -l "<body\(.*\)>"
Replace (that's more hairy)
find . -type f -print | xargs perl -i~ -pe "s:<body(.*)>:<body \\1> <p>Something new</p>:g"
Explanations:
- -pe means to execute a one liner Perl command (i.e. the expression within the " .....")
- -i~ means to replace the orginal file, but create a backup copy with a "~" appended
- The pattern s/search regexp/replacement/g defines a search/replace pattern
- Since we got a / in the closing p tag, we will use ":" to separate the two
- The final :g means to replace all occurences (not needed in our case actually).
- The grouping () don't need to be escaped in Perl. I hate regexps :)
Software
- Most good text editors provide regexp support
- Computer programming languages usually too (including scripting languages like PhP or JavaScript).
Links
- Overviews
- Regular expression (Wikipedia)
- regular-expressions.info Includes a catalogue of most popular ones)
- expreg.com
Tutorials
- Using Regular Expressions by Stephen Ramsay, Electronic Text Center, University of Virginia]
- The 30 Minute Regex Tutorial By Jim Hollenhorst
Programming languages
- In JavaScript
- Core_JavaScript_1.5_Guide:Regular_Expressions
- Introduction to Regular Expressions (microsoft)
- String Regular Expressions with JavaScript and ECMAScript
- Some explanations for a very simple chatter bot
Cheatsheets
- Regular Expressions Cheat Sheet by LoveJackDaniels.com / Dave Child.
Online tools
- regexpal.com (A testing tool for regexps)