Design science: Difference between revisions
(using an external editor) |
(using an external editor) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== Venable's model === | === Venable's model === | ||
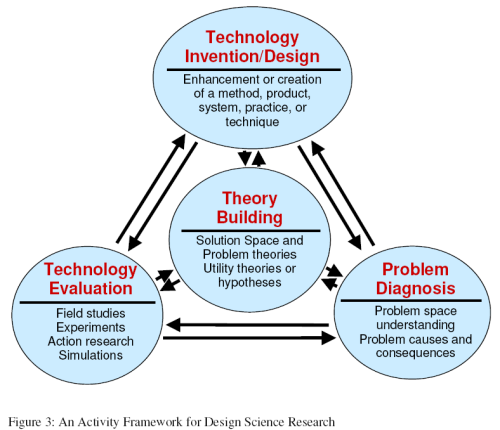
Figure 3 shows how theory building is a central activity related to problem diagnosis, | |||
technology invention or design (to solve problems), and technology evaluation. While | |||
problem diagnosis and technology evaluation may be undertaken in the empirical | |||
domains of natural and particularly social/behavioural sciences, theory building is the | |||
necessary link between them all. (Venable 2006: 16) | |||
[[Image:Framework-design-science-research-venable.png]] | [[Image:Framework-design-science-research-venable.png]] | ||
| Line 42: | Line 48: | ||
== The status of theory == | == The status of theory == | ||
Theories are design artefacts. The outcome of research is often formulated as theory; that is, | |||
highly universal representations, pretending to be independent of concrete context, practice or | highly universal representations, pretending to be independent of concrete context, practice or | ||
situation. From the point of view of design, theories are design artefacts, taking different roles in | situation. From the point of view of design, theories are design artefacts, taking different roles in | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 8 May 2006
Definition
- Design sciences related to disciplines that build things.
- See also: Design methodology, Design rule
Key elements of design-oriented approaches
The Järvinen model
(according to Pertti Järvinen, 2004)
- Technological rules
- tell you how to do things and are dependant on other theories (and beliefs)
- Bunge (quoted by Järvinen:99): "A technological rule: an instruction is defined as a chunk of general knowledge, linking an intervention or artifact with a desired outcome or performance in a certain field of application".
- Types of outcomes (artifacts, interventions):
- Constructs (or concept) form the " language " of a domain
- Models are sets of propositions expressing relationships among constructs
- Methods are a set of steps to perform a task (guidelines, algorithms)
- Instantiations are realizations of an artifact in its environment
- Types of research:
- Build: Demonstrate feasibility of an artifact or intervention
- Evaluate: Development of criteria, and assessment of both artifact building and artifact usage
What does this mean ?
- There are 4*2 ways to lead interesting design research.
- Usually, it's the not the artefact (i.e. program or course) you build that is interesting, but something behind it (constructs, models, methods, ...) or around it (conditions, perceptions, usage, ...).
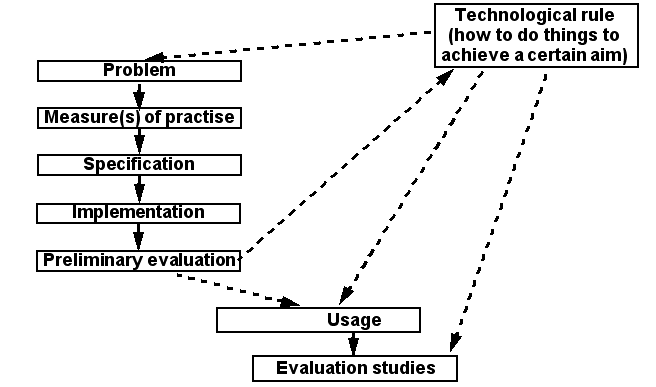
Here is picture that shows some of the relationsships between elements of a design process:
- A researcher can investigate at least on of the dotted lines
- A design rule (technological rule in terms of Järvinnen) is a theory on how to build things. It be input, output or both in a research project. See also design-based research that has become popular in educational technology research.
- See instructional design models and instructional design method for designs and methods related to education.
Venable's model
Figure 3 shows how theory building is a central activity related to problem diagnosis, technology invention or design (to solve problems), and technology evaluation. While problem diagnosis and technology evaluation may be undertaken in the empirical domains of natural and particularly social/behavioural sciences, theory building is the necessary link between them all. (Venable 2006: 16)
The status of theory
Theories are design artefacts. The outcome of research is often formulated as theory; that is, highly universal representations, pretending to be independent of concrete context, practice or situation. From the point of view of design, theories are design artefacts, taking different roles in design; from worldviews, guiding the designer and helping him assess the situations and keep the goals in mind, to tools mediating the achievement of specific results. In this way, the direct outcomes of research mediate design. (Bertelsen, :23).
References
- Pertti Järvinen: On Research Methods. Tampere: Opinpajan Kirja, ISBN 952-99233-1-7 .
- Note: This seems to be the only useful methdology book related to design-oriented research. Very dense reading, but worth to buy, directly from here (no other place sells it): http://www.uta.fi/taju ... a small and friendly university bookshop (tested by me).
- Olav W. Bertelsen, DESIGN ARTEFACTS, Towards a design-oriented epistemology, Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems, 2000, 12: 15-27 15 PDF
- Sven A. Carlsson, (2006) Towards an Information Systems Design Research Framework: A Critical Realist Perspective, First International conference on Design Science Research in Information Systems and Technology. http://ncl.cgu.edu/designconference/index.htm
- Venable, John R. (2006) The Role of Theory and Theorising in Design Science Research, http://ncl.cgu.edu/designconference/index.htm
- Van Aken, J.E. (2004): Management research based on the paradigm of design sciences: the quest for field-tested and grounded technological rules, Journal of Management Studies, 41(2), 219-246.