Learning environment: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→References) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Sandberg, J. A. (1994). Educational paradigms: issues and trends. In Lewis, R. Mendelsohn, P., (ed.), Lessons from Learning, (IFIP TC3/WG3.3 Working Conference 1993), pages 13--22, Amsterdam. North-Holland. | * Sandberg, J. A. (1994). Educational paradigms: issues and trends. In Lewis, R. Mendelsohn, P., (ed.), Lessons from Learning, (IFIP TC3/WG3.3 Working Conference 1993), pages 13--22, Amsterdam. North-Holland. | ||
* Basque, Josianne & Sylvie Doré (1998) Le concept d’environnement d’apprentissage informatisé, Journal of Distance Education/Revue de l'enseignement à distance, 13(1), ISSN 0830-0445, [http://cade.icaap.org/vol13.1/dore.html HTML] | |||
[[Category:Educational technologies]] | [[Category:Educational technologies]] | ||
[[Category:Educational theories]] | [[Category:Educational theories]] | ||
[[Category:Instructional theories]] | [[Category:Instructional theories]] | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 26 June 2006
Definition
- Conceptually speaking, the Learning Environment refers to the whole range of components and activities within which learning happens.
- Technically speaking, a Learning Environment is a Computer System such as a Learning management system, a combination of various educational technologies (including at least one communication module), virtual environments, ...
However, each kind of instructional design model has its own way of defining the learning environment.
Functions of a Learning Environment
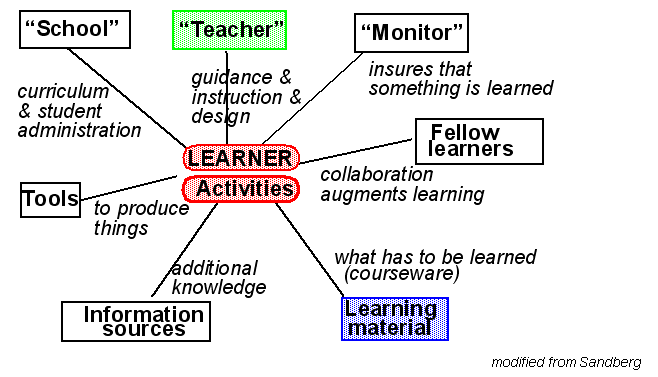
Sandberg's definition
(adapted by DSchneider)
- ``Teacher component: Its role is to provide something between loose guidance and direct instruction. It can be a human agent (present or distant), an intelligent agent, instructions like some text books provide, etc. This component provides information from the syllabus to the task level.
- ``Monitor component: Ensures that something is learned. A role taken by either the human teacher, the learner (self-control) or by some program.
- ``Fellow learners component: Improves the learning process (some research tries to implement artificial ones).
- ``Learning material, often Courseware: Contains what has to be learned in a very broad sense (knowing what, knowing how). It can be computational in various ways (exploratory hypertext, lesson and task oriented hypertext, simulation software, task solving environments, etc.).
- ``External information sources: All kinds of information which is not directly stored in the learning material (e.g. additional material, handbooks, manuals, etc.).
- ``Tools: Everything which may help the learning process other then the learning material (e.g. calculators, communication software, etc.)
- ``School [a category we added]: Something that provides a curriculum and does student administration.
References
- Sandberg, J. A. (1994). Educational paradigms: issues and trends. In Lewis, R. Mendelsohn, P., (ed.), Lessons from Learning, (IFIP TC3/WG3.3 Working Conference 1993), pages 13--22, Amsterdam. North-Holland.
- Basque, Josianne & Sylvie Doré (1998) Le concept d’environnement d’apprentissage informatisé, Journal of Distance Education/Revue de l'enseignement à distance, 13(1), ISSN 0830-0445, HTML